Unit 1 - Leona QSI Math Site
advertisement

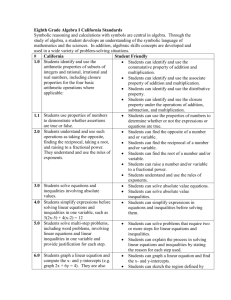
LEONA QSI Curriculum Map Algebra 1A 2014-2015 Teacher: Course Group: Algebra 1 A,B,C Pre-Requisites: None Course: Algebra 1A Department: Math Grade(s): 9-12 Unit 1: Foundations of Algebra Essential Questions: How can a relationship between quantities be represented numerically, symbolically, or graphically? What procedures must be followed to manipulate expressions? CCSS Standards (10 days) Representing Problems in a Context = Major □ = Supporting ○= Additional ★= Modeling □N-Q.A.1Use units as a way to understand problems and to remind you of your steps in problems. Interpret the scale and the origin in graphs and data displays □N-Q.A.2Define appropriate quantities for the purpose Reason with properties of real numbers Use properties to manipulate Polynomials Introduction to Problem Solving of descriptive modeling. □N-Q.A.3 choose a level of accuracy for your units Core Content (High School Standards) Use counter examples to disprove and prove ideas and properties of real numbers. Understand and apply reasoning when using properties of rational numbers and irrational numbers. depending on your problem N-RN.B.3 Explain why the sum or product of two rational numbers are rational, that the sum of a rational number and an irrational number is irrational, and that the product of a nonzero rational number and an irrational number is irrational. A-SSE.A.1a Interpret expressions that represent a quantity in terms of its context interpret parts of an expression such as terms factors and coefficients. A-SSE.A.1.b Interpret complicated expressions by viewing one of more of their parts as a single entity. A-SSE.A.2 Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. A-APR.A.1 Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to the integers, namely, they are closed under the operations of addition, subtraction, and multiplication; add, subtract and multiply polynomials. Mathematical Practices MP.1-8 Write and interpret expressions to describe a context. Compare expressions given a parameter of values. Summarize and justify processes for simplifying, and evaluating expressions. Apply 2-Column style proof to justify the process of evaluating or simplifying expressions using properties of real numbers. Key Vocabulary: Equivalent, Expressions, Variable, Coefficient, Constant, Like Terms, Simplifying, Distribution, Factor, Properties, Absolute Value, Polynomials, Degree, Monomials, Standard Form, Leading Terms, Modeling, Reasoning, Structures, Units, Estimate, Translate, Represent, Strategic Tier 3 Support Define and identify variables, operations, expressions, equations, and inequalities Translating Expressions Apply all four operations with whole numbers, fractions and decimals and equivalent forms of numbers. Apply all four operations with integers Evaluate and expand exponents Properties of exponents and radicals Relate the properties of operations with integers to the use of operations within the system of polynomials. Use substitution of numerical values for variables to evaluate expressions Apply various problem solving techniques. Formal Evaluate expressions using correct order of operations Resources 1. Rational and Irrational Properties http://map.mathshell.org/materials/download.ph p?fileid=1267 2. Simplifying Expressions http://ispeakmath.wordpress.com/2012/10/02/si mplifying-algebraic-expressions-activity/ 3. Bingo http://edubakery.com/BingoCards/Simplifying-Algebraic-Expressions-v1Bingo-Cards 4. Interactive http://www.classzone.com/cz/books/algebra_1_ 2011_na/get_chapter_group.htm?cin=1&ci=1& rg=animated_math&at=animations&var=anima tions Writing Expressions http://map.mathshell.org/materials/download.ph p?fileid=694 Pre Test Quizzes Identify words that are interpreted into math symbols such as product quotient, sum, and difference and let “s” represent salary etc. Apply all four operations to simplify polynomials. (Dividing only by monomials) Identify parts of a problem and justify processes used to solve. Assessment Unit Test Informal Checking for Understanding Questioning Completion of Project/Activity/ Assignments 5. Summarization of Learning 6. Order of Operations: Chris Shore: 4-Digit Problem See Appendix A 7. Writing Expression: Chris Shore: Number Tricks Lesson Plan See Appendix A 8. Writing Expressions in a context Pool Tile Problem http://www.learner.org/workshops/algebra/wor kshop1/lessonplan1.html 9. Introduction to Problem Solving http://illuminations.nctm.org/LessonDetail.aspx ?id=L816 Daily Exit Slip 10. Sample Task Items: http://www.illustrativemathematics.org/standar ds/hs 11. Mathalicious – Romeo and Juliet Updated: 2/8/2016 LEONA QSI Curriculum Map Algebra 1A 2014-2015 Teacher: Course Group: Algebra 1 A,B,C Pre-Requisites: None Course: Algebra 1A Department: Math Grade(s): 9-12 Unit 2: Linear Equations Essential Questions: How can