Form (6)
advertisement

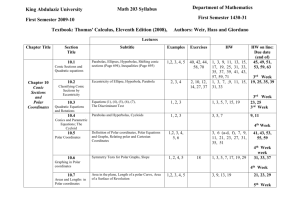
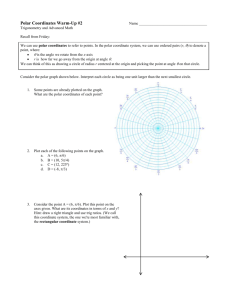
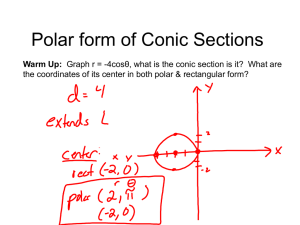
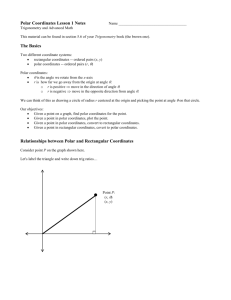
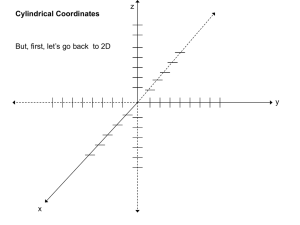
Course Description form COURSE TITLE DIFFERENTIAL ENGLISH CODE /NO CREDITS ARABIC CODE/NO. MATH203 203ر Th. Pr. Tr. TCH 3 - - - EQUATIONS (2) Pre-requisites Brief contents, to be posted in university site and documents(4-5 lines): The main ingredients of the course are: Conic Sections and Polar Coordinates, Quadratic Equations and Rotations, Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates, Vectors and the Geometry of Space, Lines and Planes in Space, Cylinders and Quadric Surfaces, Vector-Valued Functions, Modeling Projectile Motion, Planetary Motion and Satellites, Limits and Continuity in Higher Dimensions, Partial Derivatives, Directional Derivatives and Gradient Vectors, Optimization, Lagrange Multipliers, Taylor’s Formula for Two Variables. Faculties and departments requiring this course (if any) Objectives: Prefer In points On completion of the course, the students should be able to know about the basics of parameterization of plane curves, polar coordinates, and conic section; use vectors in two and three dimensions to describe lines and planes in space; understand sketching of quadric surfaces; comprehend vector-valued functions and their use to describe the motion of objects through space; grasp the idea of the epsilon-delta definition of the limit, and understand the methods for proving existence and non-existence of limit of functions of two/three variables; learn the idea of partial derivative and application of the chain rule; solve optimization problems without and with constraints. Contents: Prefer In points Contents: Prefer In points 1. Conic Sections and Polar Coordinates, Quadratic Equations and Rotations, Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates. 2. Vectors and the Geometry of Space, Lines and Planes in Space, Cylinders and Quadric Surfaces. 3. Vector-Valued Functions, Modeling Projectile Motion, Planetary Motion and Satellites. 4. Limits and Continuity in Higher Dimensions, Partial Derivatives, Directional Derivatives and Gradient Vectors, Optimization, Lagrange Multipliers, Taylor’s Formula for Two Variables. Details Unit I. Conic Sections and Polar Coordinates: Conic Sections and Quadratic Equations, Classifying Conic Sections by Eccentricity, Quadratic Equations and Rotations, Conics and Parametric Equations; The Cycloid, Polar Coordinates, Graphing in Polar Coordinates, Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates, Conic Sections in Polar Coordinates. Unit II. Vectors and the Geometry of Space: Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems, Vectors, the Dot Product, the Cross Product, Lines and Planes in Space, Cylinders and Quadric Surfaces. Unit III. Vector-Valued Functions and Motion in Space: Vector Functions, Modeling Projectile Motion, Arc Length and the Unit Tangent Vector T, Curvature and the Unit Normal Vector N, Torsion and the Unit Binomial Vector B, Planetary Motion and Satellites. Unit IV. Partial Derivatives: Functions of Several Variables, Limits and Continuity in Higher Dimensions, Partial Derivatives, The Chain Rule, Directional Derivatives and Gradient Vectors, Tangent Planes and Differentials, Extreme Values and Saddle Points, Lagrange Multipliers, Partial Derivatives with Constrained Variables, Taylor’s Formula for Two Variables. Course Outcomes: A- Knowledge: (Specific facts and knowledge of concepts, theories, formula etc.) The student will learn the basics of parameterization of plane curves, conic section, three dimensional geometry, vector-valued functions with applications, and calculus of several variables with applications. B-Cognitive Skills (Thinking, problem solving) The student will improve his/her logical thinking and imagination to conceive and solve the practical problems using the knowledge learnt in this course. C- Interpersonal skills and responsibilities (Group participation, leadership, personal responsibility, ethic and moral behavior, capacity for self directed learning) The student is expected to carry out an independent investigation of the topic by studying the available material, interacting with fellow students and the instructor to obtain sufficient information, and then analyse and manipulate this information to arrive at logical conclusions. D- Analysis and communication: )communication, mathematical and IT skills) Activities such as group discussion and report-writing play a key role in enhancing communication skills. Working independently and jointly is another important factor for developing such skills. Regular feedback on the completed oral/written assignments with constructive and moral boosting comments must be conveyed to the students in order to enhance such skills Assessment methods for the above elements Discussions, Homework, Periodic tests and final test Text book: Only one Thomas' Calculus, 11th Edition Media Upgrade, Addison Wesley, Pearson, 2008 Supplementary references Details of Weekly Distributed Material Remarks Contents Conic Sections and Quadratic Equations - Classifying Conic Sections by Eccentricity Quadratic Equations and Rotations - Conics and Parametric 10.3,10.4,10.5 Equations; The Cycloid - Polar Coordinates Graphing in Polar Coordinates - Areas and Lengths in Polar 10.6,10.7,10.8 Coordinates - Conic Sections in Polar Coordinates Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems, Vectors, The Dot 12.1,12.2,12.3 Product 12.4,12.5 The Cross Product - Lines in Space 12.5,12.6 Planes in Space - Cylinders and Quadric Surfaces 13.1,13.2 Vector Functions, Modeling Projectile Motion Arc Length and the Unit Tangent Vector T, Curvature and the 13.3,13.4 Unit Normal Vector N Torsion and the Unit Binomial Vector B, Planetary Motion and 13.5,13.6 Satellites Functions of Several Variables, Limits and Continuity in Higher 14.1,14.2 Dimensions 14.3,14.4 Partial Derivatives -The Chain Rule Directional Derivatives and Gradient Vectors - Tangent Planes 14.5,14.6,14.7 and Differentials - Extreme Values and Saddle Points Lagrange Multipliers - Partial Derivatives with Constrained 14.8,14.9,14.10 Variables Taylor’s Formula for Two Variables Review Review 10.1,10.2 Final exam. weak 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15