The Perfect Beak Equip Rubric
advertisement
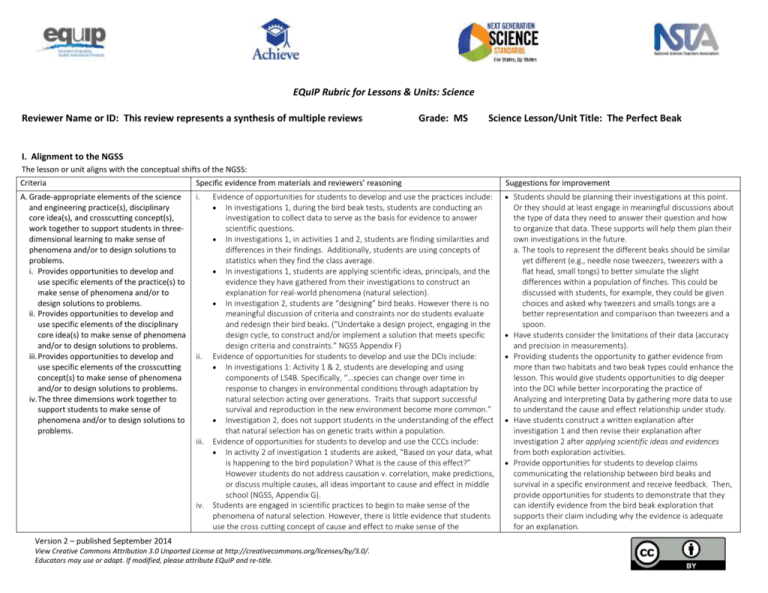
EQuIP Rubric for Lessons & Units: Science Reviewer Name or ID: This review represents a synthesis of multiple reviews Grade: MS Science Lesson/Unit Title: The Perfect Beak I. Alignment to the NGSS The lesson or unit aligns with the conceptual shifts of the NGSS: Criteria Specific evidence from materials and reviewers’ reasoning Suggestions for improvement A. Grade-appropriate elements of the science and engineering practice(s), disciplinary core idea(s), and crosscutting concept(s), work together to support students in threedimensional learning to make sense of phenomena and/or to design solutions to problems. i. Provides opportunities to develop and use specific elements of the practice(s) to make sense of phenomena and/or to design solutions to problems. ii. Provides opportunities to develop and use specific elements of the disciplinary core idea(s) to make sense of phenomena and/or to design solutions to problems. iii. Provides opportunities to develop and use specific elements of the crosscutting concept(s) to make sense of phenomena and/or to design solutions to problems. iv. The three dimensions work together to support students to make sense of phenomena and/or to design solutions to problems. i. Students should be planning their investigations at this point. Evidence of opportunities for students to develop and use the practices include: In investigations 1, during the bird beak tests, students are conducting an investigation to collect data to serve as the basis for evidence to answer scientific questions. In investigations 1, in activities 1 and 2, students are finding similarities and differences in their findings. Additionally, students are using concepts of statistics when they find the class average. In investigations 1, students are applying scientific ideas, principals, and the evidence they have gathered from their investigations to construct an explanation for real-world phenomena (natural selection). In investigation 2, students are “designing” bird beaks. However there is no meaningful discussion of criteria and constraints nor do students evaluate and redesign their bird beaks. (“Undertake a design project, engaging in the design cycle, to construct and/or implement a solution that meets specific design criteria and constraints.” NGSS Appendix F) ii. Evidence of opportunities for students to develop and use the DCIs include: In investigations 1: Activity 1 & 2, students are developing and using components of LS4B. Specifically, “…species can change over time in response to changes in environmental conditions through adaptation by natural selection acting over generations. Traits that support successful survival and reproduction in the new environment become more common.” Investigation 2, does not support students in the understanding of the effect that natural selection has on genetic traits within a population. iii. Evidence of opportunities for students to develop and use the CCCs include: In activity 2 of investigation 1 students are asked, “Based on your data, what is happening to the bird population? What is the cause of this effect?” However students do not address causation v. correlation, make predictions, or discuss multiple causes, all ideas important to cause and effect in middle school (NGSS, Appendix G). iv. Students are engaged in scientific practices to begin to make sense of the phenomena of natural selection. However, there is little evidence that students use the cross cutting concept of cause and effect to make sense of the Version 2 – published September 2014 View Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/. Educators may use or adapt. If modified, please attribute EQuIP and re-title. Or they should at least engage in meaningful discussions about the type of data they need to answer their question and how to organize that data. These supports will help them plan their own investigations in the future. a. The tools to represent the different beaks should be similar yet different (e.g., needle nose tweezers, tweezers with a flat head, small tongs) to better simulate the slight differences within a population of finches. This could be discussed with students, for example, they could be given choices and asked why tweezers and smalls tongs are a better representation and comparison than tweezers and a spoon. Have students consider the limitations of their data (accuracy and precision in measurements). Providing students the opportunity to gather evidence from more than two habitats and two beak types could enhance the lesson. This would give students opportunities to dig deeper into the DCI while better incorporating the practice of Analyzing and Interpreting Data by gathering more data to use to understand the cause and effect relationship under study. Have students construct a written explanation after investigation 1 and then revise their explanation after investigation 2 after applying scientific ideas and evidences from both exploration activities. Provide opportunities for students to develop claims communicating the relationship between bird beaks and survival in a specific environment and receive feedback. Then, provide opportunities for students to demonstrate that they can identify evidence from the bird beak exploration that supports their claim including why the evidence is adequate for an explanation. phenomena of natural selection. There is no evidence of all three dimensions working together to support each other to assist students in understanding the phenomena. Emphasize that it is the genetic traits that drive the outward expression of the beak. The engineering component suggests that animals can “choose” or “design” traits that are beneficial to a particular environment. This particular investigation can lead to or reinforce misconceptions regarding natural selection and genetics and should be modified to avoid this possibility. Consider incorporating a dominant vs. recessive trait simulation to better address the idea of predominance vs. suppression indicated in LS4.B. Make the crosscutting