Coherence-Fractions-Cards_3-7
advertisement

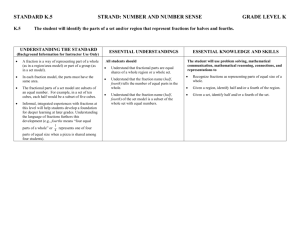
1 1 1 Understand a fraction 𝑏 as the quantity formed by 1 part when a whole is partitioned in b equal parts; understand a 𝑎 fraction 𝑏 as the quantity Understand a fraction 𝑏 as the quantity formed by 1 part when a whole is partitioned in b equal parts; understand a 𝑎 fraction 𝑏 as the quantity Understand a fraction 𝑏 as the quantity formed by 1 part when a whole is partitioned in b equal parts; understand a 𝑎 fraction 𝑏 as the quantity formed by [a] parts of size 𝑏. formed by [a] parts of size 𝑏. formed by [a] parts of size 𝑏. 1 1 1 1 1 1 Understand a fraction 𝑏 as the quantity formed by 1 part when a whole is partitioned in b equal parts; understand a 𝑎 fraction 𝑏 as the quantity Understand a fraction 𝑏 as the quantity formed by 1 part when a whole is partitioned in b equal parts; understand a 𝑎 fraction 𝑏 as the quantity Understand a fraction 𝑏 as the quantity formed by 1 part when a whole is partitioned in b equal parts; understand a 𝑎 fraction 𝑏 as the quantity formed by [a] parts of size 𝑏. formed by [a] parts of size 𝑏. formed by [a] parts of size 𝑏. 1 1 1 Explain why a fraction 𝑎⁄𝑏 is equivalent to a fraction (𝑛 × 𝑎)⁄(𝑛 × 𝑏) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and size of the parts differ even though the two fractions themselves are the same size. Use this principle to recognize and generate equivalent fractions. Explain why a fraction 𝑎⁄𝑏 is equivalent to a fraction (𝑛 × 𝑎)⁄(𝑛 × 𝑏) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and size of the parts differ even though the two fractions themselves are the same size. Use this principle to recognize and generate equivalent fractions. Explain why a fraction 𝑎⁄𝑏 is equivalent to a fraction (𝑛 × 𝑎)⁄(𝑛 × 𝑏) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and size of the parts differ even though the two fractions themselves are the same size. Use this principle to recognize and generate equivalent fractions. Explain why a fraction 𝑎⁄𝑏 is equivalent to a fraction (𝑛 × 𝑎)⁄(𝑛 × 𝑏) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and size of the parts differ even though the two fractions themselves are the same size. Use this principle to recognize and generate equivalent fractions. Explain why a fraction 𝑎⁄𝑏 is equivalent to a fraction (𝑛 × 𝑎)⁄(𝑛 × 𝑏) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and size of the parts differ even though the two fractions themselves are the same size. Use this principle to recognize and generate equivalent fractions. Explain why a fraction 𝑎⁄𝑏 is equivalent to a fraction (𝑛 × 𝑎)⁄(𝑛 × 𝑏) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and size of the parts differ even though the two fractions themselves are the same size. Use this principle to recognize and generate equivalent fractions. 𝑎 𝑎 𝑎 Understand a fraction 𝑏 with Understand a fraction 𝑏 with Understand a fraction 𝑏 with 𝑎 > 1 as a sum of fractions . 𝑎 > 1 as a sum of fractions . 𝑎 > 1 as a sum of fractions . 1 𝑏 𝑎 1 𝑏 𝑎 1 𝑏 𝑎 Understand a fraction 𝑏 with Understand a fraction 𝑏 with Understand a fraction 𝑏 with 𝑎 > 1 as a sum of fractions . 𝑎 > 1 as a sum of fractions . 𝑎 > 1 as a sum of fractions . 1 𝑏 1 𝑏 1 𝑏 Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction by a whole number. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction by a whole number. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction by a whole number. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction by a whole number. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction by a whole number. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction by a whole number. Interpret a fraction as division of the numerator by the denominator (𝑎𝑏=𝑎÷𝑏). Solve word problems involving division of whole numbers leading to answers in the form of fractions or mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the equation. Interpret a fraction as division of the numerator by the denominator (𝑎𝑏=𝑎÷𝑏). Solve word problems involving division of whole numbers leading to answers in the form of fractions or mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the equation. Interpret a fraction as division of the numerator by the denominator (𝑎𝑏=𝑎÷𝑏). Solve word problems involving division of whole numbers leading to answers in the form of fractions or mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the equation. Interpret a fraction as division of the numerator by the denominator (𝑎𝑏=𝑎÷𝑏). Solve word problems involving division of whole numbers leading to answers in the form of fractions or mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the equation. Interpret a fraction as division of the numerator by the denominator (𝑎𝑏=𝑎÷𝑏). Solve word problems involving division of whole numbers leading to answers in the form of fractions or mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the equation. Interpret a fraction as division of the numerator by the denominator (𝑎𝑏=𝑎÷𝑏). Solve word problems involving division of whole numbers leading to answers in the form of fractions or mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the equation. