Phonetic & Structural Analysis
advertisement

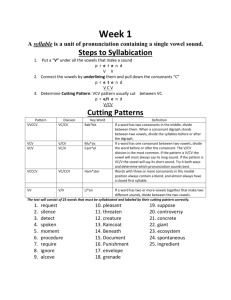
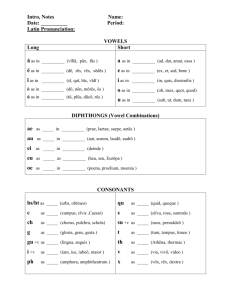
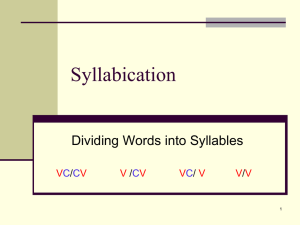
701-707 Phonetic & Structural Analysis Terms - Alphabetical Terms Affixes Alphabetic Principle Antonym Automaticity Base Word Blending Consonants Chunking Concepts About Print/ Conventions of Print Context Clue Cueing System Decodable Text Decoding Elkonin boxes Emergent Literacy Grapheme Graphophonics (Phonics) Definition A general term that refers to prefixes and suffixes. Prefixes: A morpheme that precedes a root and that contributes to or modifies te meaning of a word as re-in reprint. Suffixes: An affix attached to the end of a base, root, or stem that changes the meaning or grammatical function of the word, as-en in oxen. The understanding that spelling represents words by relating written letters to spoken phonemes. A word opposite in meaning to another word. sad and happy Reading without conscious effort or attention to decoding. A unit of meaning that can stand alone as a whole word (e.g. friend pig). Also called a free morpheme. The task of combining sounds rapidly;, to accurately represent the word. All letters except the vowels. Rank order of based on their utility in words is: s, t, m, f, r, b, l, c, h, p, p, w, n, d, g, j, k, v, z, x, y, q Consonant blends: Two or three consonant letters that appear together but each letter retains its own sound. The three categories are L blends, R blends and S blends. Consonant digraphs: Two consonant letters that commonly appear together, but do not retain their own individual sounds. They produce a new sound and are counted as one phoneme. Examples: ch-, sh-, ph-, -ng A decoding strategy for breaking words into manageable parts (e.g., yes/ter/day). Chunking also refers to the process of dividing a sentence into smaller phrases where pauses might occur naturally, An understanding of the layout of books, the relative roles of print and pictures, reading left to right, spaces between words, punctuation.. Using words or sentences around an unfamiliar word to help clarify its meaning. Semantic: The study of the meaning in language; the analysis of the meanings of words, phrases, sentences. Does it make sense? Syntactic: The pattern or structure of word order in sentences, clauses and phrases; the grammatical rules that govern sentences, Sentences have to follow certain structural rules in order to make sense. Cueing question: Does it sound right? Visual: Does it look right? Text in which a high proportion of words (80%-90%) comprise soundsymbol relationships that have been taught. The ability to translate a word form print to speech, usually by employing knowledge of sound-symbol correspondences; also the act of deciphering a new word by sounding it out. A framework used during phonemic awareness instruction. Elkonin boxes are sometimes referred to as sound boxes. When working with words, the teacher an draw one box per sound for a target word. Students push a marker into one box to segment each sound in the word. A period in children’s learning to read and write that begins when children first notice print and wonder what people are doing with it. An emergent reader is developing an association of print with meaning –the early stages of learning to read. A letter or letter combination that spells a phoneme; can be one, two, three or four letters in English (e.g., e, ei, igh, eigh). Knowledge of the relationships between letters and phonemes. Homograph Invented Spelling Letter Recognition Letter-Sound Correspondence Miscue Morpheme Orthography Phoneme Phonemic Awareness Phonogram Phonological Awareness Phonics Onset & Rime Reading Cue System Reversals Rhyming Scaffolding Schwa Self Monitoring Sight Words Words that are spelled the same but have different origins and meanings. They may or may not be pronounced the same (e.g. can as in a metal container/can as in able to) An attempt by beginning writers to spell a word when the standard spelling is unknown, using whatever knowledge of sounds or visual patterns the write has. The identification of individual letters by name and/or sound in a variety of contexts. Making