MCCONNELL PRACTICE MONETARY POLICY
advertisement
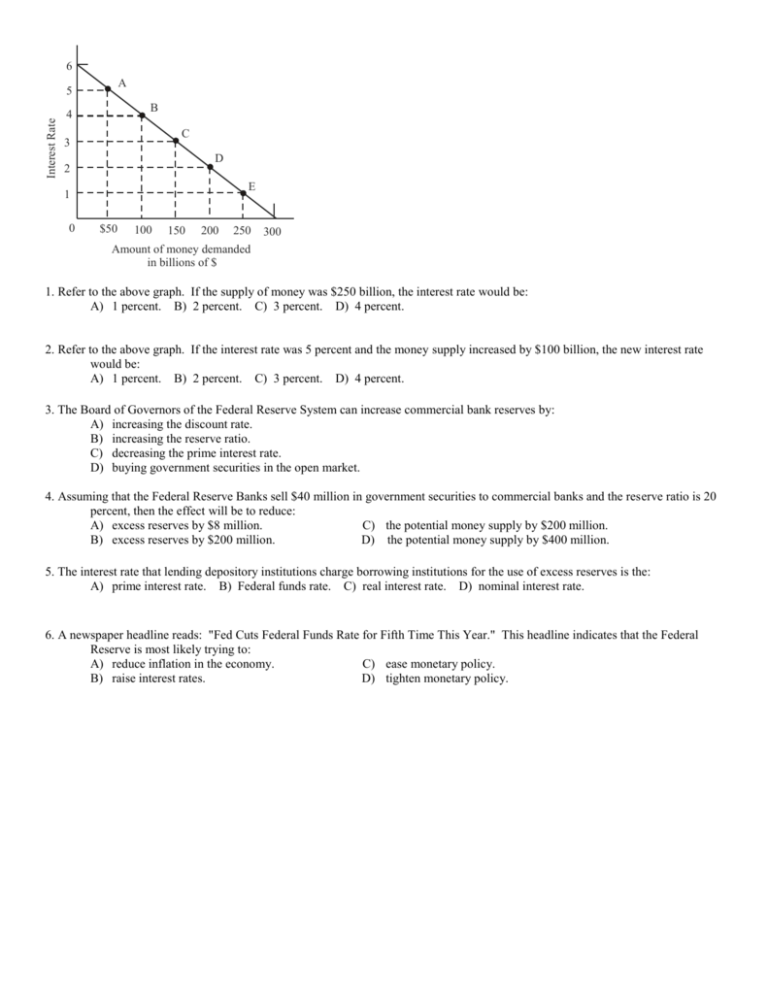
6 A Interest Rate 5 B 4 C 3 D 2 E 1 0 $50 100 150 200 250 300 Amount of money demanded in billions of $ 1. Refer to the above graph. If the supply of money was $250 billion, the interest rate would be: A) 1 percent. B) 2 percent. C) 3 percent. D) 4 percent. 2. Refer to the above graph. If the interest rate was 5 percent and the money supply increased by $100 billion, the new interest rate would be: A) 1 percent. B) 2 percent. C) 3 percent. D) 4 percent. 3. The Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System can increase commercial bank reserves by: A) increasing the discount rate. B) increasing the reserve ratio. C) decreasing the prime interest rate. D) buying government securities in the open market. 4. Assuming that the Federal Reserve Banks sell $40 million in government securities to commercial banks and the reserve ratio is 20 percent, then the effect will be to reduce: A) excess reserves by $8 million. C) the potential money supply by $200 million. B) excess reserves by $200 million. D) the potential money supply by $400 million. 5. The interest rate that lending depository institutions charge borrowing institutions for the use of excess reserves is the: A) prime interest rate. B) Federal funds rate. C) real interest rate. D) nominal interest rate. 6. A newspaper headline reads: "Fed Cuts Federal Funds Rate for Fifth Time This Year." This headline indicates that the Federal Reserve is most likely trying to: A) reduce inflation in the economy. C) ease monetary policy. B) raise interest rates. D) tighten monetary policy. A Federal funds rate (percent) 5.5 S f4 B 5.0 S f3 C 4.5 S f2 D 4.0 S f1 Df $100 $150 $200 $250 Quantity of reserves (in billions) 7. If the Federal funds market is at equilibrium at point C and the Federal Reserve decides to use open-market operations to add an additional $50 billion in available reserves, the Federal funds rate will: A) fall to 4.0 percent and the total amount of reserves will be $150. B) fall to 4.0 percent and the total amount of reserves will be $250. C) rise to 5.0 percent and the total amount of reserves will be $150. D) rise to 5.0 percent and the total amount of reserves will be $250. P Interest rate (%) 10 B 8 C 6 D 4 8. AD1 (l=120) AD3 (l=60) E 2 0 Investment demand AS Price level A $30 $60 $90 $120 $150 Investment ($) 0 AD2 (l=90) Qf Real GDP ($) Q Refer to the above graphs, in which the numbers in parentheses after the AD 1 , AD2 , and AD3 labels indicate the level of investment spending associated with each curve, respectively. All numbers are in billions of dollars. The interest rate and the level of investment spending in the economy are at point D on the investment demand curve. To achieve the goal of a noninflationary full-employment output Q f in the economy, the Fed should: (Qf is Full Employment) A) B) C) D) decrease aggregate demand by increasing the interest rate from 2 to 4 percent. decrease aggregate demand by increasing the interest rate from 4 to 6 percent. increase aggregate demand by decreasing the interest rate from 4 to 2 percent. increase the level of investment spending from $120 billion to $150 billion. 