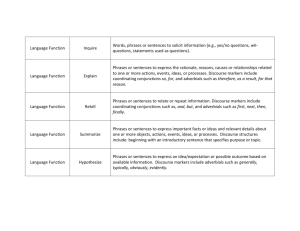
phrases discourse
advertisement
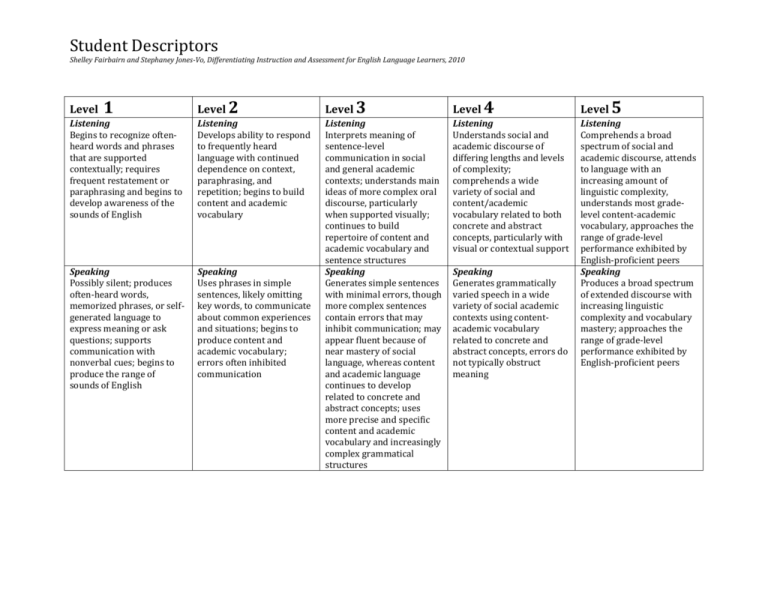
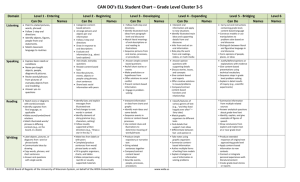
Student Descriptors Shelley Fairbairn and Stephaney Jones-Vo, Differentiating Instruction and Assessment for English Language Learners, 2010 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Listening Begins to recognize oftenheard words and phrases that are supported contextually; requires frequent restatement or paraphrasing and begins to develop awareness of the sounds of English Listening Develops ability to respond to frequently heard language with continued dependence on context, paraphrasing, and repetition; begins to build content and academic vocabulary Listening Understands social and academic discourse of differing lengths and levels of complexity; comprehends a wide variety of social and content/academic vocabulary related to both concrete and abstract concepts, particularly with visual or contextual support Speaking Possibly silent; produces often-heard words, memorized phrases, or selfgenerated language to express meaning or ask questions; supports communication with nonverbal cues; begins to produce the range of sounds of English Speaking Uses phrases in simple sentences, likely omitting key words, to communicate about common experiences and situations; begins to produce content and academic vocabulary; errors often inhibited communication Listening Interprets meaning of sentence-level communication in social and general academic contexts; understands main ideas of more complex oral discourse, particularly when supported visually; continues to build repertoire of content and academic vocabulary and sentence structures Speaking Generates simple sentences with minimal errors, though more complex sentences contain errors that may inhibit communication; may appear fluent because of near mastery of social language, whereas content and academic language continues to develop related to concrete and abstract concepts; uses more precise and specific content and academic vocabulary and increasingly complex grammatical structures Listening Comprehends a broad spectrum of social and academic discourse, attends to language with an increasing amount of linguistic complexity, understands most gradelevel content-academic vocabulary, approaches the range of grade-level performance exhibited by English-proficient peers Speaking Produces a broad spectrum of extended discourse with increasing linguistic complexity and vocabulary mastery; approaches the range of grade-level performance exhibited by English-proficient peers Level 1 Speaking Generates grammatically varied speech in a wide variety of social academic contexts using contentacademic vocabulary related to concrete and abstract concepts, errors do not typically obstruct meaning Student Descriptors Shelley Fairbairn and Stephaney Jones-Vo, Differentiating Instruction and Assessment for English Language Learners, 2010 Level 1 Reading Gains meaning primarily from visual support (e.g. pictures, graphic organizers, icons); if literate in the first language, may start to transfer those skills to English when provided with high-quality, visually supported reading instruction; preliterate students may begin to develop reading skills in English when provided with high-quality, visually supported reading instruction Writing May draw; copy written text; or write or dictate individual letters, words, or phrases (or approximations thereof to convey meaning) Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Reading May recognize and read words and phrases frequently encountered; gains meaning from simple and familiar text with visual support (e.g. pictures, graphic organizers, icons) Reading Derives meaning from increasingly complex sentence-and paragraphlevel text, but required visual and teacher support; draws upon background knowledge and previous experience to make sense of longer text Reading Comprehends increasingly complex text on known topics, while unknown topic continue to require visual or contextual support Reading Comprehends text of increasing linguistic complexity and vocabulary related to a variety of grade-appropriate subjects and genres; approaches the range of grade-level performance exhibited by English proficient peers Writing Dictates phrases and simple sentences, writes phrases and simple sentences with occasional content and academic vocabulary when supported, errors often obstruct meaning Writing Writes increasingly complex sentences with a wide range of social vocabulary and a developing range of content and academic vocabulary related to concrete and abstract concepts; errors sometimes obstruct meaning Writing Produces social and academic text using increasingly precise content/academic vocabulary and increasingly complex grammar and mechanics related to concrete and abstract concepts; errors do not typically obstruct meaning Writing Writes text varying in length, complexity, vocabulary mastery, and level of academic discourse; approaches the range of grade-level performance exhibited by Englishproficient peers