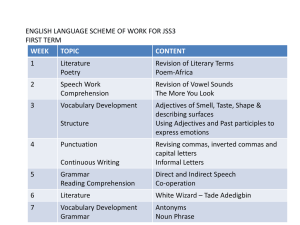
vocabulary list 2014
advertisement
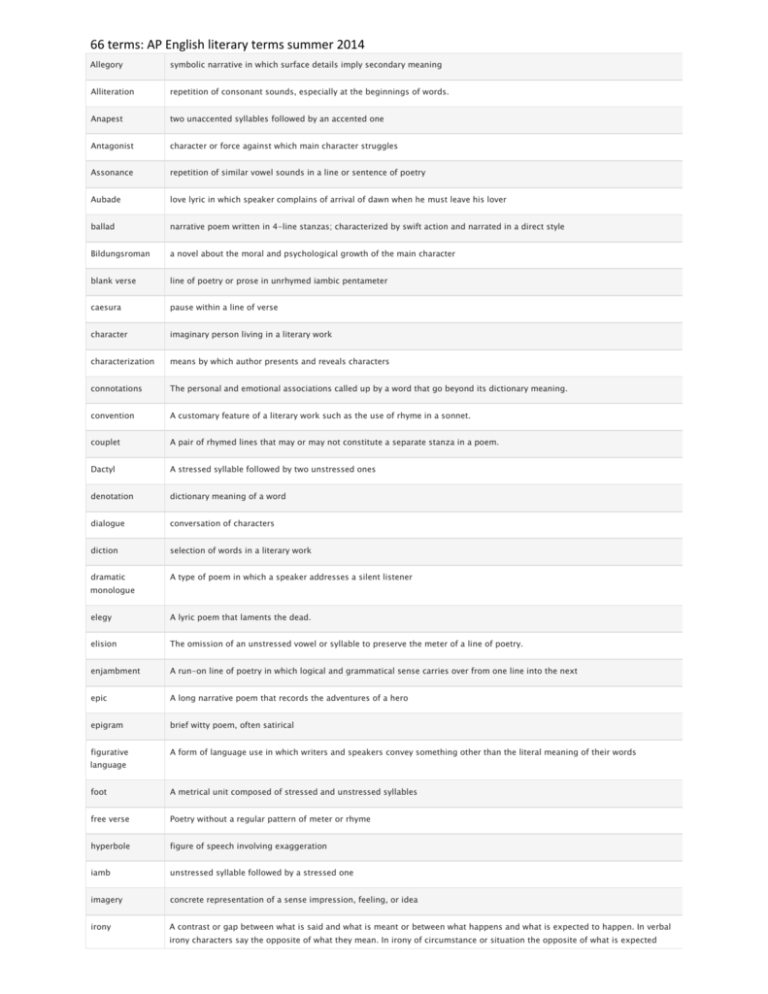
66 terms: AP English literary terms summer 2014 Allegory symbolic narrative in which surface details imply secondary meaning Alliteration repetition of consonant sounds, especially at the beginnings of words. Anapest two unaccented syllables followed by an accented one Antagonist character or force against which main character struggles Assonance repetition of similar vowel sounds in a line or sentence of poetry Aubade love lyric in which speaker complains of arrival of dawn when he must leave his lover ballad narrative poem written in 4-line stanzas; characterized by swift action and narrated in a direct style Bildungsroman a novel about the moral and psychological growth of the main character blank verse line of poetry or prose in unrhymed iambic pentameter caesura pause within a line of verse character imaginary person living in a literary work characterization means by which author presents and reveals characters connotations The personal and emotional associations called up by a word that go beyond its dictionary meaning. convention A customary feature of a literary work such as the use of rhyme in a sonnet. couplet A pair of rhymed lines that may or may not constitute a separate stanza in a poem. Dactyl A stressed syllable followed by two unstressed ones denotation dictionary meaning of a word dialogue conversation of characters diction selection of words in a literary work dramatic A type of poem in which a speaker addresses a silent listener monologue elegy A lyric poem that laments the dead. elision The omission of an unstressed vowel or syllable to preserve the meter of a line of poetry. enjambment A run-on line of poetry in which logical and grammatical sense carries over from one line into the next epic A long narrative poem that records the adventures of a hero epigram brief witty poem, often satirical figurative A form of language use in which writers and speakers convey something other than the literal meaning of their words language foot A metrical unit composed of stressed and unstressed syllables free verse Poetry without a regular pattern of meter or rhyme hyperbole figure of speech involving exaggeration iamb unstressed syllable followed by a stressed one imagery concrete representation of a sense impression, feeling, or idea irony A contrast or gap between what is said and what is meant or between what happens and what is expected to happen. In verbal irony characters say the opposite of what they mean. In irony of circumstance or situation the opposite of what is expected happens. In dramatic irony a character speaks in ignorance of a situation or event known to the audience or to other characters, literal language form of language in which a writer mean exactly what their words denote lyric poem A type of poem characterized by brevity, compression, and the expression of feeling metaphor a comparison between essentially unlike things WITHOUT using 'like' or 'as' meter measured pattern of rhythmic accents in a poem metonymy A figure of speech in which a closely related term is substituted for an object or idea narrative poem poem that tells a story narrator voice and implied speaker of a fictional work octave an eight-line unit, which may constitute a stanza or a section of a poem, as in the octave of a sonnet ode A long, stately poem in stanzas of varied length, meter, and form onomatopeia The use of words to imitate the sounds they describe. Words such as buzz and crack are onomatopoetic open form A type of structure or form in poetry characterized by freedom from regularity and consistency in such elements as rhyme, line length, and metrical pattern. parody A humorous, mocking imitation of a literary work personification The endowment of inanimate objects or abstract concepts with human qualities or actions plot organization of incidents in literary work protagonist main character of literary work quatrain 4 line stanza in a poem rhetorical a question to which an overt answer is not expected question rhyme The matching of final vowel or consonant sounds in two or more words rhythm The recurrence of accent or stress in lines of verse romance A type of narrative fiction or poem in which adventure is a central feature and in which an idealized vision of reality is presented satire A literary work that criticizes human misconduct and ridicules vices, stupidities, and follies sestet A six-line unit of verse constituting a stanza or section of a poem; the last six lines of an Italian sonnet soliloquy An extended speech in a play in which a character alone onstage expresses his thoughts sonnet A fourteen-line poem in iambic pentameter spondee A metrical foot represented by two stressed syllables style The way an author chooses words, arranges them in sentences or in lines of dialogue or verse, and develops ideas and actions with description, imagery, and other literary techniques. subject What a story or play is about subplot A subsidiary or subordinate or parallel plot in a play or story that coexists with the main plot. symbol An object or action in a literary work that means more than itself, that stands for something beyond itself synecdoche A figure of speech in which a part is substituted for the whole syntax The grammatical order of words in a sentence or line of verse or dialogue tercet theme 3 line stanza The idea of a literary work abstracted from its details of language, character, and action, and cast in the form of a generalization. tone The implied attitude of a writer toward the subject and characters of a work.