1-8 Chapter 1 Review WKST
advertisement

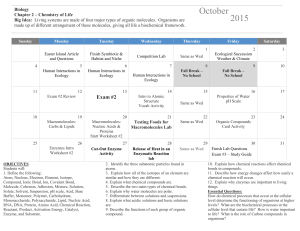
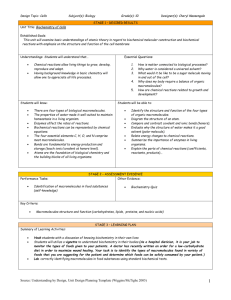
CHAPTER 1 REVIEW SHEET 1. Biochemistry: The study of _______________ processes at the _______________ level using the principles and language of _______________. 2. Studying applications of biochemical research to help solve human problems like disease and nutrition is important, but why study biochemical processes of many species? 3. Briefly describe the roles of the following scientists in the development of biochemistry. a. Friedrich Wöhler b. Eduard Buchner c. Emil Fischer d. Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty e. Watson and Crick f. Kendrew and Pentz 4. Which six nonmetallic elements account for over 97% of the weight of most organisms? What five essential ions are necessary for an organism? 5. Compare the role differences between organic and biological chemists. 6. Classify the following molecules based on their functional group. OH _______________ NH2 _______________ _______________ O _______________ _______________ SH _______________ O - O O - O O O P O - O P _______________ O - O - _______________ 7. Identify the linkages in the following molecules, and describe the type of biomolecule that would contain the linkage: O O a. O P P O - R O b. R O R - O O R N R O R H c. O O - P O R O d. - O e. R O R 8. What is the most important difference between chemical reactions in organisms and chemical reactions studied in the lab? 9. What fundamental concept of organic chemistry must be retained while studying how enzymes speed up reactions? 10. Biochemical macromolecules are _______________ created by joining small organic molecules called _______________ through _______________. 11. What difference between macromolecules and their residues leads to the fact that each new level of biological organization results in properties that cannot be predicted solely from those of the previous level? 12. Place the following levels of complexity in the correct order: Organelles Whole organisms Molecules Cells Tissues Organs Macromolecules Atoms 13. Draw the structure of a generic amino acid. 14. How and when are pepide bonds formed? 15. Identify two general functions of proteins. What determines the function of the protein? Where on proteins do chemical reactions take place? 16. What elements make up carbohydrates? What are simple sugars such as glucose called, what do they turn into when they are polymerized? 17. Draw glucose in the Haworth projection using the Fischer projection provided. H C O H C OH HO C H H C OH H C OH CH 2OH 18. Draw ribose in the Fischer projection using the Haworth projection provided. 19. Glucose is the monomeric unit of _______________, _______________ and _______________. 20. Identify the glycosidic bonds in cellulose shown below. 21. The presence of strong ___–bonding between the _______________ groups in cellulose makes it a very _______________ linear polymer found in plant stems. 22. Identify the three major components of a nucleic acid and label them on the given molecule. 23. In a _______________, a _______________ linkage forms between the _______________ group of one nucleotide and the C-3 oxygen atom of the _______________ of another nucleotide. 24. Nucleic acids have a backbone of alternating _______________ and _______________. 25. Draw a simple fatty acid. They are found as parts of _______________ and are major components of biological _______________. 26. How does a lipid bilayer form? 27. Membranes contain _______________ that allow _______________ to enter the cell, _______________ to exit the cell, and _______________ reactions at the membrane surface. 28. Most of the energy required for life comes from the __________. 29. What do photosynthetic organisms accomplish in the energy flow of life? 30. All organisms use _______________ compounds and _______________ to synthesize _______________. 31. Metabolism is the _______________ and _______________ of organic compounds to extract, store and use _______________. 32. The first cells were most likely _______________-celled organisms that would classify as _______________ today. The process of _______________ explains how such cells were able to diversify to form _______________, which are _______________-cellular organisms. 33. The evidence of common cellular _______________ includes the presence in all living organisms of common biochemical building blocks, the same general pattern of metabolism, and a common genetic code. 34. What two structural aspects do viruses contain? Why aren’t viruses considered cells? How do they reproduce? 35. Much of what we know about biochemistry comes from studying what prokaryote? 36. Identify the parts of the E coli cell below, then briefly describe their structure and/or role. A ____________________: B ____________________: C ____________________: D ____________________: E ____________________: F ____________________: G ____________________: H ____________________: I ____________________: 37. What is the most distinguishing feature of eukaryotes? What happens to DNA inside of this? 38. Identify three major differences between animal and plant cells. 39. Identify the parts of the generic animal cell below, then briefly describe their role. A ____________________: B ____________________: C ____________________: D ____________________: E ____________________: F ____________________: G ____________________: H ____________________: I ____________________: J ____________________: K ____________________: 40. What purpose does the extracellular matrix serve for cells in tissues? 41. What drives the conversion of ADP to ATP, and what is ATP used for? 42. Briefly describe the following subcellular structures found in the _______________: a. Actin b. Microtubules c. Intermediate filaments Match the organelle with its sketch: _____ 43. Endoplasmic reticulum A. B. _____ 44. Golgi apparatus _____ 45. Mitochondrion _____ 46. Chloroplast C. D. 47. The cytoplasm is densely _______________, the molecules inside are in constant _______________, and the collisions between the molecules are _______________. 48. An enzyme and a small molecule will collide one million times a _______________, and some enzymes will react to achieve a rate of catalysis far faster than 1 in every _______________. 49. It was believed that simple _______________ governed cytosolic activity, but more and more research is proving that there is _______________ to the cytosol.