concept of cause and effect more central in the lesson. Students must be able to make a connection that the cause (the genetic trait) led to the effect (the beak shape) which led to the effect of survival. It should also be done in a more grade-appropriate way (see I.A.iii.). A unit or longer lesson will also: Criteria Specific evidence from materials and reviewers’ reasoning Suggestions for improvement B. Lessons fit together coherently targeting a set of expectations. i. Each lesson links to previous lessons and provides a need to engage in the current lesson. ii. The lessons help students develop proficiency on a targeted set of performance expectations. In activity 2, Investigation 1, students are required to use understandings gained from activity 1, investigation 1 in order to make sense of what is happening in that particular exercise. Students are expected to make connections to activities 1 & 2 in after watching the video clip about natural selection. In investigation 2, students are “designing” bird beaks that best fit within both of the environments. While this design does require the students to use the data they collected in activities 1 and 2 it does not guide the student in developing proficiency of the targeted performance expectation. Remove investigation 2 as it is not an appropriate use of C. Where appropriate, disciplinary core ideas from different disciplines are used together to explain phenomena. D. Where appropriate, crosscutting concepts are used in the explanation of phenomena from a variety of disciplines. E. Provides grade-appropriate connection(s) to the Common Core State Standards in Mathematics and/or English Language Arts & Literacy in History/Social Studies, Science and Technical Subjects. There is no evidence of disciplinary core ideas from other disciplines. Consider the inclusion of ESS2.A, ESS2.C, ESS3.A There is no evidence of cross cutting concepts that support students in explaining phenomena from other disciplines. Consider using cause and effect and stability and change There is no evidence of a connection to the CCSS in Math and/or ELA (a writing task was mentioned in the cumulative assessment but without more information it is difficult to assess if it includes components of grade-appropriate writing like “the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant content” (CCSS)). Have students graph data collected in activities 1 & 2; engineering. It can lead to misconceptions about why certain traits are suppressed within a population and why others increase in numbers. And as noted it does not help students build understanding toward the identified PE MS-LS4-4. See suggestion on adding in a piece on recessive vs. dominate genes above. Consider providing a graphic representation of the storyline. to make connections across the DCIs listed above. they can also determine the best way to analyze this data. II. Instructional Supports The lesson or unit supports instruction and learning for all students: Criteria Specific evidence from materials and reviewers’ reasoning A. Engages students in authentic and meaningful scenarios that reflect the practice of science and engineering as Natural selection and the survival of the birds is motivating to many middle school students. Suggestions for improvement Providing an anchor phenomenon attached to an overarching question would improve the lesson: students 2 experienced in the real world and that provide students with a purpose (e.g., making sense of phenomena and/or designing solutions to problems). i. The context, including phenomena, questions, or problems, motivates students to engage in threedimensional learning. ii. Provides students with relevant phenomena (either firsthand experiences or through representations) to make sense of and/or relevant problems to solve. iii. Engages students in multiple practices that work together with disciplinary core ideas and crosscutting concepts to support students in making sense of phenomena and/or designing solutions to problems. iv. Provides opportunities for students to connect their explanation of a phenomenon and/or their design solution to a problem to their own experience. v. When engineering performance expectations are included, they are used along with disciplinary core ideas from physical, life, or earth and space sciences. B. Develops deeper understanding of the practices, disciplinary core ideas, and crosscutting concepts by identifying and building on students’ prior knowledge. C. Uses scientifically accurate and grade-appropriate scientific information, phenomena, and representations to support students’ three-dimensional learning. D. Provides opportunities for students to express, clarify, justify, interpret, and represent their ideas and respond to peer and teacher feedback orally and/or in written form as appropriate to support student’s three-dimensional learning. E. Provides guidance for teachers to support differentiated instruction in the classroom so that every student’s needs are addressed by including: i. Suggestions for how to connect instruction to the students' home, neighborhood, community and/or culture as appropriate. ii. Appropriate reading, writing, listening, and/or speaking alternatives (e.g., translations, picture support, graphic organizers) for students who are English language learners, have special needs, or read well below the grade level. iii. Suggested extra support (e.g., phenomena, representations, tasks) for students who are struggling to meet the performance expectations. iv. Extensions for students with high interest or who have already met the performance expectations to develop The lesson provides students with relevant phenomena (through representations with the bird beak activities) that help them to make sense of natural selection. Multiple practices (e.g., investigations, analyzing data) are used together with disciplinary core ideas. There is no evidence that students are able to connect the phenomenon to their own experience. a. As currently written, the students design their own bird beak to address this particular component. However, this activity is not real-world