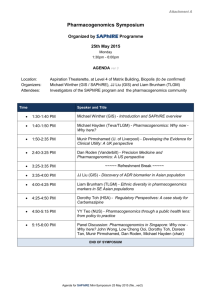
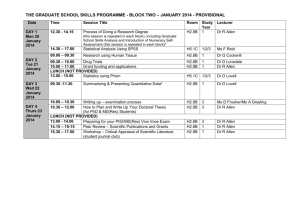
REVISED Session description
advertisement

Pharmacogenomics-guided treatment for improved patient care Session T2 Revised Session Description Pharmacogenomics (PGx) is a clinical specialty concerned with how a patient’s genetic makeup affects his or her response to medications. Variations in drug absorption, distribution in the body, metabolism and excretion (referred to as ADME in the pharmaceutical industry) due to genetic variations (called polymorphisms) have been linked to significant inter-patient variability in drug responses and outcomes; variation in metabolism is, perhaps, the major cause for a large number of common medications. Genetic factors can influence both drug efficacy (how well it works) and the likelihood of an adverse event (such as toxic effects).1 Patients with reduced metabolism on prodrugs (drugs requiring activation by our bodies) such as Plavix and Tamoxifen are expected to experience therapeutic failures, while active medications (drugs already active in our bodies but requiring inactivation to clear the drugs from our systems) may backup in our blood and become highly toxic. Various clinical trials in psychiatry have demonstrated that PGx-guided psychotherapy is more effective than standard of care,2-5 while aberrant patient metabolism has been associated with an increased incidence of adverse drug events (ADE)6. In a recent study, PGx-guided treatment helped physicians identify 30% of patients with severe drug-gene interactions who had the greatest improvement in depressive symptoms when switched to genetically suitable medication regimens7. According to the Institute of Medicine, there are nearly 1.5 million preventable ADE’s that occur every year; however, studies have shown that ADEs are under-reported (possibly by 10-fold or more) and, thus, the real rate of preventable ADE’s could be ten times that number. It is estimated that global sales of pharmaceuticals are in excess of $760,000,000.00, though as much as $400,000,000.00 in sales is wasted on ineffective medicines—this waste is due to a few different reasons, including non-compliance, but variations in drug ADME a major contributor to this loss of revenue. This presentation will provide a basic background for clinical PGx, examples of studies and key examples of the clinical benefits of PGx testing; it will also cover how practitioners can implement PGx testing within their clinical practice. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Wang, L., McLeod, H. L. & Weinshilboum, R. M. (2011). Genomics and drug response. The New England Journal of Medicine, 364(12), 1144. Altar, C. A., Hornberger, J., Shewade, A., Cruz, V., Garrison, J. & Mrazek, D. (2013). Clinical validity of cytochrome P450 metabolism and serotonin gene variants in psychiatric pharmacotherapy. International Review of Psychiatry, 25(5), 509–533. Winner, J., Allen, J., Altar, C. A. & Spahic-Mihajlovic, A. (2013). Psychiatric pharmacogenomics predicts health resource utilization of outpatients with anxiety and depression. Translational Psychiatry, 3(3), e242. Nature Publishing Group. Hall-Flavin, D., Winner, J., Allen, J., Jordan, J., Nesheim, R., Snyder, K., Drews, M., et al. (2012). Using a pharmacogenomic algorithm to guide the treatment of depression. Translational Psychiatry, 2(10), e172. Hall-Flavin, D. K., Winner, J. G., Allen, J. D., Carhart, J. M., Proctor, B., Snyder, K. A., Drews, M. S., et al. (2013). Utility of integrated pharmacogenomic testing to support the treatment of major depressive disorder in a psychiatric outpatient setting. Pharmacogenetics and Genomics, 23(10), 535–548. Joseph B, Angela K, Joseph D. Ma, Uwe F, C. Lindsay D. “Developing Perspectives on Pharmacogenomics.” Pharmacogenomics: An Introduction and Clinical Perspective. Ed. McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc, New York, 2013. Winner JG, Carhart JM, Altar CA, Allen JD, Dechairo BM (2013). A prospective, randomized, double-blind study assessing the clinical impact of integrated pharmacogenomic testing for major depressive disorder. Discovery Medicine, 16(89), 219-27. 10301 Stella Link Rd. Suite C, Houston, Texas 77025 | phone 832.538.1600 | fax 832.538.1001 companiondxlab.com