Ecosystem Interactions: Food Chains, Webs, and Cycles
advertisement

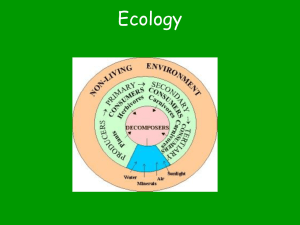
Chapter 18, section 3 Interactions of living things What is the difference between a food chain and a food web? How does energy flow through ecosystems? What makes the first link of a food chain different from all the rest? Compare and contrast producers, consumers, and decomposers. Energy Flow Through Ecosystems Most of the interactions among members of different species occur when one organism eats another. Food contains nutrients and energy needed for survival. Energy pass from one organism to the other. Producers take energy from the Sun to produce Carbohydrates through a process called photosynthesis. Consumers take energy when they feed on producers or other consumers. When an organism dies, decomposers take leftover energy as they break down the remains. This movement of energy is shown in food chains and food webs. Food Chains A food chain is a model to illustrate how energy passes from one organism to another organism. The arrows point in the direction energy is traveling. The amount of available energy decreases at each level. Food Webs A food web is a series of overlapping food chains that exist in an ecosystem. A food web is a more complex and complete model of how energy moves through an ecosystem. Ecological pyramids Most of the energy in the biosphere comes from the Sun. Producers take in this light energy to make (produce) an organic form of energy that can be consumed by herbivores and then by other consumers. The bottom of the pyramid represents the number of producers and so on as you go up the pyramid. Energy Pyramids Can be described as a cross between an ecological pyramid and a food chain. Since producers contain all the energy for an ecosystem they are at the bottom and then the energy decreases at each level. Only about 10% of the energy is passed on from one level to the next. Chapter 18, section 3 Interactions of living things How does Carbon flow through ecosystems? Why is the Water cycle such an important part of our ecosystem? Why to biotic organisms need nitrogen? Cycles of Matter The law of conservation of mass states that matter on Earth is never lost or gained, it is recycled. Water Cycle Water molecules on Earth constantly rise into the atmosphere and fall to the ground. The water cycle involves the processes of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation. Heat from the sun causes water on Earth’s surface to evaporate (change from a liquid to a gas) rise into the atmosphere as water vapor. As the vapor rises it encounters colder air which slow the molecules down. The water vapor begins to condense (change from a gas to a liquid) and these water droplets form clouds. When they get heavy enough they fall to the Earth as some for of precipitation. Carbon Cycle and Oxygen Cycle All biotic organisms contain Carbon. The atmosphere contains carbon dioxide, which is a gas. Producers “breath” in CO2 in order to make their food and release O2 (oxygen). Consumers’ breath in O2 in order to burn the energy we absorbed from producers and release CO2. This is how the Carbon and Oxygen cycles are connected in our ecosystems. Nitrogen Nitrogen can be found in proteins and nucleic acids (DNA). Nitrogen cycle begins as N2 is transferred from atmospheric nitrogen into a more usable form for producers and consumers, through a process call nitrogen fixation, by decomposers and bacteria. Then the Nitrogen moves back into the atmosphere.