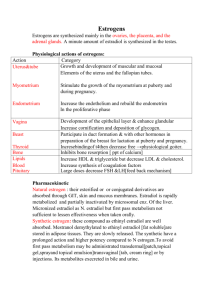
Description
advertisement

contraception 1-Hormonal contraception They are among the most prescribed and effective drugs. Oral contraceptive pills: Two types of preparations are used for oral contraception: Combinations of estrogens and progestins .They are further divided into monophasic forms (constant dosage of both components during the cycle) and biphasic or triphasic forms (dosage of one or both components is changed once or twice during the cycle). Continuous progestin therapy without concomitant administration of estrogens. Postcoital pills which contains either estrogen alone or progestrin alone or progestrin antagonists. 2-Other non hormonal measures eg mechanical :local spermicidal , barriers ,intrauterine devices, surgial. 3-physiological: safe period,lactation, coitus interaption 4- Hormonal: Implantation[norgesterel] for1 year or 3 years Parentral[ medroxyprogesteron"depopro vera"]for 3 months just after labour , 1month injectable (mesigyna) . Oral contraceptive pills: : combined or progesterone only. 1-Progestrin only contraceptive pills: -They include: *Daily short acting small dose progestrin tablets: norethindrone *Long acting depot progestrin injections or implants: medroxyprogesterone acetate injection or implants. Mechanism of action: -Inhibition of ovulation -Inhibition of sperm penetration in the uterus due to increase viscosity of cervical mucous. -endometrial change [For 30 day not stop,effective as IUD,indicated in obese, lactating , over 40 ,hypertention , thromboembolism] Advantages: -Contraception with progestins is useful in patients with hepatic disease, hypertension (less hypertension than combined pills), psychosis or mental retardation, or prior thromboembolism -They do not suppress lactation. They can be used in lactating women Disadvantages: -Long term progestrin injection are not desirable for women planning a pregnancy soon after cessation of therapy because ovulation suppression can sometimes persist for as long as 18 months after the last injection - Almost all users experience episodes of unpredictable spotting and bleeding, particularly during the first year of use. Spotting and bleeding decrease with time, and amenorrhea is common Side effects: The side effects include headache, dizziness, bloating and weight gain of 1–2 kg, and a reversible reduction of glucose tolerance , depression, acne. 2-Combined contraceptive pills a. postcoital b. monthly a. Postcoital contraceptive pills: through 72 h of coitus,2 tab./twice/5days ethinyl estradiol+norgestrerl or stilbesteron Pregnancy can be prevented following coitus by the administration of estrogens alone, progestin alone, or in combination ("morning after" contraception), when treatment begins within 72 hours, Mechanism of action: 1-: increases uterine motility. 2-Progestrins interferes with implantation of ovum by changing the structure of endometriam. 3-Withdrawal bleeding occur at the end of the course . Disadvantages: 1-High incidence of side effects mainly nausea ,vomiting headache headache, dizziness, breast tenderness, and abdominal and leg cramps. . The hormones are often administered with antiemetics,. 2-The high doses of hormones used in this type of contraceptives are teratogenic.If this type of contraception failed , therapeutic abortion should be performed because of high incidence of fetal abnormalities. 3-Less effective than other types of contraception. 4-Mifepristone stops ovulation and may prevent pregnancy few months after stoppage as a result of long action. b. monthly -They contain estrogen and progestrin .They are taken for 21 days starting from the 5th day of the cycle and are omitted for 7days. -Monophastic pills containing higher estrogen contents are 100% effective. It the woman forgets one pill,she has to take two pills on the next day. -On the other hand ommition of one of the biphasic or triphasic pills (low estrogen content) leads to loss of protection. Triphasic contraceptive pills are taken according to the following schedule: 6 days :0.03 mg estrogen + 0.05 mg progestin. 5 days :0.04 mg estrogen + 0.075 mg progestin. 10 days:0.03 mg estrogen +0.125 mg progestin. -This method has low incidence of break through bleeding and thromboembolic disorders. Mechanism of action: *Estrogen inhibits FSH and progestrins inhibit LH. *Producing thick mucus from the cervical glands and hence imending the penetration of sperm cells into the uterus. *Impending the transfer of the ovum so preventing implantation of the fertilized ovum should fertilization take place. Disadvantages &Side effects: Mild side effects :nausea , breast tenderness, edema , weight gain ,headache ,migraine ,irritability ,breakthrough bleeding , loss of libido ,skin pigmentation and acne. Severe side effects: Thromboembolic diseases,hypertension ,myocardial infarction , cholestatic jaundice , cholecystasis , gall stones ,severe depression and impaired glucose tolerance. Advantages : 1-Reduced menstrual blood and thus less iron deficiency anemia. 