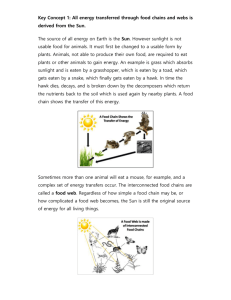
Food Chains
advertisement

Unit 3 Ecosystems Chapter 6 & 7 Part 1 The Web Of Life p. 92 & Food Relationships p. 93 Questions #3-9 in the book Define Ecosystem Ecosystem = the network of relationships (interactions) among living (plants, animals) and the non-living parts (soil, climate, water etc.) in an environment. Differentiate the terms producers, consumers decomposers. P. 93 Other examples: Grasses Trees shrubs Water lilies Flowers Vegetables Fruits Producer = a plant which can synthesize carbohydrates using carbon dioxide and the sun’s energy. Actually “produce” their own food and food for the rest of the ecosystem Differentiate the terms producers, consumers, decomposers. P. 93 Consumers = All those organisms that have to eat (consume) plants or animals to obtain their food. Types of consumers Primary Consumers: Animals that eat producers. Also called 1st. order consumers. (Ex. Rabbit, squirrels, grouse, insects) Secondary Consumers: Animals that eat primary consumers. Also called 2nd. order consumers. (fox, owl, mink ) Tertiary Consumers: Animals that eat secondary consumers. Also called 3rd. order consumers. (Wolf, coyote, hawk) Differentiate the terms producers, consumers, decomposers. P. 94 Examples: Worms Bacteria Fungi Protozoa • Decomposers = Simple organisms that obtain their food from dead/decaying organisms and wastes. Differentiate the terms food chain & food web. P. 94 Food chain = linear sequence representing the nutrition of various species from the simplest plant to the top carnivore. Food web = a series of interconnecting food chains in an ecosystem. Food web is more complex and is composed of several food chains Food web is a more realistic picture of an ecosystem. Food Chain vs Food Web Identify ALL examples of each trophic level. Producers Shrubs, grass, trees Primary Consumers Grasshopper, rabbit, deer, squirrel Secondary Consumers Mountain lion, snake, shrew, insect-eating bird, hawk Tertiary Consumers Hawk, snake, mountain lion Decomposers Bacteria, fungi Give an example of a food chain from fig. 6.4. P. 95 Tree insect → Producer → Primary consumer insect eating hawk bird → 2nd order consumer 3rd order consumer Note: The arrows indicate the flow of energy & nutrients from one level to the next Sample Food Chain Draw an example of a food web containing humans. P. 94 Mosquito Hawk Cow Grass Man Decomposer Phytoplankton Fish Draw an example of a food web containing humans. P. 94 Hawk Mosquito Cow Grass Man Decomposer fish Phytoplankton What happens to energy? (Handout) What happens to energy? 85-90% is LOST or USED up: maintaining the organism (Ex. metabolism, reproduction etc.) 10-15% is stored: Available or transferred to other animals when it is eaten. And as heat!!! IF NOT EATEN: Energy is transferred to the decomposers . What happens to the energy at the decomposer level? Same thing….ALMOST !? Most is lost or used up through heat and maintaining the organism. If eaten (Ex. A mushroom) energy gets passed on. HOWEVER, once a decomposer dies…. The energy is LOST FOREVER!!! Summary – Energy & Food Webs The ultimate source of energy (for most ecosystems) is the sun The ultimate fate of energy in ecosystems is for it to be lost as heat, metabolism, reproduction, etc.. Energy and nutrients are passed from organism to organism through the food chain as one organism eats another. Decomposers remove the last energy from the remains of organisms. Inorganic nutrients are cycled, energy is not. Summary – Energy & Food Webs Question #14, 15 & #16 p. 98 make perfect review questions for the test.