9. From the monetarist perspective,: A) changes in investment spending are a major source of macroeconomic instability. B) inappropriate monetary policy is a major source of macroeconomic stability. C) adverse aggregate supply shocks are a major source of macroeconomic instability. D) the fact that prices and wages are flexible is a major source of macroeconomic instability. 10. Given the equation of exchange, if V is stable, an increase in M will necessarily increase: A) B) C) D) the demand for money. government spending. nominal GDP. velocity. 11. If the amount of money in circulation is $8 billion and the value of total output is $40 billion in an economy, the: A) velocity of money is 5. C) level of the price index is 320. B) money supply is $40 billion. D) equilibrium level of GDP is $320 billion 12. Credit cards have which of the following effects on M1velocity and why do they have it? A. B. C. D. They increase it by reducing the amount of M2 in the economy They decrease it because they reduce the amount of M2 in the economy They increase it because they decrease the cash and checks held by the public They increase it because the change expectations of future economic growth 13. Changes in interest rates cause a shift in: A) neither the investment demand curve nor the aggregate demand curve. B) the investment demand curve, but not the aggregate demand curve. C) the aggregate demand curve, but not the investment demand curve. D) the investment demand curve and the aggregate demand curve. 14. If Federal Reserve officials attempt to pull the economy out of a recession when the price level is relatively stable, the policies they would most likely use would be to: A) buy government securities and increase the discount rate. B) sell government securities and decrease the discount rate. C) buy government securities and decrease the discount rate. D) sell government securities and increase the discount rate. 15. Which of the following best describes what occurs when monetary authorities sell government securities? NOTE: THIS IS A VERBAL VERSION OF THE FLOW CHART WE USED IN CLASS A) There is a decrease in the size of commercial banks' excess reserves, the money supply increases, and interest rates fall, thereby causing a decrease in investment spending and real GDP. B) There is a decrease in the size of commercial banks' excess reserves, the money supply decreases, and the interest rates rise, thereby causing a decrease in investment spending and real GDP. C) There is a decrease in the size of commercial banks' excess reserves, the money supply decreases, and interest rates rise, thereby causing an increase in investment spending and real GDP. D) There is an increase in the size of commercial bank reserves, the money supply increases, and interest rates fall, thereby causing an increase in investment spending and real GDP. 1. A 2. C 3. D 4. C 5. B 6. C 10. C 11. A 12. C 13. C 14. C 15. B 1. 2. C 3. D 4. C 5. B 6. C 10. C 11. A 12. C 13. C 14. C 15. B 1. 2. C 3. D 4. C 5. B 6. C 10. C 11. A 12. C 13. C 14. C 15. B 1. 2. C 3. D 4. C 5. B 6. C 10. C 11. A 12. C 13. C 14. C 15. B 1. 2. C 3. D 4. C 5. B 6. C 10. C 11. A 12. C 13. C 14. C 15. B 1. 2. C 3. D 4. C 5. B 6. C 10. C 11. A 12. C 13. C 14. C 15. B 1. 2. C 3. D 4. C 5. B 6. C 11. A 12. C 13. C 14. C 15. B A A A A A A 10. C 7. B 8. B 9. B 7. B 8. B 9. B 7. B 8. B 9. B 7. B 8. B 9. B 7. B 8. B 9. B 7. B 8. B 9. B 7. B 8. B 9. B