2015 department of medicine research day
advertisement
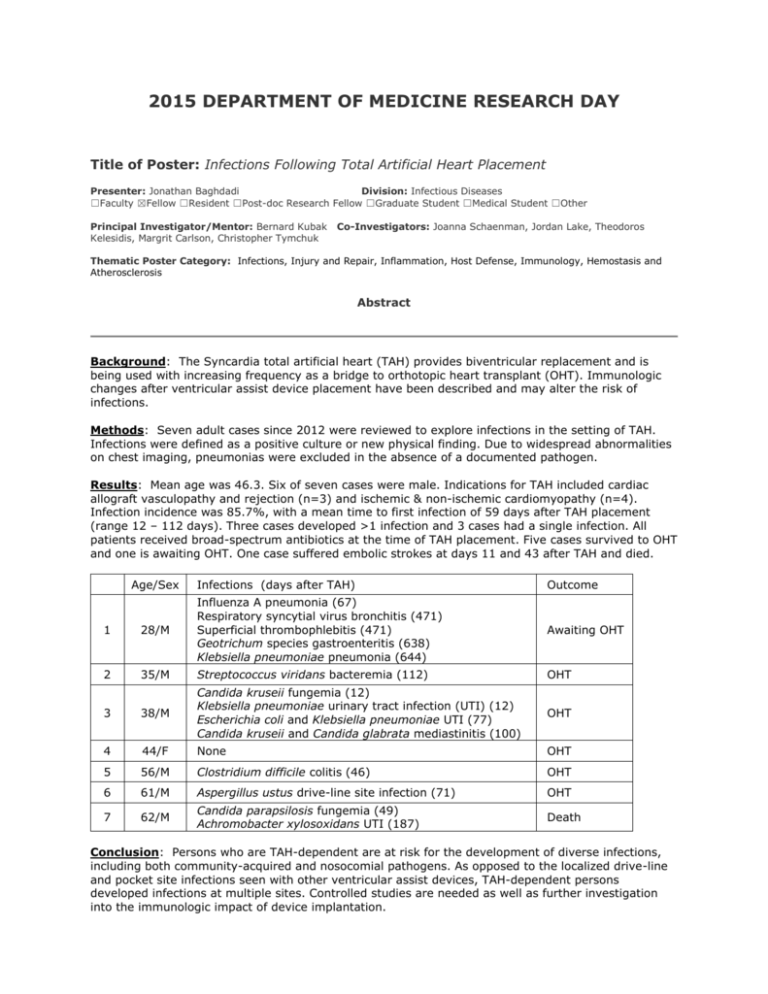
2015 DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE RESEARCH DAY Title of Poster: Infections Following Total Artificial Heart Placement Presenter: Jonathan Baghdadi Division: Infectious Diseases ☐Faculty ☒Fellow ☐Resident ☐Post-doc Research Fellow ☐Graduate Student ☐Medical Student ☐Other Principal Investigator/Mentor: Bernard Kubak Kelesidis, Margrit Carlson, Christopher Tymchuk Co-Investigators: Joanna Schaenman, Jordan Lake, Theodoros Thematic Poster Category: Infections, Injury and Repair, Inflammation, Host Defense, Immunology, Hemostasis and Atherosclerosis Abstract Background: The Syncardia total artificial heart (TAH) provides biventricular replacement and is being used with increasing frequency as a bridge to orthotopic heart transplant (OHT). Immunologic changes after ventricular assist device placement have been described and may alter the risk of infections. Methods: Seven adult cases since 2012 were reviewed to explore infections in the setting of TAH. Infections were defined as a positive culture or new physical finding. Due to widespread abnormalities on chest imaging, pneumonias were excluded in the absence of a documented pathogen. Results: Mean age was 46.3. Six of seven cases were male. Indications for TAH included cardiac allograft vasculopathy and rejection (n=3) and ischemic & non-ischemic cardiomyopathy (n=4). Infection incidence was 85.7%, with a mean time to first infection of 59 days after TAH placement (range 12 – 112 days). Three cases developed >1 infection and 3 cases had a single infection. All patients received broad-spectrum antibiotics at the time of TAH placement. Five cases survived to OHT and one is awaiting OHT. One case suffered embolic strokes at days 11 and 43 after TAH and died. Age/Sex Infections (days after TAH) Outcome Awaiting OHT 1 28/M Influenza A pneumonia (67) Respiratory syncytial virus bronchitis (471) Superficial thrombophlebitis (471) Geotrichum species gastroenteritis (638) Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia (644) 2 35/M Streptococcus viridans bacteremia (112) OHT 3 38/M Candida kruseii fungemia (12) Klebsiella pneumoniae urinary tract infection (UTI) (12) Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae UTI (77) Candida kruseii and Candida glabrata mediastinitis (100) OHT 4 44/F None OHT 5 56/M Clostridium difficile colitis (46) OHT 6 61/M Aspergillus ustus drive-line site infection (71) OHT 7 62/M Candida parapsilosis fungemia (49) Achromobacter xylosoxidans UTI (187) Death Conclusion: Persons who are TAH-dependent are at risk for the development of diverse infections, including both community-acquired and nosocomial pathogens. As opposed to the localized drive-line and pocket site infections seen with other ventricular assist devices, TAH-dependent persons developed infections at multiple sites. Controlled studies are needed as well as further investigation into the immunologic impact of device implantation.