Food webs - biology-field
advertisement

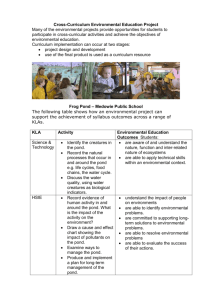
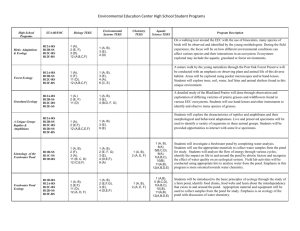
Drawing a food web (adapted from Nelson Biology Units 1 and 2 Activity Manual: Activity 11.1) Introduction A food web is a network of food chains, showing how organisms get their food and energy from other organisms. Purpose To construct food webs from second-hand data. Procedure Part A – A pond community Organisms Carp Prawns Snails Flycatchers (bird) Pond flies Frogs Kingfisher (bird) Waterbird Turtles Dragonflies Trout Water snake Food Algae, water weeds Algae, water weeds Algae, water weeds Dragonflies, pond flies Decomposing water weeds Dragonflies, pond flies Carp Snails, Prawns Snails, Water weeds Pond flies Carp, prawns Frog eggs, chicks of kingfisher and flycatchers Use the above data to draw a food web of the pond community. Arrows between the organisms should indicate the direction in which the energy (food) travels. Discussion Questions 1. Identify and label all the producers, first and second order consumers. Explain how you made your selections. 2. Fertilisers from nearby farmland wash into the pond after heavy rain. This causes a blue-green algae bloom in the pond. How would this affect the inhabitants of the pond? 3. A biological control in the form of a virus is introduced to control the population of carp in the pond. What would be the effect of a reduction in carp numbers on the food web? Part B – A Mangrove community Mangroves flourish in warm, shallow water environments around Australia. They can produce about 10 tonnes of organic matter per hectare annually. The leaves, fruits and woody parts of the grey mangrove (Avicennia marina) fall from the tree into the water where they are broken down by bacteria and fungi. It may take a year for a leaf to be completely broken down. Crabs, prawns, worms and snails feed on the bacteria and fungi and in turn may be eaten by larger animals such as the white-faced heron. The bullseye fish feeds on the decaying leaves and itself provides food for the pelican. Ultimately the organic matter produced by mangroves provides for human consumption in the form of the fish, crabs and prawns caught by the rich estuarine fisheries. Construct a food web of the mangrove community using the above description. Discussion Questions 1. Identify all the producers, first and second order consumers in the food web of the mangrove community. Explain how you made your selections. 2. Chemical analysis of the area carried out by scientists has identified a high level of heavy metals in the water of the mangrove. Suggest the impact that a heavy metal such as mercury may have on the organisms in the food web. 3. Mangroves are often located in beachfront areas of our coastline. These areas are highly sought-after for the development of housing for humans. What would be the long-term effects of clearing mangrove areas to allow for urban development? Explain. Conclusion Refer back to the purpose of this activity and write a conclusion based on what you have learnt by undertaking this activity.