about Latvia
advertisement

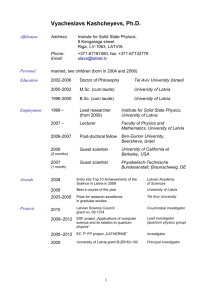
... about Latvia Latvia lies on the western edge of the East European plain. It borders on Estonia, Lithuania, the Russian Republic and Belarus. It occupies an area of 64,000 km2. The territory of Latvia extends for 450 kilometres from east to west and 210 kilometres from north to south. It lies from 100 m to 200 m above the sea level. The environmental regions of Latvia and their differences are controlled by the direct influence of the Baltic Sea. The Coastal Lowland covers the area along the coast of the Baltic Sea and the Gulf of Riga from the Lithuanian to the Estonian border. The territory of Latvia can be divided into: the Western Highlands of Kurzeme, the Zemgale Flatlands, the Highlands of Vidzeme and the Highlands of Latgale. The highest point in Vidzeme is Gaiziņš - 312 m, Lielais Liepukalns - 289 m in Latgale and Krievukalns - 184 m in Kurzeme. The climate of Latvia is determined by its geographical location in the northwest of the continent of Eurasia and the Atlantic ocean. An average of 120-140 cyclones a year cross over Latvia creating very frequent weather changes. The average temperature in January is between —2.6° to -6.6°, in July it varies between 16.8° and 17.6°. Snow accumulation is not great due to frequent thawing. The hilly surface area and the damp climate has helped to form a complex network of rivers in Latvia. There are 12.4 thousand rivers, but only 17 are over 100 km long, the largest are: the Daugava (357 km in the territory of Latvia) and the Gauja - 200 km in length. The Daugava with its tributary the Aiviekste, as well as the Lielupe, the Venta, the Bārta, the Salaca contain the most water. Their basins cover 80 % of the territory of Latvia. Lakes take up 1.7 % of the territory. Rāzna Lake Is the largest in Latvia. Most of the lakes are shallow. Only 8 lakes have an average depth over 10 m. The lakes are concentrated mostly in the highlands, over 40% are In the Latgale Highlands. Forests cover 43 % of the territory of Latvia. Half of them consist of pines, less of birch and fir trees. The largest forests are in the northern paid of Kurzeme and the northern Vidzeme. About 10 % of Latvia is swampland, mostly in the Coastal Lowland. About 14 thousand different animal species exist in Latvia. In the 20th century two species - wild boars and beavers have been reintroduced. In the last 20 years brown bears as well as muskrats have come into the territory of Latvia. Almost 300 plants and animal species are also on the endangered species list. About 700 areas and objects are under environmental protection of the state. The Gauja National park and 5 other nature preserves encompass most of this territory - «Slītere», «Grīņi», «Moricsala», «Krustkalni», «Teiči». Latvia is not rich in minerals. Peat is of significant economic importance. Its production level is 530 million tons. The largest peat bogs are in the area of Riga, Preiļi, Ludza, Valka, Aizkraukle. Economically, the most important minerals are raw materials for the -construction industry - dolomite, limestone, gypsum, clay, sand, gravel. Latvia has significant deposity of mineral water and medical mud. The largest cities in Latvia are the Capital City Riga, Daugavpils, Jelgava, Rēzekne. The ports of Riga, Liepāja and Ventspils are ice-free during winter. About 2,500 Indo-European tribes have arrived on the shores of the Baltic Sea. In Latvia the inhabitants split into several tribes: Zemgaļi, Sēļi, Latgaļi, Kurši. Most European languages can be traced back to these origins. Latvian and Lithuanian are the closest still surviving languages to the origin. The Līvs, a Finno-Ugric people whose language is related to Estonian, are equally ancient settlers, but only a few hundred of them survive today. Now the number of inhabitants in Latvia is 2 270 00. The ethnic composition of the population is the following: 56.6 % - Latvians, 30.3 % - Russians, 2.7% - Ukrainians, 4.3 % - Belarussians, 2.6 % - Polish, 1.4 % - Lithuanians. Not all inhabitants are also Latvian citizens. Since the USSR’s massive russification campaign has left Latvians almost a minority within their own country, the authorities granted citizenship on]у to pre-wax citizens and their descendants. The national currency, the Lat (Ls) replaced the transitional Latvian rouble in 1993. There are 100 santimi to the Lat, with 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50 santimi and 1 and 2 Ls coins. Bank notes come in denominations of 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 500 Ls. People can do the Baltics (Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia) by bike as the countryside is flat. However, not all roads are suited for that kind of adventure and cars rarely watch out for cyclists. It is more convenient to do Latvia in a car. Tourists can make a leisury drive to the scented pines and sandy beaches of Jūrmala - a popular 19th century health resort. It lies 20 km from Riga and stretches for 30 km along the beach of the Baltic Sea. Tourists might go on a sightseeing tour to Sigulda which lies in the Gauja National Park 60 km from Riga. It is known as the Latvian Switzerland. You should include a visit to the Turaida Castle built in the 13th century as the residence of the Livonian Master, a visit to Gutmanis’ cave - a monument of nature and to the Sigulda Castle - the former residence of the Master of the Livonian Order. The training and recreation park of Līgatne will give you a chance to meet a roe, wild bear, moose and other animals of Latvian fauna. The Botanic track will introduce you to the plants of the valley; on the' Fairy-tale track you will meet well-known legendary characters. The National Park of Gauja covers 92,048 hectares. 19 camps have been established on the banks of the Gauja. Going by boat you will better feel and understand the character of the river, the beauty of its rocky banks and the impressive Gauja valley. Situated at the crossroads of Eastern and Western Europe, Latvia has been the battleground for political struggles throughout the centuries. It has been invaded by Germans, Poles, Swedes, Russians and even the Napoleonic French. It has been saddled with many different foreign names: Terra Mariana, Livonia, Livland, Courland, Letgallia, Lettland. Yet, it has persisted as an ethnic entity due to the tenacity of the Latvian people. Known and unknown, free and subjugated, misunderstood by friends and misrepresented by foreign powers - Latvia exists. It is larger than Denmark, Switzerland, Israel. Of the 170 countries represented in the United Nations, one third are smaller than Latvia in size and population. Government in Latvia The Republic of Latvia declared Independence on November 18, 1918. A Constitutional Assembly was elected in April 1920 and the Satversme (Constitution) was adopted on February 15, 1922. Following the restoration of independence in 1991, the Satversme once again became the foundation of government in Latvia. Among the core features of Latvia’s system of government are the following: - the one-chamber Saeima (parliament) consisting of one hundred deputies elected for a term of 4 years; - the Saeima elects the State President for a term of 4 years; - the Prime Minister is nominated by the State President and, together with the Cabinet, must gain the approval of a majority in the Saeima; - the appointment of judges is confirmed by the Saeima. Political parties and associations must submit lists of candidates to the Central Electoral Commission and parliamentary elections take place on the first Sunday of October and the preceding Saturday. Lists of candidates are elected on the basis of proportional representation. To gain representation in the Saeima, an electoral list must garner at least five percent of all votes cast (before the 1995 elections, the threshold was four percent). Elections to the Saeima were held in 1922, 1925, 1928, 1931 and following the restoration,.of independence, in 1993 and 1995. There are 12 Government ministries in Latvia - the Ministries of Agriculture, Culture, Defence, Economy, Education and Science, Environmental Protection and Regional Development, Finance, Foreign Affairs, Interior, Justice, Transport and Welfare, Labour and Health, Neither the Prime Minister nor the members of the Cabinet are required to be Saeima deputies.