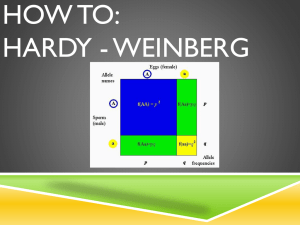
Popluations in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
advertisement

Name: _HINTS_ Popluations in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Worksheet HINTS: You will need to use the two equations we learned yesterday, write them down at the top of your page so you will have them handy!!!! I have highlighted the information that you will need to start off with, and told you what variable it is referring to. 1. A population of birds is in Hardy-Weinberg (genetic) equilibrium. 20 percent of the birds have short tail feathers, which is a recessive trait. Determine the genotype and allele frequencies of the population. a recessive trait means we are talking about the homozygous recessive genotype (aa). So, aa = q2 = 20% = 0.20 2. In a population of ferns, a biologist has determined that 60 percent of leaf-shape genes in the population carry the dominant allele for curly leaves (C). The remaining 40 percent of the genes carry the recessive allele for straight leaves (c). Determine the genotype and allele frequencies of the next generation of ferns. Because they use the word dominant allele we are referring to: C = p = 60% = 0.60 Because they use the word recessive allele we are referring to: c = q = 40% = 0.40 3. Allele Z is dominant, and is present in a population at a frequency of 37 per 100 individuals. Assuming the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, what proportion of individuals in the population would be expected to be (a) homozygous dominant, (b) heterozygous, and (c) homozygous recessive? allele Z means we are talking about allele frequency of the dominant allele: Z = p = 37/100 = 0.37 4. In a large, random-mating population, 85 in every 1000 humans carry the recessive allele for red hair. a) What percentage of the population carries this allele but does not exhibit red hair? Carries the recessive allele refers to individuals who carry it as homozygous recessive AND in the heterozygous form. So we are talking about allele frequency: q = 85/1000 = 0.085 Name: _HINTS_ b) Would you expect to see a change in allele frequencies if members of this population preferentially mated with individuals with red hair? Explain your answer. go over Hardy-Weinberg conditions 5. If a small, random-mating population has 18 percent of individuals exhibiting a recessive trait, could you calculate the genotype and allele frequencies of the next generation? Explain your answer. go over Hardy-Weinberg conditions 6. 45 percent of individuals in a population of raccoons have a recessive trait. If the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, calculate the frequency of the dominant allele in the population. Having the recessive trait means we are referring to the homozygous recessive genotype (aa) So, aa = q2 = 45% = 0.45