Gene Expression Activity PSI Biology
advertisement

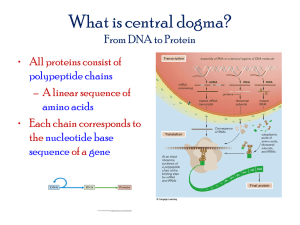
Gene Expression Activity PSI Biology Name__________________________ Background A gene is a segment of DNA needed to make a specific protein. The shapes of proteins are determined by the sequence of their amino acids. Proteins must be "coded" with the correct sequence of amino acids to have the right shape. Gene expression is the process of translating the "code" in the nucleic acid and producing the protein. Gene expression occurs whenever a specific protein is needed by the cell. This process requires: • Producing a messenger RNA from the DNA template in the nucleus • Transferring the mRNA to the ribosome • At the ribosome, using the messenger RNA molecule, along with transfer RNA molecules to attach amino acids in the correct primary sequence to produce the desired protein. Question 1: What messenger RNA molecule would be produced from this DNA template strand? 3' TAC GGC TTC CCC CTA ACT 5' template (parent) strand 5' _______ _______ _______ ______ _______ _______ 3' new messenger RNA molecule The mRNA "message" is read in 3-base letter codons. Codons each contain one of three different “messages” 1. Start translation (AUG/Methionine is always the first amino acid in a sequence) 2. Bring X amino acid (61 codons) 3. Stop translation (3 codons: UAA, UAG, and UGA) Question 2: If UCU codes for serine and CCU codes for proline, “translate” this messenger RNA molecule: AUG CCU UCU UAA _________________________________________________________________________________________________ www.njctl.org PSI Biology Genes Use this chart of amino acids and their corresponding codons to answer the next questions. This is known as the universal genetic code because all organisms from the smallest bacteria to the largest tree or animal utilize the same code to produce all cellular proteins. Question 3: Bradykinen is a polypeptide that causes smooth muscles to relax and blood vessels to dilate, which reduces blood pressure. The sequence of amino acids that comprise this polypeptide are: Met-Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg. Working backwards, construct the messenger RNA sequence that would code for this polypeptide: (Include a stop codon) Met-Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg 5' ______-_______-_______-______-_______-________-________-______-_______-_______-_______ 3' Question 4: From the messenger RNA molecule produced in question 4, produce the DNA molecule. template strand 3' ______ _______ _______ ______ _______ ________ ________ ______ _______ _______ _______ 5' non-template strand 5' ______ _______ _______ ______ _______ ________ ________ ______ _______ _______ _______ 3' Part 2: It is possible for the DNA or RNA molecule to replicate incorrectly. Mistakes are termed mutations. What are some possible consequences of mutations? Question 5: Suppose during the replication of the following DNA molecule, the base in red was replicated incorrectly: 5' AAT TCG CCC CGT TTA 3' non-template strand 3' TTA AGC GCG GCA AAT 5' template strand www.njctl.org PSI Biology Genes What messenger RNA would be produced from this new strand? 5' _____________ _____________ ____________ _____________ ___________3' Question 6: Referring to the messenger RNA molecule in question 6, how would the mutation affect the protein produced from this section? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Question 7: Suppose a mutation resulted in the following messenger RNA section. The mutated section is highlighted in yellow: 5' AGU AGG CGG CGU UUG 3' Here is the correct mRNA section: 5' AGU AGG CGA CGU UUG 3' How will this mutation affect the resulting polypeptide? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Question 8: Glucagon is a peptide that raises the level of glucose in the blood. The amino acid sequence is: His-Ser-Gln-Gly-Thr-Phe-Thr-Ser-Asp-Tyr-Ser-Lys-Tyr-Leu-Asp-Ser-Arg-Arg-Ala-Gln-Asp-Phe-Val-Gln-Trp-Leu-Met-Asn-Thr What are two completely different messenger RNA sequences that would code for this amino acid sequence? (Change at least one letter for each amino acid.) Answer 1: 5' _________ ________ ________ _______ _______ ______ ________ ________ _______ _______ ________ ________ ________ _______ _______ ______ ________ ________ _______ _______ ______ ________ ________ _______ _______ ______ ________ ________ _______ 3' Answer 2: 5' _________ ________ ________ _______ _______ ______ ________ ________ _______ _______ ________ ________ ________ _______ _______ ______ ________ ________ _______ _______ www.njctl.org ______ ________ ________ _______ _______ ______ ________ ________ _______ 3' PSI Biology Genes Part 3: Each codon on mRNA corresponds to the anticodon loop section of the tRNA molecule that brings the amino acid to the ribosome. The transfer RNA molecules line up in the appropriate order coded for in the mRNA molecule. As the amino acids are released from the tRNA molecules and joined together, the polypeptide is elongated. Question 9: What are the corresponding transfer RNA anticodons that would attach to the messenger RNA molecule created in question 8? Answer: Messenger RNA molecule used 5'_____________________________________________________________________________________________3' Transfer RNA codons: Question 10: Build your own DNA model. Using the information from previous questions, construct a three-dimensional model of a possible gene from DNA that would code for glucagon. Rules: 1. Cannot use a pre packaged "kit". Instead use everyday materials such as candy, buttons, or beads. 2. Must be three-dimensional. 3. Label the sugars, phosphates, and all bases. Include a legend. 4. Be sure to arrange each side with a 5’ and 3’ end. 5. Must code for glucagon. www.njctl.org PSI Biology Genes