and does not assist the students in making sense of their world. While engineering is included along with life science, the engineering performance expectation does not properly address the LS DCI. Traits cannot be “chosen” and beneficial phenotypes are not naturally designed. The lesson begins with instructions to teachers to use the anticipation guide as a form of pre-assessment. However, there is no guidance in regards to how teachers should build on this or differentiate their lessons through the use of the three dimensions. The lesson uses scientifically accurate and grade appropriate scientific information in activities 1 & 2 of investigation 1. Investigation 2 is not scientifically accurate for reasons previously stated. There is a writing opportunity at the end that is not very fleshed out. Students have opportunities to respond to peers and the teacher orally. Students respond to the written questions after the activities in the investigations. would be working towards an explanation of a phenomenon (as the identified practice states on page 1) as well as improve the opportunities to blend the three dimensions together on the road to the explanation. Have students research the affects of invasive species on native populations to show a connection to an environment changing and the organism having/not having the genotype necessary for survival. Student could also research organisms which have become extinct and/or adapted to their environment and provide explanations as to why that has occurred. These opportunities would better connect the phenomena to real-world scenarios. Additionally, student should have an opportunity to connect this phenomena to their lives. The idea of artificial selection could be introduced and compared to natural selection. Students could become involved in some type of phenotype/genotype modeling with Punnett squares to illustrate pattern of traits becoming more common over successive generations. Provide a variety of questions, some with higher depth of knowledge levels, to ensure that students are using all three dimensions to deepen their understandings. See previous suggestions. Consider increasing the rigor of the questions to further emphasize the crosscutting concepts and to ensure that students are using all three dimensions. See suggestions above about connecting to students lives. Writing supports should be provided for students who need them. Students may need supports in engaging in the practices (for example, see suggestions in I.A to support students in learning how to plan an investigation and collect data). There are lots of current issues regarding environmental changes or invasive species that could be used to create extensions for students with high interest. Additionally, extensions should allow for more rigorous practices and crosscutting concepts. 3 deeper understanding of the practices, disciplinary core ideas, and crosscutting concepts. A unit or longer lesson will also: Criteria Specific evidence from materials and reviewers’ reasoning F. Provides guidance for teachers throughout the unit for how lessons build on each other to support students developing deeper understanding of the practices, disciplinary core ideas, and crosscutting concepts over the course of the unit. G. Provides supports to help students engage in the practices as needed and gradually adjusts supports over time so that students are increasingly responsible for making sense of phenomena and/or designing solutions to problems. Suggestions for improvement Due to the length of this evidence, this criterion was not used. Due to the length of this evidence, this criterion was not used. III. Monitoring Student Progress The lesson or unit supports monitoring student progress: Criteria Specific evidence from materials and reviewers’ reasoning A. Elicits direct, observable evidence of threedimensional learning by students using practices with core ideas and crosscutting concepts to make sense of phenomena and/or to design solutions. There are some opportunities to elicit direct and observable evidence of understanding such as through discussion and writing, but it is not three dimensional. B. Formative assessments of three-dimensional learning are embedded throughout the instruction. C. Includes aligned rubrics and scoring guidelines that provide guidance for interpreting student performance along the three dimensions to support teachers in (a) planning instruction and (b) providing ongoing feedback to students. There is no evidence that learning would be altered, therefore, assessments are not formative. D. Assessing student proficiency using methods, vocabulary, representations, and examples that are accessible and unbiased for all students. Suggestions for improvement Create a list of questions that are more rigorous and incorporate all three dimensions as a guide for teachers. Consider using CCC as a lens for questioning. Writing tasks are excellent resources for three dimensional assessment. Consider making the writing task a more robust opportunity for students to demonstrate learning. It could be an explanation that is started earlier and revised over time based on new experiences and information the students obtain. Provide guidance to teachers about what steps to take if assessments identify that students are struggling. Rubrics should be included, especially for the writing task, that are three-dimensional and support teachers in providing feedback to students and planning instruction. As noted previously, the engineering component should be removed. A unit or longer lesson will also: Criteria Specific evidence from materials and reviewers’ reasoning E. Includes pre-, formative, summative, and selfassessment measures that assess three- Due to the length of this evidence, this criterion was not used. Suggestions for improvement 4 dimensional learning. F. Provides multiple opportunities for students to demonstrate performance of practices connected with their understanding of disciplinary core ideas and crosscutting concepts and receive feedback. Due to the length of this evidence, this criterion was not used. 5