a connection between individual letters by name and/or sound in a variety of contexts. Any substitution of a word in a text that a reader makes. Miscue Analysis: An examination of reading errors or substitutions (miscues) as the basis for determining the strengths and weaknesses of students’ reading skills. Smallest meaningful unit of language Morphemic Analysis: An analysis of words formed by adding prefixes, suffixes or other meaningful word units to a base word. Morphology: The system of meaningful parts from which words may be created. A writing system for representing language. The smallest part of spoken language that makes a difference in spoken words. English has about 44 sounds or phonemes represented by consonant and vowel sounds. The ability to hear, identify and manipulate individual sounds (phonemes) in spoken words. A succession of letters that represent the same phonological unit in different words such as igh in high, sigh, tight, might. A broad term that includes phonemic awareness. In addition to phonemes, phonological awareness activities an involve work with rhymes, words, syllables, and onsets and rimes. The study of the relationships between letters and the sounds they represent; also used to describe reading instruction that teaches soundsymbol correspondences. In a syllable, the onset is the initial consonant or consonants, and the rime is the vowel and any consonants that follow it (e.g., the word sat, the onset is s and the rime is at.) Graphophonic or Visual: Referring to the relationship between the letters and the letter sounds of a language. Cueing Question: Does it look right? Syntactic or Structure: Grammatical Patterns and Language Structures Cueing Question: Does it sound right? Semantic or Meaning: Cueing Question: Does it make sense? The result of reversing the order of letters in a word (tap/pat), or confusing similar letters such as d-b, or writing letters backwards. Not uncommon with Emergent readers and writers. Words that have the same ending sound. dog and log. An instructional technique in which the teacher models the desired learning strategy or task then gradually shifts responsibility to the student. The vowel sound in the unaccented syllable that always makes the same sound. For example: the uh sound in the 2nd syllable in tu lip Paying attention to one’s own reading process while reading, and taking steps to reread or make corrections as needed to make sense of the text. A bank of words that are stored in our memory and are instantly (High Frequency Words) Structural Analysis Syllable Synonym Systematic Instruction Vowels recognized. A procedure for teaching students to read words formed with prefixes, suffixes, or other meaningful word parts. A segment of a word that contains one vowel sound. The vowel may or may not be preceded and/or followed by a consonant. Words that have similar meanings such as sadness and grief. A carefully planned sequence for instruction. Instruction is clearly linked within, as well as across the five components (Phonemic awareness, phonics, fluency, vocabulary, and comprehension) The vowels are a, e, i, o and u. The consonants w and y often act as vowels as in the words show, fly, and happy. Short Vowels: The vowel patterns that represent the short sound are: VC at, Ed, it, ox, up & CVC cat, can, in Long Vowels: The vowel patterns that represent the long sound are: CV go. CVCe ice & use. CVVC mean, Vowel Digraphs: Pairs of vowels representing a single sound. Examples: /ea/ in heat. This is the CVVC rule. The rule says: Two vowels together in a word or syllable, the first vowel says its name and the second vowel is silent (load, blue) Vowel Diphthongs: Vowel combination that begins with one sound and moves to another sound in the same syllable or only make one sound. oo= cook, book, /au/=haul, /aw/=saw, /ew/=new. Controlled Vowels: r-controlled vowels: When a vowel is followed by an r, often the sound is neither long nor short but called r-controlled vowel. Examples: ar (star), er (covre), ir (circus), or (for), and ur (fur) Schwa: The vowel sound in the unaccented syllable that always makes the same sound. Examples: a (a go), e (a gent), i (tu lip)