Click here for the resource
advertisement
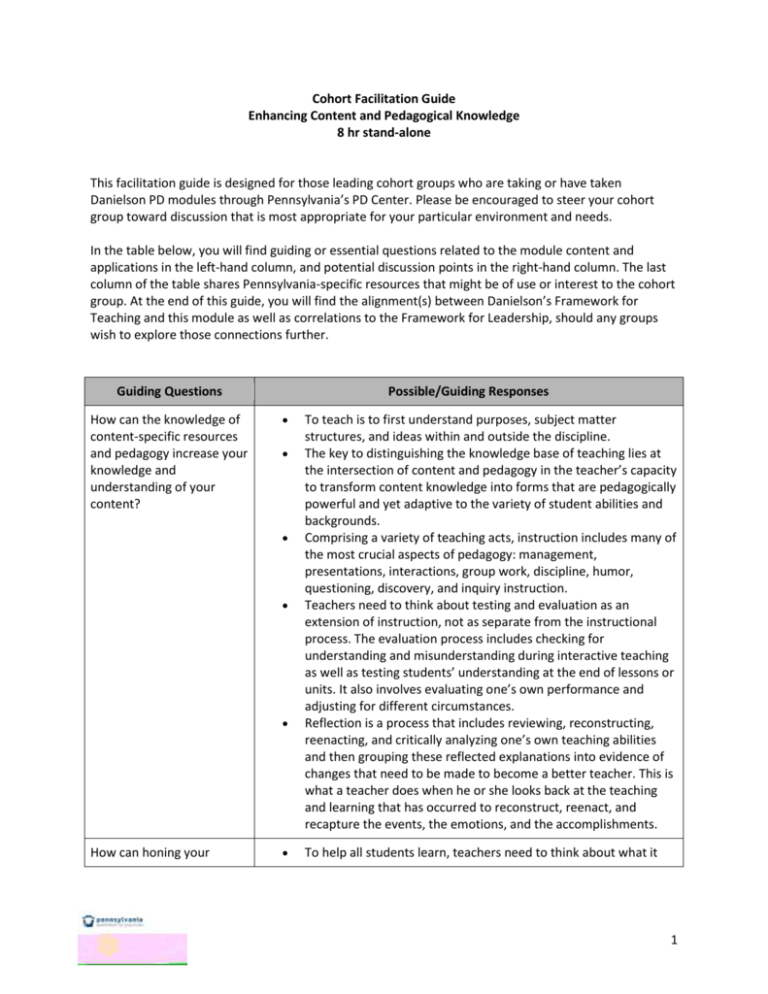
Cohort Facilitation Guide Enhancing Content and Pedagogical Knowledge 8 hr stand-alone This facilitation guide is designed for those leading cohort groups who are taking or have taken Danielson PD modules through Pennsylvania’s PD Center. Please be encouraged to steer your cohort group toward discussion that is most appropriate for your particular environment and needs. In the table below, you will find guiding or essential questions related to the module content and applications in the left-hand column, and potential discussion points in the right-hand column. The last column of the table shares Pennsylvania-specific resources that might be of use or interest to the cohort group. At the end of this guide, you will find the alignment(s) between Danielson’s Framework for Teaching and this module as well as correlations to the Framework for Leadership, should any groups wish to explore those connections further. Guiding Questions How can the knowledge of content-specific resources and pedagogy increase your knowledge and understanding of your content? Possible/Guiding Responses How can honing your To teach is to first understand purposes, subject matter structures, and ideas within and outside the discipline. The key to distinguishing the knowledge base of teaching lies at the intersection of content and pedagogy in the teacher’s capacity to transform content knowledge into forms that are pedagogically powerful and yet adaptive to the variety of student abilities and backgrounds. Comprising a variety of teaching acts, instruction includes many of the most crucial aspects of pedagogy: management, presentations, interactions, group work, discipline, humor, questioning, discovery, and inquiry instruction. Teachers need to think about testing and evaluation as an extension of instruction, not as separate from the instructional process. The evaluation process includes checking for understanding and misunderstanding during interactive teaching as well as testing students’ understanding at the end of lessons or units. It also involves evaluating one’s own performance and adjusting for different circumstances. Reflection is a process that includes reviewing, reconstructing, reenacting, and critically analyzing one’s own teaching abilities and then grouping these reflected explanations into evidence of changes that need to be made to become a better teacher. This is what a teacher does when he or she looks back at the teaching and learning that has occurred to reconstruct, reenact, and recapture the events, the emotions, and the accomplishments. To help all students learn, teachers need to think about what it 1 teaching skills in your content area improve your teaching, your crosscurricular connections, and student learning? How can professional development increase your understanding of content and pedagogy? In what ways can you map out your own growth plan in order to maximize your own teaching potential? means to learn different kinds of material for different purposes and how to decide which kinds of learning are most necessary in different contexts. Teachers must be able to identify the strengths and weaknesses of different learners and must have the knowledge to work with students who have specific learning disabilities or needs. Teachers need to know about curriculum resources and technologies to connect their students with sources of information and knowledge that encourage them to explore ideas, acquire and synthesize information, and frame and solve problems. Teachers need to know about collaboration: how to structure interactions among students so that more powerful shared learning can occur, how to collaborate with other teachers, and how to work