Animal Systems-AG1
advertisement
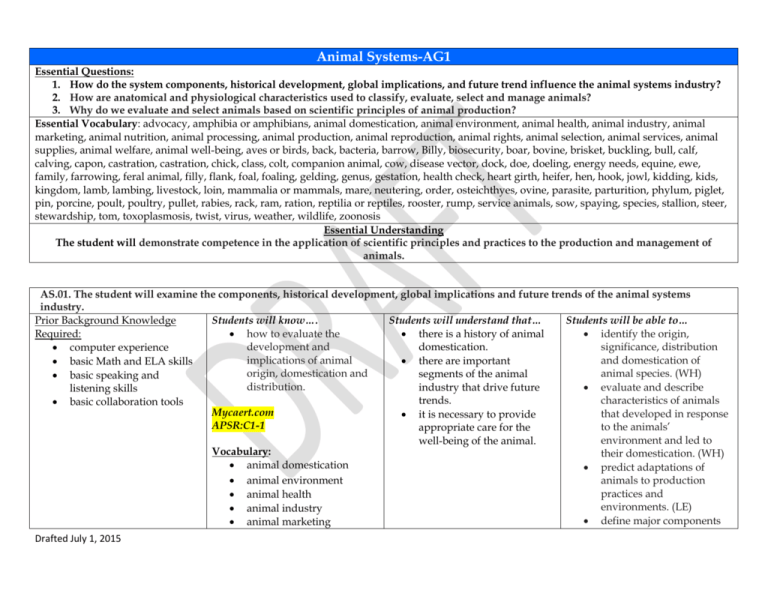
Animal Systems-AG1 Essential Questions: 1. How do the system components, historical development, global implications, and future trend influence the animal systems industry? 2. How are anatomical and physiological characteristics used to classify, evaluate, select and manage animals? 3. Why do we evaluate and select animals based on scientific principles of animal production? Essential Vocabulary: advocacy, amphibia or amphibians, animal domestication, animal environment, animal health, animal industry, animal marketing, animal nutrition, animal processing, animal production, animal reproduction, animal rights, animal selection, animal services, animal supplies, animal welfare, animal well-being, aves or birds, back, bacteria, barrow, Billy, biosecurity, boar, bovine, brisket, buckling, bull, calf, calving, capon, castration, castration, chick, class, colt, companion animal, cow, disease vector, dock, doe, doeling, energy needs, equine, ewe, family, farrowing, feral animal, filly, flank, foal, foaling, gelding, genus, gestation, health check, heart girth, heifer, hen, hook, jowl, kidding, kids, kingdom, lamb, lambing, livestock, loin, mammalia or mammals, mare, neutering, order, osteichthyes, ovine, parasite, parturition, phylum, piglet, pin, porcine, poult, poultry, pullet, rabies, rack, ram, ration, reptilia or reptiles, rooster, rump, service animals, sow, spaying, species, stallion, steer, stewardship, tom, toxoplasmosis, twist, virus, weather, wildlife, zoonosis Essential Understanding The student will demonstrate competence in the application of scientific principles and practices to the production and management of animals. AS.01. The student will examine the components, historical development, global implications and future trends of the animal systems industry. Students will know…. Students will understand that… Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to evaluate the there is a history of animal identify the origin, development and domestication. significance, distribution computer experience implications of animal and domestication of there are important basic Math and ELA skills origin, domestication and animal species. (WH) segments of the animal basic speaking and distribution. industry that drive future evaluate and describe listening skills trends. characteristics of animals basic collaboration tools Mycaert.com that developed in response it is necessary to provide APSR:C1-1 to the animals’ appropriate care for the environment and led to well-being of the animal. Vocabulary: their domestication. (WH) animal domestication predict adaptations of animal environment animals to production practices and animal health environments. (LE) animal industry define major components animal marketing Drafted July 1, 2015 animal nutrition animal processing animal production animal reproduction animal selection animal services animal supplies animal well-being castration companion animal feral animal livestock neutering poultry ration service animals spaying wildlife of the animal industry. (AAP) outline the development of the animal industry and the resulting products, services and careers. (AAP) predict trends and implications of future development of the animal systems industry. (AAP) AS.02. The student will classify, evaluate, select and manage animals based on anatomical and physiological characteristics. Students will know…. Students will understand that… Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to classify animals livestock anatomy can be explain how animals are according to hierarchical compared to determine classified using Linnaeus’s computer experience taxonomy and agricultural quality of characteristics taxonomical classification basic Math and ELA skills use. given standards. system. (AAP) basic speaking and how to apply principles of desired livestock anatomy compare and contrast the listening skills comparative anatomy and is determined by intended hierarchical classification of basic collaboration tools physiology to uses within use. the major agricultural various animal systems. animal species. (AAP) you can classify common livestock and companion how to select animals for appraise and evaluate the specific purposes and animals on their species, economic value of animals maximum performance age, and sexual state. for various applications in based on anatomy and the agriculture industry. physiology. (AAP) Drafted July 1, 2015 Agednet.com SA101 Vocabulary: amphibia or amphibians aves or birds back bovine brisket castration class dock equine family flank genus gestation heart girth hook jowl kingdom loin mammalia or mammals order osteichthyes ovine parturition phylum pin porcine poultry rack Drafted July 1, 2015 explain how the components and systems of animal anatomy and physiology relate to the production and use of animals. (LE) explain the impact of animal body systems on performance, health, growth and reproduction. (LE) identify ways an animal’s health can be affected by anatomical and physiological disorders. (AAP) compare and contrast desirable anatomical and physiological characteristics of animals within and between species. (WH)(AAP) evaluate and select animals to maximize performance based on anatomical and physiological characteristics that affect health, growth and reproduction. (LE) create a program to develop an animal to its highest potential performance. (AAP) assess an animal to determine if it has reached its optimal performance AS.03. The student will provide for the proper health care of animals. Students will know…. Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to prescribe and implement a prevention computer experience and treatment program for basic Math and ELA skills animal diseases, parasites basic speaking and and other disorders. listening skills how to provide for the basic collaboration tools biosecurity of agricultural animals and production facilities. http://www.cfsph.iastate.edu/Zo onoses/index.php agednet.com VS016 Vocabulary: bacteria biosecurity disease vector health check parasite rabies toxoplasmosis virus zoonosis Drafted July 1, 2015 level based on anatomical and physiological characteristics. (LE) reptilia or reptiles rump species twist Students will understand that… health checks are common and important in animal production and care. there are common vectors of disease transmission. zoonotic diseases are spread in various ways and passed between animals and humans. biosecurity has ethical and economic impacts. Students will be able to… explain methods of determining animal health and disorders. (LE) explain characteristics of causative agents and vectors of diseases and disorders in animals. (WH) evaluate preventive measures for controlling and limiting the spread of diseases, parasites and disorders among animals. (WH) identify and describe zoonotic diseases. (WH) explain the importance of biosecurity to the animal industry. (WH) AS.04. The student will apply principles of animal nutrition to ensure proper growth, development, reproduction, and economic production of animals. Students will know…. Students will understand that… Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to formulate feed different animals are used appraise the adequacy of rations to provide for the for different purposes. feed rations using data computer experience nutritional needs of from the analysis of basic Math and ELA skills animals. feedstuffs, animal basic speaking and Vocabulary: requirements and listening skills performance. (LE) energy needs basic collaboration tools AS.05. The student will evaluate and select animals based on scientific principles of animal production. Students will know…. Students will understand that… Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to evaluate the male livestock anatomy can be and female reproductive compared to determine computer experience systems in selecting quality of characteristics basic Math and ELA skills animals. given standards. basic speaking and how to evaluate animals for desired livestock anatomy listening skills breeding readiness and is determined by intended basic collaboration tools soundness. use. how to apply scientific principles in the selection and breeding of animals. Vocabulary: barrow billy boar buckling bull calf calving Drafted July 1, 2015 Students will be able to… select breeding animals based on characteristics of the reproductive organs. (LE) evaluate and select animals for reproductive readiness. (LE) treat or cull animals with reproductive problems.(LE) select a breeding system based on the principles of genetics. (LE) select animal breeding methods based on reproductive and economic efficiency. (LE) select animals based on quantitative breeding capon chick colt cow doe doeling ewe farrowing filly foal foaling gelding heifer hen kidding kids lamb lambing mare piglet poult pullet ram rooster sow stallion steer tom weather AS.06. The student will prepare and implement animal handling procedures for the safety of animals, producers and consumers of animal products. Students will know…. Students will understand that… Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to demonstrate safe animal rights and animal Drafted July 1, 2015 values for specific characteristics. (LE) perform procedures for estrous synchronization, superovulation, flushing, embryo transfer and other reproductive management practices. (LE) demonstrate artificial insemination techniques. (LE) Students will be able to… explain the implications of computer experience basic Math and ELA skills basic speaking and listening skills basic collaboration tools animal handling and management techniques. how to implement procedures to ensure that animal products are safe. Vocabulary: animal rights animal welfare welfare are different. understanding of livestock psychology and proper handling practices improve productivity and animal welfare. being aware of current legislation regarding animal welfare ensures the protection of the rights of animals, producers, and consumers. animal welfare and animal rights for animal agriculture. (LE) identify animal production practices that could pose health risks or are considered to pose risks by some. (LE) describe how animal identification systems can track an animal’s location, nutrition requirements, production progress and changes in health. (LE) AS.07. The student will select animal facilities and equipment that provide for the safe and efficient production, housing and handling of animals. Students will know…. Students will understand that… Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to design animal facility and attitude identify facilities needed to housing, equipment and considerations should be house and produce each computer experience handling facilities for the made when handling animal species safely and basic Math and ELA skills major systems of animal livestock to ensure safety efficiently. (LE) (AAP) basic speaking and production. and efficiency. list the general standards listening skills (e.g., environmental, how to comply with basic collaboration tools government regulations zoning, construction) that and safety standards for must be met in facilities for facilities used in animal animal production. (WH) production. Agednet.com LA013 Mycaert.com APSR: C1-3 Drafted July 1, 2015 AS.08. The student will analyze environmental factors associated with animal production. Students will know…. Students will understand that… Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to reduce the effects of environmental monitoring animal production on the is important to livestock computer experience environment. producers. basic Math and ELA skills how to evaluate the effects there are several broad that basic speaking and of environmental should be included in listening skills conditions on animals. environmental monitoring basic collaboration tools programs. Agednet.com LA039 Vocabulary: stewardship advocacy Drafted July 1, 2015 Students will be able to… evaluate the effects of animal agriculture on the environment. (AAP) (WH) outline methods of reducing the effects of animal agriculture on the environment. (AAP) (WH) implement measures to reduce the impact of animal agriculture on the environment. (AAP) (WH) identify optimal environmental conditions for animals. (AAP) (WH) describe the effects of environmental conditions on animal populations and performance. (LE)