Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Reading
advertisement

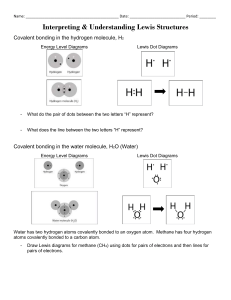
Lewis Dot Diagrams A Lewis dot structure is like a simplified electron energy level model. The Lewis structure contains the element symbol with dots representing electrons. The only electrons shown are those on the outer energy level or valence electrons. The electrons are placed around the element symbol, one at a time, clockwise or counterclockwise, and then grouped in pairs as more electrons are added. Covalent Bonding Lewis dot structures can also be used to show the bonded atoms in a molecule. The two dots together between the Hydrogen atoms represent the electrons in the covalent bond between the hydrogen atoms. The line is a short-hand version of the two dots. The Lewis dot structure for water shows the electron from hydrogen and an electron from oxygen being shared in a covalent bond. The other four valence electrons in oxygen are in pairs at the bottom. The lines are a short-hand version of the two dots representing the covalent bonds. The two pairs of dots between the Oxygen atoms represent the double covalent bond in the oxygen molecule. The two lines are a short-hand version of the two pairs of dots. The two pairs of dots between the C and the Os represent the double covalent bond between the carbon and each oxygen atom in the carbon dioxide molecule. The two sets of two lines are a shorthand version to show the two double covalent bonds. When sodium (salt) loses its only valence electron to become an ion, the Lewis structure shows it with no dots (electrons). The Na and Cl are near each other but the two dots from the Cl should not be interpreted as a covalent bond. Reflection Questions: 1. How are electrons arranged around the nucleus of an atom? 2. What charge do electrons carry? 3. Describe the energy levels of electrons around a nucleus. 4. How do you read a Lewis Dot Structure? (What do the dots represent?) 5. How can Lewis Dot Structures help you visualize how electrons interact?