Name Nuclear Chemistry 1. In which type of atom would radioactive
Name ______________________ Nuclear Chemistry
1.
In which type of atom would radioactive decay most likely occur?
A. atoms with unstable nuclei
B. atoms with more than 8 valence electrons
2.
P-32 has a half-life of about 14 days. If you start with 100 g of P-32, how many grams will remain after 28 days?
C. an atom with less than 26 protons
D. atoms with less than 8 valence electrons
C. 50 grams
D. 75 grams
A. 100 grams
B. 25 grams
3. Cobalt-60 has a half-life of about 5 years. If you start with a pure sample of Co-60, how much time will it take for 75% of the original Co-60 to decay into other products?
A. 5 years B. 10 years C. 15 years D. 20 years
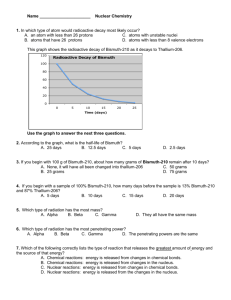
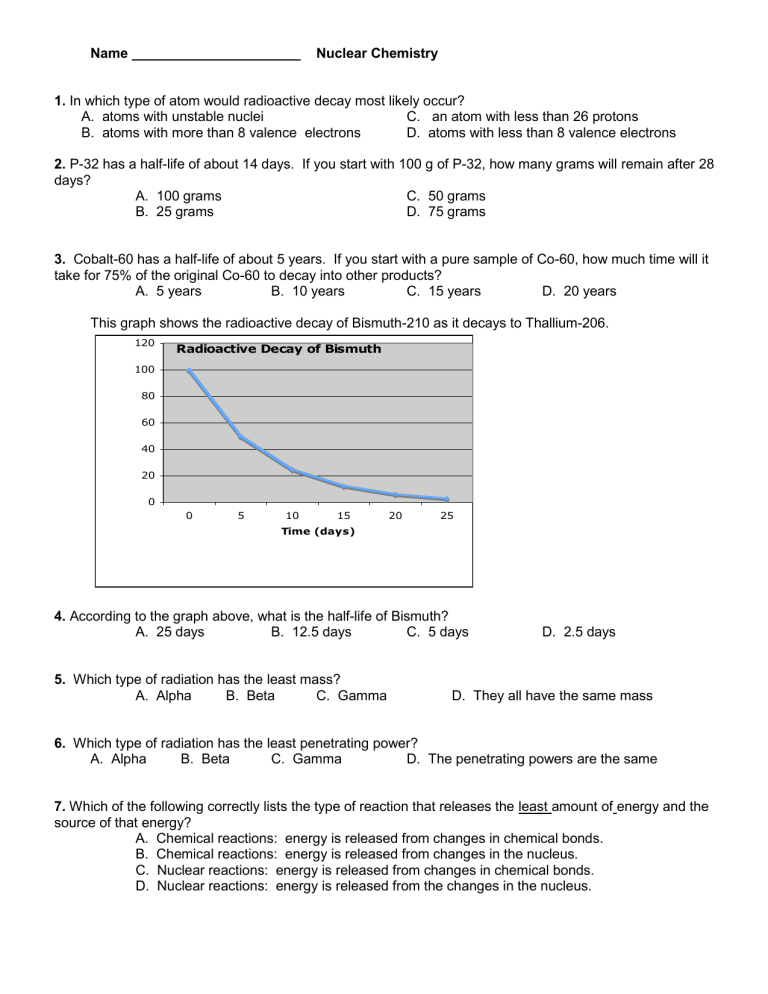
This graph shows the radioactive decay of Bismuth-210 as it decays to Thallium-206.
120
Radioactive Decay of Bismuth
100
80
60
40
20
0
0 5 10 15
Time (days)
20 25
4.
According to the graph above, what is the half-life of Bismuth?
A. 25 days B. 12.5 days C. 5 days
5. Which type of radiation has the least mass?
A. Alpha B. Beta C. Gamma
6.
Which type of radiation has the least penetrating power?
D. 2.5 days
D. They all have the same mass
A. Alpha B. Beta C. Gamma D. The penetrating powers are the same
7.
Which of the following correctly lists the type of reaction that releases the least amount of energy and the source of that energy?
A. Chemical reactions: energy is released from changes in chemical bonds.
B. Chemical reactions: energy is released from changes in the nucleus.
C. Nuclear reactions: energy is released from changes in chemical bonds.
D. Nuclear reactions: energy is released from the changes in the nucleus.
8. A radioactive particle is attracted to a positive charge and repelled by a negative charge. What is most likely the identity of the particle? a. alpha b. beta c. gamma
9. Which reaction takes place in a nuclear power plant using uranium as a fuel source?
A. a chemical reaction B. nuclear fission C. nuclear fusion
10. What creates the light of the sun?
A. combustion of hydrogen and oxygen gas B. nuclear fission
11. How would exposure to high levels of nuclear radiation affect a human?
C. nuclear fusion
A. loss of hair, nausea, vomiting, illness, death
B. skin and eyes begins to glow in the dark, extra limbs sprout from body
C. develops extraordinary strength, size, and/or supernatural abilities
D. high levels of nuclear radiation do not affect humans
12 . What can be emitted by atomic nuclei as they decay?
A. Particles only
B. Wavelike radiations only
C. Wavelike radiations and particles
D. Nothing; atomic nuclei do not decay
13. What is the main concern about building nuclear power plants?
A. greenhouse gas emissions
B. causing global warming
C. cost ($)
D. long-term storage of nuclear wastes
14. Which force is strongest? a. The electrostatic force repelling two protons within the same nucleus b. The electrostatic force repelling electrons of one atom from the electrons of another atom. c. The strong nuclear force between two protons in the same nucleus d. The force of attraction between the positive nucleus and the negative electrons
15. Which reaction will produce the greatest amount of energy? c. the combustion of 10 kg of hydrogen gas with an excess of oxygen gas d. the combustion of 10 kg of dynamite with oxygen
16 . Which particles given off by an unstable nucleus have a mass of four atomic mass units and a positive charge? a. the nuclear fusion of 10 kg of hydrogen b. the reaction of 10 kg of sodium with an excess of water b. beta radiation c. alpha radiation a. gamma radiation
17.
The half-life of a radioactive element a. is the time it take for half of a radioactive element to decay b. is half the time it takes for all of a radioactive element to decay c. is half the mass of product remaining after a radioactive element decays d. is the same for all radioactive elements, no matter what their identity
18.
What force is responsible for the energy released in nuclear reactions? a. the force of attraction between the nucleus and the electrons orbiting that nucleus b. the nuclear force which holds protons and neutrons together within a nucleus c. the force of gravity which pulls matter together d. the electromagnetic force of attraction between the positive nucleus of one atom and the electrons of another atom