2-Reduced incidence of menorrhagia and irregular bleeding. 3-Lower incidence of breast and endometrial cancers. 4-Less incidence of salpingitis and increase bone density. Contraindications: Thromboembolic diseases, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, congestive heart failure, patients above 35 years of age, undiagnosed vaginal bleeding ,cancer breast and fibroids ,liver diseases. Drug interactions: 1. Drugs decrease contraception effect: Enzyme inducers as phenbarbitone, phenytoin & rifampicin. Mineral oils decrease pills absorption. 2. Pills decrease effect of other drugs: Oral anticoagulants. Insulin & oral hypoglycemics. Antihypertensives. Antihypercholesterolemics. 1.Drugs increase side effects of pills: Aminocaproic acid and tobacco smoking increase incidence of thromboembolic disorders. Uses of contraceptive pills: Contraception. Suppression of lactation: 3 pills/day for 7 days. Better use the dopamine agonist bromocriptine. Amenorrhea: induction of artificial cycle [ menopause]. Dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Endometriosis. To postpone menstruation e.g during pilgrimage. Preparations of Oral combined Contraceptive pills Estrogen (mg) Progestin (mg) Monophasic combination tablets Alesse, Aviane, Lessinea, Levlite Ethinyl estradiol 0.02 L-Norgestrel 0.1 Levlen, Levora, Nordette, Portia Ethinyl estradiol 0.03 L-Norgestrel 0.15 Crysella, Lo-Ovral, LowOgestrel Ethinyl estradiol 0.03 Norgestrel 0.30 Ethinyl estradiol 0.03 Drospirenone 3.0 Ethinyl estradiol 0.035 Norethindrone 1.0 Ethinyl estradiol 0.035 Norgestimate 0.25 Ethinyl estradiol 0.035 Norethindrone 1.0 Ovcon-35 Ethinyl estradiol 0.035 Norethindrone 0.4 Demulen 1/50, Zovia 1/50E Ethinyl estradiol 0.05 Ethynodiol diacetate 1.0 Ovcon 50 Ethinyl estradiol 0.05 Norethindrone 1.0 Yasmin Brevicon, Modicon, Necon 0.5/35, Nortrel 0.5/35 Ortho-Cyclen, Sprintec Necon 1/35, Norinyl 1+, Nortrel 1/35, Ortho-Novum 1/35 Ovral-28 Ethinyl estradiol Norinyl 1/50, Ortho-Novum Mestranol 1/50 0.05 D,L-Norgestrel 0.5 0.05 Norethindrone 1.0 Biphasic combination tablets Ortho-Novum 10/11, Necon 10/11 Days 1–10 Ethinyl estradiol 0.035 Norethindrone 0.5 Days 11–21 Ethinyl estradiol 0.035 Norethindrone 1.0 Triphasic combination tablets Enpresse, Triphasil, Tri-Levlen, Trivora Days 1–6 Ethinyl estradiol 0.03 L-Norgestrel 0.05 Days 7–11 Ethinyl estradiol 0.04 L-Norgestrel 0.075 Days 12–21 Ethinyl estradiol 0.03 L-Norgestrel 0.125 Days 1–7 Ethinyl estradiol 0.035 Norgestimate 0.18 Days 8–14 Ethinyl estradiol 0.035 Norgestimate 0.215 Days 15–21 Ethinyl estradiol 0.035 Norgestimate 0.25 Ortho-Tri-Cyclen Preparations of progestrin only contraceptive pills Progestrin Dose Norethindrone 0.35 Ovrette D,L-Norgestrel 0.075 Implanon Etonogestrel (one tube of 68 mg) Nora-BE, Nor-QD, Ortho Micronor, Jolivette, Camila, Errin 3-Postcoital contraceptive pills: Pregnancy can be prevented following coitus by the administration of estrogens alone, progestin alone, or in combination ("morning after" contraception), when treatment begins within 72 hours, Mechanism of action: 1-Estrogen and progesterone antagonists : increases uterine motility. 2-Progestrins interferes with implantation of ovum by changing the structure of endometriam. 3-Withdrawal bleeding occur at the end of the course . Disadvantages: 1-High incidence of side effects mainly nausea ,vomiting headache headache, dizziness, breast tenderness, and abdominal and leg cramps. . The hormones are often administered with antiemetics,. 2-The high doses of hormones used in this type of contraceptives are teratogenic.If this type of contraception failed , therapeutic abortion should be performed because of high incidence of fetal abnormalities. 3-Less effective than other types of contraception. 4-Mifepristone stops ovulation and may prevent pregnancy few months after stoppage as a result of long action. Referenecs: Lippincott 5th Edition goodman Table 40–4 Schedules for Use of Postcoital Contraceptives. Conjugated estrogens: 10 mg three times daily for 5 days Ethinyl estradiol: 2.5 mg twice daily for 5 days Diethylstilbestrol: 50 mg daily for 5 days Mifepristone: 600 mg once with misoprostol, 400 mcg once1 L-Norgestrel: 0.75 mg twice daily for 1 day (eg, Plan B2) Norgestrel, 0.5 mg, with ethinyl estradiol, 0.05 mg (eg, Ovral, Preven2): Two tablets and then two in 12 hours