Evolution Note Sheet
advertisement
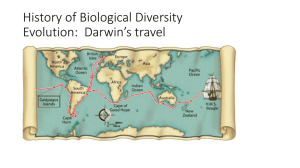
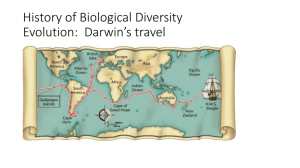
Name: ___________________ Period:____ History of Biological Diversity Evolution: Darwin’s travel Developing the Theory of Evolution The Galápagos Islands Darwin noticed that the different islands all seemed to have their own, _________ different varieties of animals. Somewhat similar species that suited their _________________ environment. Origin of Species: _________________________ In 1859 On the Origin of Species presented evidence and proposed a mechanism for evolution that he called __________________ ________________. Today, scientists use _______________ to mean cumulative change in a group of organisms through time. Natural selection is _____ synonymous with evolution – it is a _________________ by which evolution occurs. Peppered Moth: Natural Selection • The light colored form was the predominant form in ___________ prior to the Industrial Revolution. • • th Around the middle of the 19 century the darker form began to appear. It was first reported in 1848. By 1895 _______ of the moths in Manchester were the dark variety. In recent years, the burning of cleaner fuels and Clean Air regulations has reduced the pollution there and the lighter colored moths have increased in numbers. Types of Selection a. ____________ _____________ – humans select for variations in plants and animals that they find useful. b. _____________ ___________also means “Survival of the Fittest”. - Fitness in this sense does ______ mean strongest. - Fitness in Darwin terms means reproduction. The one who ____________ long enough to reproduce the most is the one with the ________________ fitness. Types of Natural Selection Evolution acts on the phenotype of the individual, not the genotype. There are 4 types of selection that can occur on a population. 1. Directional Selection – when individuals at _________end of the curve have a higher fitness than individuals in the middle or at the ___________ end of the curve. 1 2. Stabilizing Selection – when individuals near the _____________ of the curve have higher fitness than individuals at either end of the curve, narrowing of the graph. 3. Disruptive Selection – when individuals at either end have a higher fitness and individual near the _____________ of the curve are selected against. Over time with enough selection a population can go through genetic drift. a. ____________ _________________ – random change in allele frequency. 4. Sexual Selection: the ability to attract a ______________ Support for Evolution Evidence for evolution comes from: 1. The ____________ record: remains in layers of rock 2. Comparative ________________ a. ______________ Structures b. ______________ Structures c. _______________Structures 3. Comparative _______________________ 4. Comparative _______________________ 5. ___________________ distribution 1. Support of Evolution: Fossil Record • Fossil Record – Fossils are the remains of ancient organisms found in ________________ of rock in the Earth. • The layers of rock tell the _____________ of the Earth, while the fossils found within the rock tell a history of life. • The fossils are thought to be the _________ _________ as the rock they are found in. 2 Researchers consider __________ major classes of traits when studying transitional fossils: • __________ traits are newly ______________ features, such as feathers, that do not appear in the fossils of common ancestors. • __________ traits are more ______________ features, such as teeth and tails, that do appear in ancestral forms. • 2. Support for Evolution: Comparative Anatomy • A. Homologous structures are anatomically similar ________________ inherited from a common _______________. • Similar _____________ with ________________ function (similar bones) • (common ancestor) • • • • • B. Analogous structures can be used for the same ____________ and be superficially similar in construction, but are ______ inherited from a common ancestor. Structures are ______________ but have _____________ function C. Vestigial structures are structures that are the _____________ forms of functional structures in other organisms. Evolutionary theory predicts that features of ancestors that __________ longer have a function for that species will become _____________over time until they are lost. 3. Support for Evolution: Comparative embryology • Embryos of many animals with back-bones are very __________________. 4. Support for Evolution: Comparative Biochemistry ________________ ancestry can be seen in the complex metabolic molecules that many different organisms share. The more ______________ related species are to each other, the greater the biochemical similarity. Similarities in _________ and protein sequences suggest relatedness. 5. Support for Evolution Geographic distribution The distribution of ______ and animals that Darwin were what first suggested evolution to him. 3 The distribution of plants and animals around the world is studied in the field of ____________. Evolution is linked to migration patterns, climate, and geological forces (such as plate tectonics). _________________- an inherited trait that increases a population’s chance of survival and reproduction in a particular environment _______________ is a measure of the relative contribution an individual trait makes to the next generation. The better an organism is _______________ to its environment, the greater its chances of survival and reproductive success. Through _______________, populations often become suited to a specific job called a niche. • 1. niche – the role a population plays in a habitat - job, profession, role • 2. Competition arises when 2 populations ____________ the same niche. Adaptation Types of adaptations ________________ is a suite of morphological adaptations that allow an organism to blend into its environment. ______________ is a type of morphological adaptation where a species evolves to resemble another species. Antimicrobial resistance develops in some bacteria in response to sub-lethal exposure to __________________. Population Genetics - study of the traits in a population A. Population – a group of interbreeding organisms (a species) living in a ______________ area B. Gene Pool – ____________ genetic material of all the members of a population C. Gene Flow-the transfer of allele or genes from __________ population to ___________ D. Genetic Drift- any change in the allelic frequency in a population that results from __________. E. Allele – forms that a _________ can take F. Allele Frequency – the number of each allele for a trait This “changing of the gene pool” (allele frequency) has a name —› Evolution. Evolution – the changes in the gene pool of a population over time. Speciation – formation of a _______ species Reproductive Isolation - 2 or more species _________ _________ interbreed Prezygotic: Its happens ___________ fertilization: different reproductive times and different mating songs. Postzygotic: Its happens ___________ fertilization: fertilization has occurred but results in sterile offspring (Mule) 4 1. Behavioral Isolation occurs when 2 populations are capable of interbreeding but have differences in _________ ________ or breed at different ___________ 2. Geographic /Allopatric Isolation: 2 populations are separated by _____________barriers ●examples: rivers, mountains, bodies of water Types of Evolution Convergent Evolution: less alike to __________ alike Divergent Evolution=Adaptive Radiation: more alike to _________ alike Coevolution: evolve _____________ Punctuated equilibrium: happens in _________ period of time Convergent Evolution: Occurs when ______________ organisms that live in ____________ environments become more alike in appearance and _______________. Less alike to more alike Examples: - Bird wings/insect wings - Shark fins/dolphin fins Divergent/Adaptive Evolution __________ species give rise to _______ species More alike to less alike Also known as adaptive radiation. Examples: - Darwin’s Finches. - Brown bears and polar bears Co-evolution Co-evolution occurs when, ___________or more organisms evolve _____________. Gradual equilibrium Predicts that little of evolutionary change takes place in _________ gradual steps Punctuated equilibrium predicts that a lot of evolutionary change takes place in ____________ periods of time tied to speciation events. 5 6