with parents to learn more about their children and to shape supportive experiences at school and home. Acquiring knowledge and developing a practice that is different from what teachers themselves experienced as students requires learning opportunities that are more powerful than simply reading and talking about new pedagogical ideas. Teachers learn best by studying, by doing and reflecting, by collaborating with other teachers, by looking closely at students and their work, and by sharing what they see. Good settings for teacher learning–in both colleges and schools– provide lots of opportunities for research and inquiry, for trying and testing, and for talking about and evaluating the results of learning and teaching. The combination of theory and practice occurs most productively when questions arise in the context of real students and work in progress and where research and disciplined inquiry are also at hand. When teachers investigate the effects of their teaching on students’ learning and if they read about what others have learned, they become aware of variation and of what works for what purposes and in what situations. Training in inquiry also helps teachers learn how to look at the world from multiple perspectives and to use this knowledge to reach across disciplines and with diverse learners. Reflecting on current practice and seeking to improve upon it. Exploring what PD opportunities exist and participating in those that are appropriate. Collaborating with team members for cross-curricular ideas and also with peers who teach the same content. Keeping current with PA Core Standards. Beginning, continuing, and maintaining strategy sharing sessions. 2 *What forms of assessment do you utilize to collect data to determine the Present Levels of Educational and Functional Performance of your students? Offering and improving ongoing curriculum based assessment. Creating a consistent assessment schedule to monitor student progress. *How do you set IEP goals and/or determine short term objectives that are aligned with content state standards and with your student’s present educational levels? Having a knowledge of state and national curricular standards. Applying standards when formulating annual and short term IEP goals and objectives. *How do you differentiate and individualize instruction to meet the specific needs for your students? Utilizing data from curriculum based assessments to develop appropriate instruction to meet the student’s current level of functioning. *What resources do you use, beyond the curriculum and teacher edition of a textbook? Exploring outside resources such as the local newspaper or awardwinning literature. Implementing appropriate use of technology and Internet resources. What PA-specific online resources are available to you that will enhance your content and pedagogical knowledge? SAS http://www.pde.sas.org PaTTAN http://www.pattan.net/ Intermediate Units https://www.paiu.org/ Pennsylvania Learning Forward http://www.learningforwardpa.org/ Pennsylvania Association for Curriculum Development http://www.pascd.org/ Primary alignment between Enhancing Content and Pedagogical Knowledge and the Framework for Teaching: 1a: Demonstrating Knowledge of Content and Pedagogy Correlations between Enhancing Content and Pedagogical Knowledge and the Framework for Leadership: 1c: Builds a Collaborative and Empowering Work Environment 3b: Aligns Curricula, Instruction, and Assessment 3c: Implements High Quality Instruction 3 3d: Sets High Expectations for All Students 4a: Maximizes Parent and Community Involvement and Outreach 4b: Shows Professionalism 4c: Supports Professional Growth * Modified from Guiding Questions: Conversations Between Principals and Teachers © Pennsylvania Department of Education, 2013. 4