12_4_HSW_interferenc..
advertisement

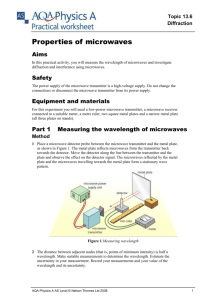
Topic 12. 12.4 Wave properties 2 Two source interference using microwaves Aims In this activity you will design an experiment to make an interference pattern with microwaves. You will need to plan and describe the experimental method carefully. You will then be provided with some data in order to measure the wavelength of microwaves and asked to evaluate the errors in the experiment. Safety This is a planning and analysis activity; there are no experimental safety issues. Experiment You are provided with the following equipment: three metal sheets on stands, a microwave receiver connected to a data logger, a 3 cm microwave transmitter and a metre ruler. Draw a diagram to show how this equipment could be set up to produce and record an interference pattern from two sources. Explain how you could record the intensity of the interference pattern using the receiver and the data logger. Include a suggested sample rate for the data logger. 1 Suggest suitable values for the gap between the metal sheets and the distance between the metal sheets and the receiver (D). Sample data Use the sample readings in the table on the next page to plot a graph of millivolts against distance from the centre point between the two gaps. Draw a smooth line of best fit (a curve) through the points. Measure the fringe spacing w and hence calculate the wavelength of the microwaves using ws the equation λ = , where s is the gap separation equal to 8 cm and D is the distance from D the metal sheets to the receiver, equal to 35 cm at the centre. AQA Physics A AS Level How science works © Nelson Thornes Ltd 2008 1 Topic 12. 12.4 Wave properties 2 Table: Intensity of microwave diffraction fringes Distance from centre to left / cm 30 28 26 24 22 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 Receiver reading / mV 10 1 2 2 1 2 5 23 41 23 9 7 2 9 33 Distance from centre to right / cm 30 28 26 24 22 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Receiver reading / mV 14 28 20 11 9 3 2 13 14 22 40 28 10 9 28 40 Analysis of errors Estimate the error in the fringe spacing w, the distance D and the error in the measurement of the slit separation s. Hence find an estimate for the error in the calculated value of wavelength. AQA Physics A AS Level How science works © Nelson Thornes Ltd 2008 2 Topic 12. 12.4 Wave properties 2 Two source interference using microwaves Aims To plan an investigation to measure the wavelength of microwaves using two sources, using appropriate apparatus and methods, including ICT. To plot and use an appropriate graph and to measure the fringe spacing from the graph and hence to calculate the wavelength. To make reasonable estimates of errors based on data and methods. Link to specification The following “How science works” concepts are practiced in this activity: C Use appropriate methodology, including ICT, to answer scientific questions and solve scientific problems E Analyse and interpret data to provide evidence, recognising correlations and causal relationships F Evaluate methodology, evidence and data, resolving conflicting evidence Safety This is a planning and data analysis activity; there are no experimental safety issues. Teaching notes Experiment 2 3 The probe should be moved along the length of the ruler from left to right, producing a series of maxima and minima on the data logger. The data logger should be programmed to take readings about every 2 cm. If the probe is moved across 50 cm in a time of about 10 s this equates to a sample rate of 2 or 3 readings per second. AQA Physics A AS Level How science works © Nelson Thornes Ltd 2008 3 Topic 12. 12.4 Wave properties 2 4 The gap between the metal sheets should be about 2 cm since this is comparable to the wavelength of microwaves. The distance between the metal sheets and the probe (D) should be about 40 cm. It may be worth pointing out to students that since the equation assumes that sin θ = tan θ, which only works for small angles, the relationship will only work for a range of about 28 cm (based on a value of D = 35 cm). Sample data The distance between the first maximum on each side of the centre line should be measured and divided by two to find the average separation. The value of wavelength comes to approximately 2.7 cm. Analysis of uncertainty The uncertainty in the measurement between the maxima on the graph has a value of about 1 cm in 10 cm, i.e. 10%. This is the most significant uncertainty in this experiment. The error in D is about 0.5 cm in 35 cm, which is about 1.5%. The uncertainty in s, the gap separation, is about 0.5 cm in 8 cm, which is about 6%. The total percentage uncertainty is therefore about 18%. AQA Physics A AS Level How science works © Nelson Thornes Ltd 2008 4