Converting fractions to decimals
advertisement
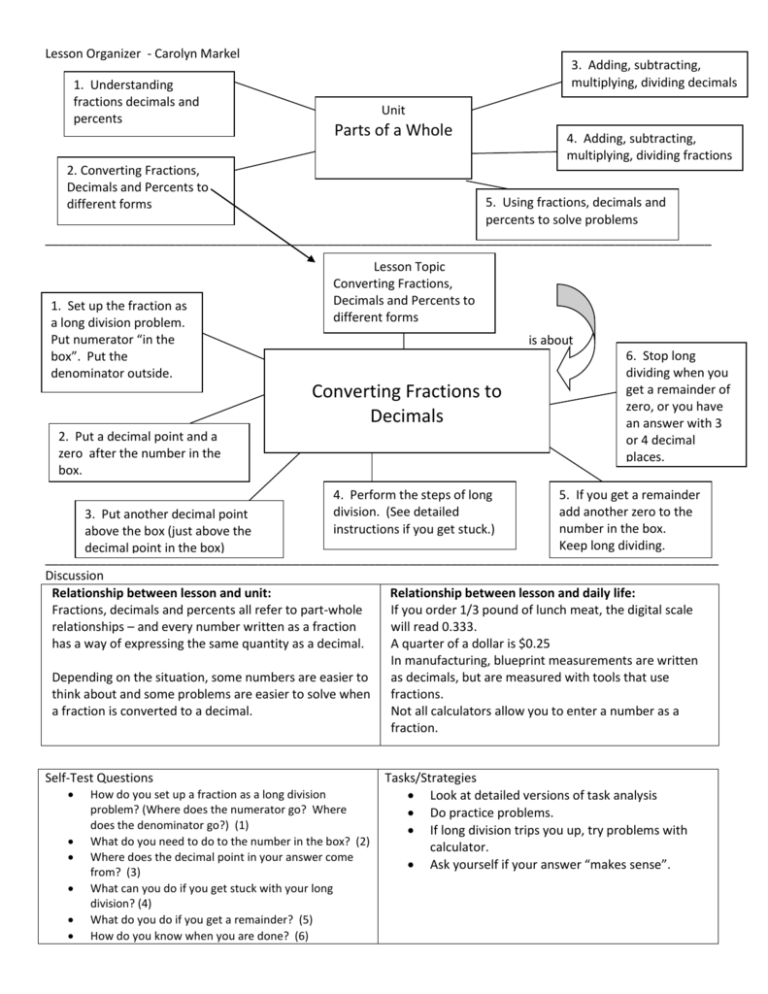
Lesson Organizer - Carolyn Markel 1. Understanding fractions decimals and percents 3. Adding, subtracting, multiplying, dividing decimals Unit Parts of a Whole 4. Adding, subtracting, multiplying, dividing fractions 2. Converting Fractions, Decimals and Percents to different forms 5. Using fractions, decimals and percents to solve problems _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 1. Set up the fraction as a long division problem. Put numerator “in the box”. Put the denominator outside. Lesson Topic Converting Fractions, Decimals and Percents to different forms is about Converting Fractions to Decimals 2. Put a decimal point and a zero after the number in the box. 6. Stop long dividing when you get a remainder of zero, or you have an answer with 3 or 4 decimal places. 4. Perform the steps of long division. (See detailed instructions if you get stuck.) 5. If you get a remainder add another zero to the 3. Put another decimal point number in the box. above the box (just above the Keep long dividing. decimal point in the box) __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Discussion Relationship between lesson and unit: Relationship between lesson and daily life: Fractions, decimals and percents all refer to part-whole If you order 1/3 pound of lunch meat, the digital scale relationships – and every number written as a fraction will read 0.333. has a way of expressing the same quantity as a decimal. A quarter of a dollar is $0.25 In manufacturing, blueprint measurements are written Depending on the situation, some numbers are easier to as decimals, but are measured with tools that use think about and some problems are easier to solve when fractions. a fraction is converted to a decimal. Not all calculators allow you to enter a number as a fraction. Self-Test Questions How do you set up a fraction as a long division problem? (Where does the numerator go? Where does the denominator go?) (1) What do you need to do to the number in the box? (2) Where does the decimal point in your answer come from? (3) What can you do if you get stuck with your long division? (4) What do you do if you get a remainder? (5) How do you know when you are done? (6) Tasks/Strategies Look at detailed versions of task analysis Do practice problems. If long division trips you up, try problems with calculator. Ask yourself if your answer “makes sense”.