5.4 Guided Notes
advertisement

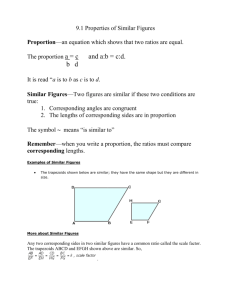
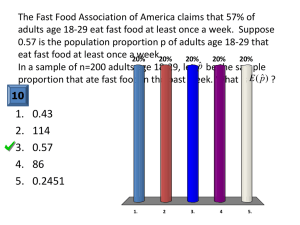
STA220- 5.4 Guided Notes Large-Sample Confidence Interval for a Population Proportion The point estimate for p, the population proportion of successes, is given by the proportion of successes in a sample and is denoted by: ____________ where x is the number of successes in the sample and n is the number in the sample. The point estimate for the number of failures is 𝑞̂ = 1 − 𝑝̂ .The symbols 𝑞̂ and 𝑝̂ are read as “p hat” and “q hat. Example 1: In July of 2008, a Quinnipiac University Poll asked 1783 registered voters nationwide whether they favored or opposed the death penalty for persons convicted of murder. 1123 were in favor. Obtain a 90% confidence interval for the proportion of registered voters nationwide who are in favor of the death penalty for persons convicted of murder. Example 2: The graph shown below is from a survey of 935 adults. Construct a 99% confidence interval for the proportion of adults who think that airplanes are the safest mode of transportation. CAUTION!!!!!!! Unless ‘n’ is extremely large, the large-sample procedure presented in this section performs poorly when ‘p’ is near 0 or near 1. If p is close to 0 or 1, Wilson’s adjustment for estimating p yields better results where Example 3: Suppose in a particular year the percentage of firms declaring bankruptcy that had shown profits the previous year is .002. If 100 firms are sampled and one had declared bankruptcy, what is the 95% CI on the proportion of profitable firms that will tank the next year? Example 4: According to True Odds: How Risk Affects Your Everyday Life (Walsh, 1997), the probability of being the victim of a violent crime is less than 0.01. Suppose that, in a random sample of 200 Americans, 3 were victims of a violent crime. Use a 95% confidence interval to estimate the true proportion of Americans who were victims of a violent crime.