Module: Accuracy and Precision, Confidence Intervals
advertisement

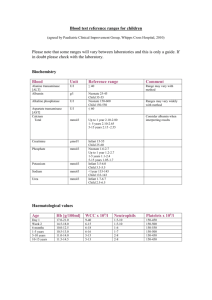
RBH-1 Module: Accuracy and Precision, Confidence Intervals Instructions: Please write down your answers in this document. Take care that you save the copy of the document on your local PC BEFORE you start writing. At the end of the practical send the document to ibz@mefst.hr. Exercises 1. What is the standard error of the following measures: a) Mean cholesterol levels in 30-60 year olds recruited from GP practices in northern Croatia where: M=5.1 mmol/L Sample size=1600 SD=2.3 mmol/L b) The proportion of women with breast cancer in women in a small town in Croatia where: Number of cases of women with skin cancer=30 Number of women in a study sample=5700 c) Mean blood glucose levels on ward where: M= 5.1 mmol/L SD= 2.3 mmol/L Sample size= 16 2. As the size of a random sample increases a) The standard deviation decreases b) The standard error of the mean decreases c) The mean increases d) The range may increase e) The precision of my parameter estimate increases 3. Assuming normal distribution of variables calculate the confidence intervals for the following datasets: a) The 95 per cent confidence interval (CI) for the forced expiratory volume (FEV1) of children with asthma, where the mean is 1.47 L, the standard deviation is 0.34 L and the sample size is 1089 b) The 99 per cent CI for the proportion of babies born with birth defects to mothers who had an infection during pregnancy, where the number of babies with birth defects is 7 and the total number of babies in the study is 43. (NB: In the normal distribution, 99 per cent of the data lie within 2.58 standard deviations of the mean.) 4. Suppose that we want to estimate the average height of Dalmatian males. By using a simple random sampling, you chose 1000 males from a population of 1,000,000 males and you measured their height. Mean height was 180 cm, and standard deviation was 30 cm. What was 95% confidence interval for mean? (A) 180 + 1.86 (B) 180 + 3.0 (C) 180 + 5.88 (D) 180 + 30 (E) None of the above 5. The famous newspaper has chosen a random sample of 1600 readers from their subscribers’ list of 100,000 subscribers. Examinees were asked if they think the coverage of local news should be reduced. Forty percent of the sample agreed with the reduction. What is 99% confidence interval for readers which voted in favour of reduction? (A) 0.30 to 0.50 (B) 0.32 to 0.48 (C) 0.35 to 0.45 (D) 0.37 to 0.43 (E) 0.39 to 0.41 Based on the data presented make the editor’s decision: PRO or CON of reduction? 6. A 95 percent CI for a mean A. Is narrower than a 99 percent CI B. Is a useful way of describing the precision of a study C. Includes 95 percent of the observations in a study D. Will include the population mean 95 percent of the time in repeated samples 7. Brain tissues of 9 patients with schizophrenia were sampled. For each patient, the concentration of the particular enzyme was determined. Enzyme levels were also determined in 9 controls. Following statistics were calculated: mean of 𝑥̅ 1 = 39.8 mmol/L and standard deviation s1 = 8.16 mmol/L in the control group, and 𝑥̅ 2 = 35.5 mmol/L, and s2 = 6.93 mmol/L in the patient groups. What can you conclude about difference in enzyme activity between the control and the patient group? Calculate and elaborate your conclusion. 8. Researchers evaluated the effectiveness of standardized consultations for patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Standardized consultations involved three goal oriented visits, which comprised education about osteoarthritis and treatment management, as well as information on physical exercises and weight loss. A cluster randomized controlled trial was used. Control treatment was usual care. Participants were recruited from primary care. Inclusion criteria included age 45-75 years and a diagnosis by a rheumatologist of osteoarthritis of the knee according to the American College of Rheumatology clinical and radiological definition. Main outcome measures included change in body weight at four months from baseline. In total, 336 patients were included, with 154 allocated to standardized consultation and 182 to usual care. At four months, the standardized consultation group showed greater weight loss than the usual care group: mean 1.11 kg (95% CI 0.70 to 1.52) vs. 0.37 kg (0.02 to 0.72). The authors concluded that, compared with usual care, a structured consultation programme for patients with osteoarthritis of the knee resulted in significantly greater short term weight loss. Which one of the following statements best describes the information provided by the 95% confidence interval for mean weight loss at four months for the standardized consultation group? Elaborate your choice. a) 95% of sample participants in the standardized consultation group achieved a weight loss between 0.70 kg and 1.52 kg b) 95% of the population would achieve a weight loss between 0.70 kg and 1.52 kg if they received a standardized consultation c) There is a probability of 0.95 that the population mean weight loss at four months with standard consultation would be between 0.70 kg and 1.52 kg d) There is a probability of 0.95 that the sample mean weight loss for the standardised consultation group was between 0.70 kg and 1.52 kg 9. Researchers investigated whether antidepressant drug prescribing and referrals to specialist services for depression by general practitioners were associated with patients’ scores on depression severity questionnaires measured at the start of treatment. Anonymised data from the medical records of 38 general practices were investigated. The nine item patient health questionnaire (PHQ-9) was used in 1658 patients and the depression subscale of the hospital anxiety and depression scale (HADS) was used in 548 patients. The distribution of HADS questionnaire scores for the sample was approximately normal, whereas the PHQ-9 scores were negatively skewed. The mean PHQ-9 score was 15.5 (standard deviation 6.0) and the mean HADS score was 11.1 (4.6). It was reported that patients with higher depression severity scores were more likely to receive prescriptions for antidepressants and be referred to specialist services. However, other factors were independently associated with treatment and referral, including patient age and concurrent physical illness and geographical area. Which of the following statements, if any, are true? Explain your choice. a) The normal distribution approximated by the HADS scores can be uniquely described by the sample mean and standard deviation b) The normal distribution approximated by the HADS scores is symmetrical about the sample mean value c) For the distribution of PHQ-9 scores, the tail on the right was longer than the tail on the left d) The sample mean PHQ-9 score was smaller than the median PHQ-9 score 10. Among the British respondents in the National Child Development Study, those who are vegetarian at age 42 have significantly higher childhood general intelligence than those who are not vegetarian at age 42. (Childhood general intelligence was measured with 11 different cognitive tests at three ages before 16.) Vegetarians have the mean childhood IQ of 109 (n=175) whereas meat eaters have the mean childhood IQ of 100.9 (n=6,531). Authors claim that the difference is large and highly statistically significant and present figure below to substantiate their findings. Data presented in this excercise do include all data which are presented in a paper. Do you think their findings are valid? Explain