Jeffersonian vs. Jacksonian Democracy Comparison
advertisement
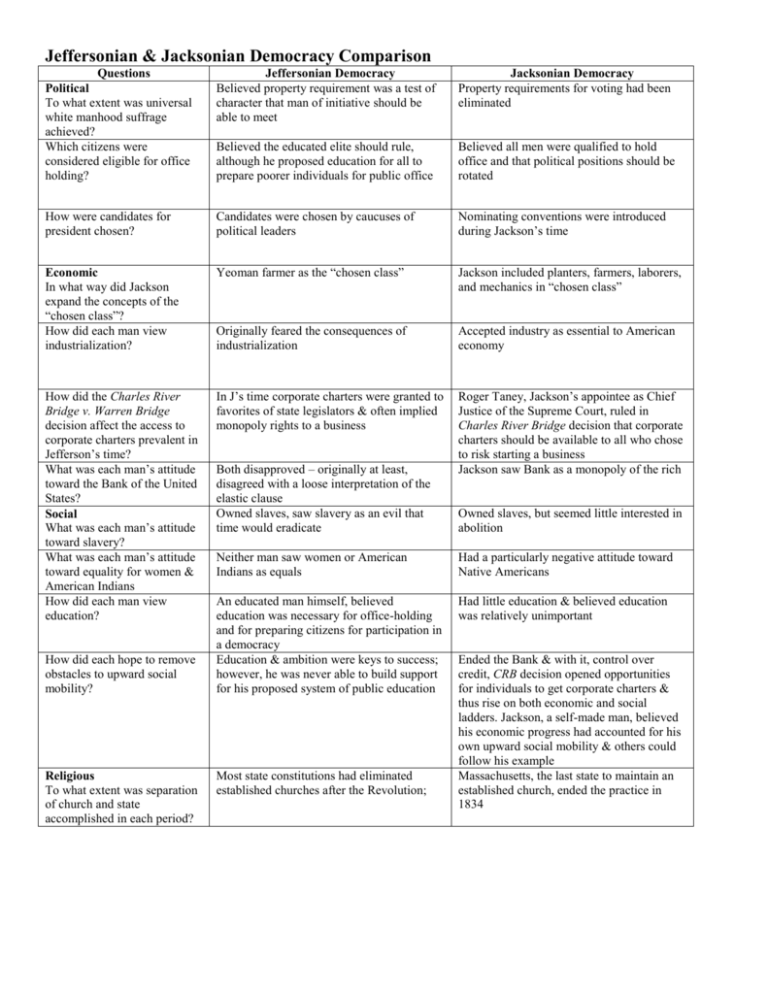
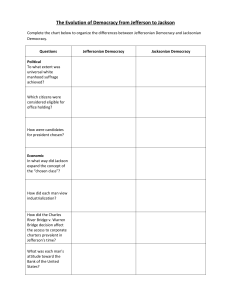
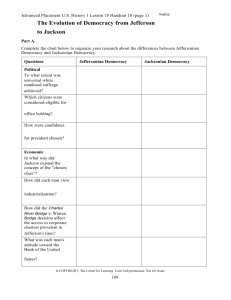
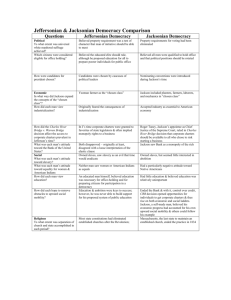
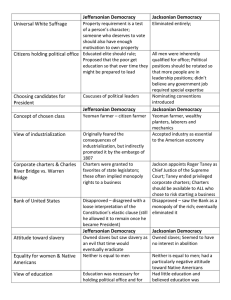
Jeffersonian & Jacksonian Democracy Comparison Questions Political To what extent was universal white manhood suffrage achieved? Which citizens were considered eligible for office holding? Jeffersonian Democracy Believed property requirement was a test of character that man of initiative should be able to meet Jacksonian Democracy Property requirements for voting had been eliminated Believed the educated elite should rule, although he proposed education for all to prepare poorer individuals for public office Believed all men were qualified to hold office and that political positions should be rotated How were candidates for president chosen? Candidates were chosen by caucuses of political leaders Nominating conventions were introduced during Jackson’s time Economic In what way did Jackson expand the concepts of the “chosen class”? How did each man view industrialization? Yeoman farmer as the “chosen class” Jackson included planters, farmers, laborers, and mechanics in “chosen class” Originally feared the consequences of industrialization Accepted industry as essential to American economy How did the Charles River Bridge v. Warren Bridge decision affect the access to corporate charters prevalent in Jefferson’s time? What was each man’s attitude toward the Bank of the United States? Social What was each man’s attitude toward slavery? What was each man’s attitude toward equality for women & American Indians How did each man view education? In J’s time corporate charters were granted to favorites of state legislators & often implied monopoly rights to a business Roger Taney, Jackson’s appointee as Chief Justice of the Supreme Court, ruled in Charles River Bridge decision that corporate charters should be available to all who chose to risk starting a business Jackson saw Bank as a monopoly of the rich How did each hope to remove obstacles to upward social mobility? Religious To what extent was separation of church and state accomplished in each period? Both disapproved – originally at least, disagreed with a loose interpretation of the elastic clause Owned slaves, saw slavery as an evil that time would eradicate Owned slaves, but seemed little interested in abolition Neither man saw women or American Indians as equals Had a particularly negative attitude toward Native Americans An educated man himself, believed education was necessary for office-holding and for preparing citizens for participation in a democracy Education & ambition were keys to success; however, he was never able to build support for his proposed system of public education Had little education & believed education was relatively unimportant Most state constitutions had eliminated established churches after the Revolution; Ended the Bank & with it, control over credit, CRB decision opened opportunities for individuals to get corporate charters & thus rise on both economic and social ladders. Jackson, a self-made man, believed his economic progress had accounted for his own upward social mobility & others could follow his example Massachusetts, the last state to maintain an established church, ended the practice in 1834 Use American Pageant p. 256-272 and the chart titled “Jeffersonian & Jacksonian Democracy Competition” to answer the following 1. In what respects was Jacksonian Democracy more democratic than Jeffersonian Democracy? 2. In what ways did each of the following contribute to the growth of democracy between 1800 and 1840? a. b. c. d. State constitutions: Charles River Bridge v. Warren Bridge decision: Changes in political party procedures: Actions taken by Jackson himself: 3. To what extent was Andrew Jackson responsible for changes in the period often called “Jacksonian Democracy”? 4. Did democratic changes in the “Age of Jackson” have greater political or economic impact? Explain your answer. 5. Both Jefferson and Jackson used the slogan “Equal rights for all, special privileges for none.” To what extent did neither one achieve his goals? 6. How did the periods of Jeffersonian Democracy and Jacksonian Democracy illustrate the idea that democracy is a process rather than a conclusion?