Review Sheet

Biology Genetics Study Guide & 3 rd 6 weeks test review
Go back over Protein Synthesis Review (Edmodo) from last test for a complete review experience!
1. If ‘n’ stands for ‘different types of chromosomes’. In humans:
2n would equal:________________ , n by itself would equal:_____________________
2. Know what kind of cell Meiosis begins with and what it ends with
3. What makes siblings from the same parents look different from each other?
4. What is fertilization?
5. Give an example of a Homozygous Dominant Genotype:_______
6. Give an example of a Homozygous recessive Genotype:_______
7. Give an example of a Heterozygous Genotype:________
8. What is the difference between a genotype and phenotype?
9. What is the difference between sex cells and sex chromosomes? (Use vocabulary from chapter!)
10. Know the difference between Incomplete Dominance, Co-Dominance, and Polygenic Inheritance.
11. Explain the difference between a haploid and a diploid cell (give examples)
12. Explain how crossing over creates genetic variation.
YOU WILL NEED TO BE ABLE TO:
- Read and complete Punnett squares
- Complete a Punnett for an X-linked trait
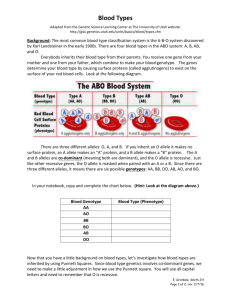
- Complete a Blood Type Punnett square
- Complete a Co-Dominance Punnett square
- Figure out Gamete allele combinations (like for a dihybrid cross: FOIL)
- Read a dihybrid cross
- The Law of Segregation and The Law of Independent Assortment
- Know the Blood Type Genotypes and how to do Punnett squares with Multiple Alleles
- Know structure and function of DNA and RNA
- Compare Mitosis with Meiosis and know the purpose of each
- Be able to replicate, transcribe and translate lines of DNA or RNA code as well as identify pictures of the process
Practice:
1. Cross Bb x bb
2. How in the Punnett above did you model the Law of Segregation? Explain.
3. Is it possible for a mother with type A and a father with type B to have a child with type o blood? Explain with a Punnett square and with words!
4. Complete the Dihybrid and answer the questions.
5. Mickey is normal (X B Y)for color blindness but his wife Minnie is heterozygous (X B X b )for color blindness.
Complete the punnett square. Colorblindness is Recessive
More Practice!! (Complex Inheritance)
Incomplete Dominance
1.
In snapdragons, flower color is controlled by incomplete dominance. The two alleles are red (R) and white (W). The heterozygous genotype is expressed as pink. a) What is the phenotype of a plant with the genotype RR? ___________ b) What is the phenotype of a plant with the genotype WW? ___________ c) What is the phenotype of a plant with the genotype RW? ___________
2.
A pink-flowered plant is crossed with a white-flowered plant. Show the Punnett Square. What is the probability of producing a pink-flowered plant? ____%
3.
What cross will produce the most pink-flowered plants? Show a punnett square to support your answer.
Co-dominance
Human blood types are determined by genes that follow the CODOMINANCE pattern of inheritance. There are two dominant alleles (A and B) and one recessive allele (O).
9.
Write the genotype for each person based on the description: a.
Homozygous for the “B” allele ______ b.
Heterozygous for the “A” allele c.
Type O ______
______
______
______ d.
Type “A” and had a type “O” parent e.
Type “AB”
10.
Pretend that Brad Pitt is homozygous for the type B allele, and Angelina Jolie is type “O.” What are all the possible blood types of their baby?
11.
Two parents think their baby was switched at the hospital. Its 1968, so DNA fingerprinting technology does not exist yet. The mother has blood type “O,” the father has blood type “AB,” and the baby has blood type “B.” a.
Mother’s genotype: _______ b.
Father’s genotype: _______ c.
Baby’s genotype: ______ or ________ d.
Punnett square showing all possible genotypes for children produced by this couple e.
Was the baby switched?
12.
Based on the information in this table, which men could not be the father of the baby? Justify your answer with a Punnett square.
Name
Mother
Blood Type
Type A
Type B
Type O
Baby
Sammy the player
George the sleeze
The waiter
The cable guy
Type AB
Type A
Type B
14.
In shorthorn cattle, when a red bull (RR) is crossed with a white cow (WW), all the offspring are roan—a spotted, red and white or milky red color. What offspring are expected from mating a roan bull and a roan cow? Show the Punnett Square.
15.
What phenotypes would you expect from a cross between a red bull and a white cow? Show the
Punnett Square.
16.
If a roan bull were crossed with a red cow, what would be the possible phenotypes of their offspring? Show the Punnett Square.