Unit 1 Transformations: 6basic graphs Inverse: asymptotes at x=0
advertisement

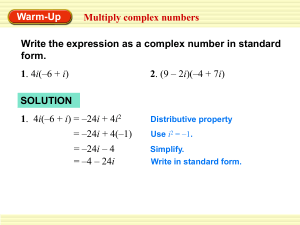
Unit 1 Transformations: 6basic graphs Inverse: asymptotes at x=0 and y=0 Y=2x y-int at (0,1) asymptote at y=0 Horizontal: With x (inside the function) acts opposite of expected Translation: (added or subtracted inside to x) Reflection: negative multiplied inside by x (reflect over y) Dilation: number multiplied by x inside function (affects x-coordinates opposite of expected) Vertical: Outside the Function. Acts as expected Translation: added or subtracted outside the function (acts as expected) Reflection: negative outside(in front of) the function: reflects over x axis Dilation: number multiplied by outside of function (affects y-coordinates) as expected Trig: y=asin[b(x+c)] +d Amplitude: “a” vertical dilation-distance from highest or lowest point to center of graph/could cause reflection if negative Period: “b” length of time to complete one cycle(period). To find period Phase Shift: “c” Acts opposite-horizontal Vertical Shift: “d” acts as expected-vertical Remember to transform the 5 main points of either sine or cosine 2𝜋 𝑏 Vectors: Addition=tip to tail Subtraction= Set up the addition of the negative vector, or set up addition to find missing vector Dot product: u ∙ v = x1x2 + y1y2 where u = <x1,y1> and v= <x2,y2> Magnitude: Pythagorean theorem Direction angle: tan-1 but then remember to consider which quadrant the vector falls in Component form: <magnitude cos𝜃 , magnitude sin𝜃> Factoring: If you factor and your leading coefficient is not +1, you have to use factor sum tree ax2 + bx + c what multiplies to be a times c and adds to be b. Then split up the middle term into those factors and factor by grouping 𝑥= −𝑏±√𝑏2 −4𝑎𝑐 2𝑎 use to solve for x in a quadratic function. If you use quadratic function and you end up with a negative under radical, simplify and change into complex numbers Complex numbers: i=√−1 , i2 = -1 Multiply complex numbers: foil and simplify Divide complex numbers: multiply numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator, foil and simplify. The absolute value of complex number- use Pythagorean theorem Rational Functions x-intercepts: set numerator =o and solve for x (If any other function set y=o and solve for x) y-intercepts: set all x’s to be zero and simplify VA: set denominator=0 and solve -> related to the domain HA: deg num > deg den: none (could be a slant if it is exactly 1 more) use long division to find Deg num = deg den : divide leading coefficients Deg num < deg den: y=0 (x-axis) To simplify: factor top and bottom and cancel common factors To add/subtract: get a common denominator DO NOT CANCEL UNTIL THE END! Multiply: factor and cancel- multiply straight across Divide: Flip second fraction and multiply Solve: set= and cross multiply. Set results EQUAL to each other and then solve for x. OR find common denominator and set numerator = 0 Symmetry: x-axis; set all y’s to (-y) and simplify Check to see if it is same as original y-axis: set all x’s to (-x) and simplify Check to see if it is same as original origin: set both x and y to (-x) and (-y) and simplify Check to see if it is same as original. *If you multiply a fraction by -1, only multiply numerator OR denominator NOT BOTH!