File
advertisement
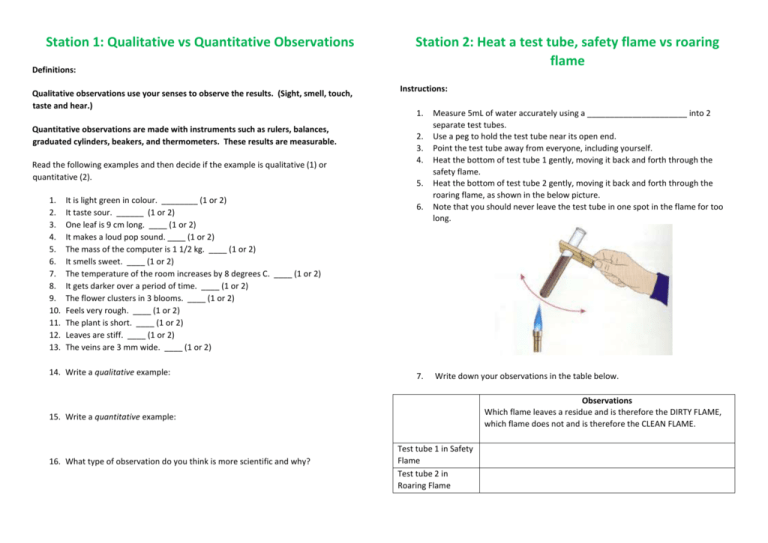
Station 1: Qualitative vs Quantitative Observations Definitions: Qualitative observations use your senses to observe the results. (Sight, smell, touch, taste and hear.) Quantitative observations are made with instruments such as rulers, balances, graduated cylinders, beakers, and thermometers. These results are measurable. Read the following examples and then decide if the example is qualitative (1) or quantitative (2). 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. It is light green in colour. ________ (1 or 2) It taste sour. ______ (1 or 2) One leaf is 9 cm long. ____ (1 or 2) It makes a loud pop sound. ____ (1 or 2) The mass of the computer is 1 1/2 kg. ____ (1 or 2) It smells sweet. ____ (1 or 2) The temperature of the room increases by 8 degrees C. ____ (1 or 2) It gets darker over a period of time. ____ (1 or 2) The flower clusters in 3 blooms. ____ (1 or 2) Feels very rough. ____ (1 or 2) The plant is short. ____ (1 or 2) Leaves are stiff. ____ (1 or 2) The veins are 3 mm wide. ____ (1 or 2) 14. Write a qualitative example: Station 2: Heat a test tube, safety flame vs roaring flame Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Measure 5mL of water accurately using a ______________________ into 2 separate test tubes. Use a peg to hold the test tube near its open end. Point the test tube away from everyone, including yourself. Heat the bottom of test tube 1 gently, moving it back and forth through the safety flame. Heat the bottom of test tube 2 gently, moving it back and forth through the roaring flame, as shown in the below picture. Note that you should never leave the test tube in one spot in the flame for too long. Write down your observations in the table below. Observations Which flame leaves a residue and is therefore the DIRTY FLAME, which flame does not and is therefore the CLEAN FLAME. 15. Write a quantitative example: 16. What type of observation do you think is more scientific and why? Test tube 1 in Safety Flame Test tube 2 in Roaring Flame Station 3: Observations vs Inference Instructions: Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4. Station 4: Can you relight a candle from a distance? Touch or smell the item in the box by putting your hand through the hole Do not try to look at the item Write down your observations Write down an inference for your observation Observation Inference 1. 2. Light the candle Using all of your senses, except taste, write down as many observations as possible (Michael Faraday, a nineteenth century scientist made 53 observations!) Observations _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Box 1 - Touch Item 1 Item 2 Item 3 Item 4 _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 3. 4. Gently blow the candle out. Attempt to relight it by moving a lit match down the smoke trail as shown in the picture. Describe what happened? _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Box 2 - Smell _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Item 1 Item 2 Explain why you think this happened? _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Item 3 _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Item 4 Station 5: Observations, Inferences and Predictions In a group of three you need to come up with three scenarios which include an observation, inference and prediction. For example the first person could say… Observation: Jonathon is smiling when he is eating his cake. The next person in the group could come up with a possible inference. Inference: Jonathon likes his cake. The third person makes a prediction. Prediction: Jonathon will want to eat cake again. Scenario 1: _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Scenario 2: _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Scenario 3: _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________