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction or a whole number by a fraction. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction or a whole number by a fraction. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction or a whole number by a fraction. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction or a whole number by a fraction. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction or a whole number by a fraction. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction or a whole number by a fraction. Solve real world problems involving multiplication of fractions and mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the problem. Solve real world problems involving multiplication of fractions and mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the problem. Solve real world problems involving multiplication of fractions and mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the problem. Solve real world problems involving multiplication of fractions and mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the problem. Solve real world problems involving multiplication of fractions and mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the problem. Solve real world problems involving multiplication of fractions and mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the problem. Apply and extend previous understandings of division to divide unit fractions by whole numbers and whole numbers by unit fractions. Apply and extend previous understandings of division to divide unit fractions by whole numbers and whole numbers by unit fractions. Apply and extend previous understandings of division to divide unit fractions by whole numbers and whole numbers by unit fractions. Note: Students able to multiply fractions in general can develop strategies to divide fractions in general, by reasoning about the relationship between multiplication and division. But division of a fraction by a fraction is not a requirement at this grade. Note: Students able to multiply fractions in general can develop strategies to divide fractions in general, by reasoning about the relationship between multiplication and division. But division of a fraction by a fraction is not a requirement at this grade. Note: Students able to multiply fractions in general can develop strategies to divide fractions in general, by reasoning about the relationship between multiplication and division. But division of a fraction by a fraction is not a requirement at this grade. Apply and extend previous understandings of division to divide unit fractions by whole numbers and whole numbers by unit fractions. Apply and extend previous understandings of division to divide unit fractions by whole numbers and whole numbers by unit fractions. Apply and extend previous understandings of division to divide unit fractions by whole numbers and whole numbers by unit fractions. Note: Students able to multiply fractions in general can develop strategies to divide fractions in general, by reasoning about the relationship between multiplication and division. But division of a fraction by a fraction is not a requirement at this grade. Note: Students able to multiply fractions in general can develop strategies to divide fractions in general, by reasoning about the relationship between multiplication and division. But division of a fraction by a fraction is not a requirement at this grade. Note: Students able to multiply fractions in general can develop strategies to divide fractions in general, by reasoning about the relationship between multiplication and division. But division of a fraction by a fraction is not a requirement at this grade. Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. Note: Computations with rational numbers extend the rules for manipulating fractions to complex fractions. Note: Computations with rational numbers extend the rules for manipulating fractions to complex fractions. Note: Computations with rational numbers extend the rules for manipulating fractions to complex fractions. Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. Note: Computations with rational numbers extend the rules for manipulating fractions to complex fractions. Note: Computations with rational numbers extend the rules for manipulating fractions to complex fractions. Note: Computations with rational numbers extend the rules for manipulating fractions to complex fractions.