Unit Overview
advertisement

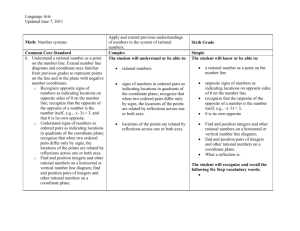
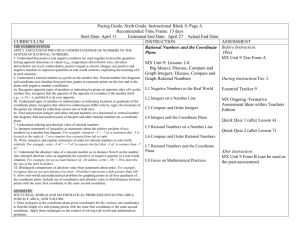
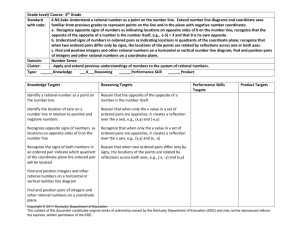
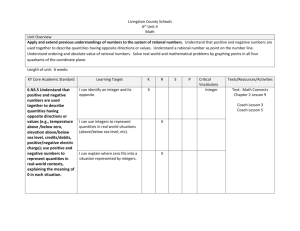
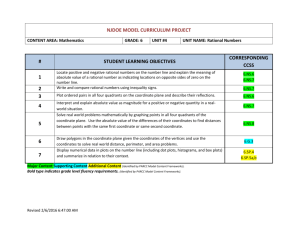
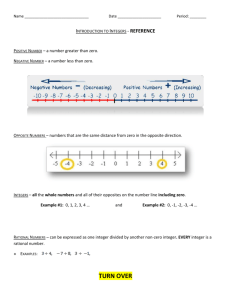
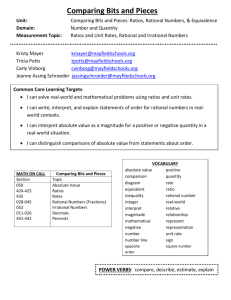
WVU K12 Partnerships Unit Overview Construction Tool Course: Sixth Grade Math Unit: Don’t Be Irrational Unit Length: 6 lessons and a capstone performance task—Fourteen 45-minute class periods Next Generation Content Standards and Objectives: M.6.NS.5 (CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.6.NS.5) Understand that positive and negative numbers are used together to describe quantities having opposite directions or values; use positive and negative numbers to represent quantities in real-world contexts, explaining the meaning of 0 in each situation. M.6.NS.6 (CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.6.NS.6) Understand a rational number as a point on the number line. Extend number line diagrams and coordinate axes familiar from previous grades to represent points on the line and in the plane with negative number coordinates. a. Recognize opposite signs of numbers as indicating locations on opposite sides of 0 on the number line; recognize that the opposite of the opposite of a number is the number itself, and that 0 is its own opposite. b. understand signs of numbers in ordered pairs as indicating locations in quadrants of the coordinate plane; recognize that when two ordered pairs differ only by signs, the locations of the points are related by reflections across one or both axes. c. Find and position integers and other rational numbers on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram; find and position pairs of integers and other rational numbers on a coordinate plane. M.6.NS.7 (CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.6.NS.7) Understand ordering and absolute value of a rational number. a. Interpret statements of inequality as statements about the relative position of two numbers on a number line diagram. b. Write, interpret, and explain statements of order for rational numbers in real-world contexts. c. Understand the absolute value of a rational number as its distance from 0 on the number line; interpret absolute value as magnitude for a positive or negative quantity in a real-world situation. d. Distinguish comparisons of absolute value from statements about order. M.6.NS.8 (CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.6.NS.8) Solve real-world and mathematical problems by graphing points in all four quadrants of the coordinate plane. Include use of coordinates and absolute value to find distances between points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate. Standards for Mathematical Practices: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. Reason abstractly and quantitatively Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. Model with mathematics. Use appropriate tools strategically. Attend to precision. Look for and make use of structure. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Driving question: What are rational numbers, and how are they represented in mathematical and real-world contexts? Overview Welcome to the world of rational numbers! Throughout the next six lessons in unit 2, you will be immersed in the world of rational numbers, opposites, and the coordinate plane. The driving WVU K12 Partnerships Unit Overview Construction Tool questions in this unit are: How are positive and negative rational numbers used in everyday scenarios, and what exactly do those numbers mean? What are opposite numbers, and how are they plotted on a number line? How do you know which number is greater on a number line? How do greater than and less than symbols relate to the position of numbers on a number line? What does the term absolute value mean? How do you compare integers using absolute value? How do you graph points on a coordinate plane? Can you determine the location of a point based upon the signs of the ordered pair? How can you compare non-similar coordinates on a coordinate plane to find the distance between points when one of the coordinates is the same? How can you recognize the use of absolute value when determining distance between two points? How are rational numbers used in different mathematical concepts including absolute value, graphing, and ordering? What are ways rational numbers are used in everyday scenarios? In this unit you will learn how to: Represent scenarios using rational numbers Give meaning to those rational numbers Compare rational numbers with inequalities Order integers in ascending and descending order Describe the meaning of zero in a variety of situations Identify the opposites of rational numbers Write multiple representations of inequalities What absolute value is and its relation to distance Plot points in the coordinate plane Use the defining characteristics of the four quadrants in a coordinate plane to determine coordinate pair locations Find distance between points using absolute value You may be asking yourself, “Why do I need to learn this?” You will use rational numbers almost every day in your life! The temperature outside, the balance in your bank account, your debt to lenders, when you travel, and when you fly or climb a mountain are examples of when you’ll use rational numbers! For example, if you were a pilot you would need to use the coordinate plane and altitude (elevation). When you fly a plane you start at a specific elevation and must get to your cruising altitude. The pilot will use rational numbers to determine what this latitude is. They must also successfully get you to your final destination on the flight. Pilots use coordinate planes in the form of longitude and latitude to find the exact position. At the end of the unit, you will complete a culminating performance task. During this task, you will apply the various concepts learned in this unit to find a treasure. Now, your adventure awaits! WVU K12 Partnerships Unit Overview Construction Tool The students will know: Vocabulary (noted in individual lessons) Represent scenarios using rational numbers Compare rational numbers with inequalities Order integers in ascending and descending order Give meaning to rational numbers The meaning of zero in a variety of situations Characteristics of opposites Multiple representations of inequalities Absolute value and its relation to distance How to plot points in the coordinate plane Characteristics of the four quadrants in a coordinate plane How to find distance between points using absolute value The students will do: Create inequalities that describe relationships Identify opposites and plot them on a number line Use rational numbers to represent real-world scenarios Determine the absolute value of rational numbers Graph in all four quadrants Identify reflections across quadrants Identify locations in a coordinate plane based on signs of ordered pair Graph numbers on a number line Use graphing calculators to plot points on a coordinate plane Organize rational numbers according to their values Find the distances between two points using absolute value WVU K12 Partnerships Unit Overview Construction Tool