Polar Coordinates Lesson 1 Notes
advertisement

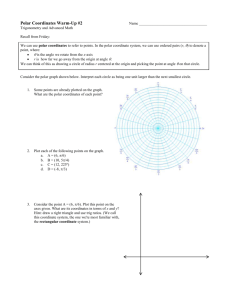
Polar Coordinates Lesson 1 Notes Name ____________________________________ Trigonometry and Advanced Math This material can be found in section 5.6 of your Trigonometry book (the brown one). The Basics Two different coordinate systems: rectangular coordinates -- ordered pairs (x, y) polar coordinates -- ordered pairs (r, ) Polar coordinates: is the angle we rotate from the x-axis r is how far we go away from the origin at angle . o r is positive move in the direction of angle . o r is negative move in the opposite direction from angle . We can think of this as drawing a circle of radius r centered at the origin and picking the point at angle on that circle. Our objectives: Given a point on a graph, find polar coordinates for the point. Given a point in polar coordinates, plot the point. Given a point in polar coordinates, convert to rectangular coordinates. Given a point in rectangular coordinates, covert to polar coordinates. Relationships between Polar and Rectangular Coordinates Consider point P on the graph shown here. Let's label the triangle and write down trig ratios… Point P: (r, ) (x, y) Thus, we have the following conversions: Conversion If we know these coordinates… We can find these coordinates as follows: Rectangular to Polar (x, y) r= = Polar to Rectangular (r, ) x= y= Examples Convert to polar. a. (3, 3) b. ( 2 3 , -2) Convert to rectangular a. 20 , 4 b. (-3, 120º) Homework: Trig book, Section 5.6: #1-21 odd, 27-33 odd