equations be used to solve problems in context? How can the structure of an equation help determine a solution strategy? CCSS Standards (15 days) = Major □ = Supporting ○= Additional ★= Modeling ○N-RN.3, □N-Q.1, □N-Q.2, □N-Q.3, Single Variable Equations in Context Applications of Ratios & Proportions* Rewriting Literal Equations & Formulas Solve Equations that Include Radicals** A-SSE.1a, A- SSE.1.b, A-SSE.2 A-CED.1Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. Include equations arising from linear and quadratic functions, and simple rational and exponential functions. Tasks are limited to linear, quadratic, or exponential equations with integer exponents. A-CED.3 Represent constraints by equations or inequalities, and by systems of equations and/or inequalities, and interpret solutions as viable or nonviable options in a modeling context. For examples, represent inequalities describing nutritional and cost constraints on combinations of different foods. A-CED.4 Rearrange formulas to highlight a quantity of interest, using the same reasoning as in solving equations. A-REI.1 Explain each step in solving a simple equation as following from the equality of numbers asserted at the previous step, starting from the assumption that the original equation has a solution. Construct a viable argument to justify a solution method. A-REI.3 *8th grade standard that will be tested ** Not tested – Advanced Concept Solve linear equations and inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters . Mathematical Practices MP.1-8 Key Vocabulary: Equivalent, Variable, Coefficient, Constant, Like Terms, Simplifying, Distribution, Factor, Properties, Modeling, Reasoning, Structures, Units, Estimate, Translate, Represent, Strategic, Equations, Inverse Operations, Reciprocal, Identity, Formula, Reasonable Solutions, Critique, Rearrange, Quantity of Interest Core Content (High School Standards) Tier 3 Support Represent a situation in context with an algebraic equation. Identify and interpret word problems using math symbols including substituting letters for values such as let “s” represent Sally’s salary etc. Identifying constraints within a context to determine if a solution is viable or non-viable. Assessment Formal Quizzes Unit Test Informal Express constraints symbolically based on the given context and related to the solution and equation. Solve equations (including absolute value) and interpret their solution. Identify the use of real number properties in order to maintain the balance of equations while solving equations. Summarize processes for solving equations. Apply 2-Column style proof to justify the process of solving equations using properties of real numbers. Compare and evaluate various strategies for solving multistep equations. *Use ratios and proportional reasoning to solve as an equation in a context. Understand and Apply inverse operations. Substitute values in equations to check if solutions are correct. Combine like terms to simplify expressions. Apply the distributive property to expressions with integers and fractions. Know the definition of absolute value and understand why there are two solutions to absolute value equations. Checking for Understanding Questioning Completion of Project/Activity/ Assignment Summarizatio n of Learning Daily Exit Slip Resources 1. Introduction to Solving Equations http://www.funbrain.com/guess2/index.html 2. Solving Equations with Balance Scale http://illuminations.nctm.org/LessonDetail.aspx? ID=U170 3. Interactive App for solving Equations with Balance www.mathplayground.com/algebraequations.htm l 4. http://www.mathplayground.com/algebraic_reaso ning.html 5. Interactive App for solving Equations with Balance http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/framesasid324g4t2.ht ml?open=instructions&from=categoryg4t2.html 6. Interactive Solving Equations with Properties:http://www.shodor.org/interactivate/ac tivities/EquationSolver/ http://www.shodor.org/interactivate/activities/Al gebraFour/ 7. Interactive: http://www.classzone.com/cz/books/algebra_1_2 011_na/get_chapter_group.htm?cin=3&rg=anim ated_math&at=animations&npos=1&spos=3&va r=animations 8. Solving Equation and Identities http://map.mathshell.org/materials/lessons.php?ta skid=218 9. Mathalicious – Text Me Later 10. Dan Meyer: Falling Glow Sticks http://mrmeyer.com/threeacts/fallingglowsticks/ 11. Dan Meyer: Fort Steuben https://s3.amazonaws.com/threeacts/fortsteuben.z ip 12. Dan Meyer: Bolt https://s3.amazonaws.com/threeacts/bolt.zip 13. Proportions Hook http://www.101qs.com/2115minime 14. Application of Ratios and Proportions Pepsi Points Updated: 2/8/2016 LEONA QSI Curriculum Map Algebra 1A 2014-2015 Teacher: Course Group: Algebra 1 A,B,C Pre-Requisites: None Course: Algebra 1A Department: Math Grade(s): 9-12 http://mrpiccmath.weebly.com/1/post/2012/07/3acts-pepsi-points.html 15. Proportional Reasoning - Investigation of Evaluate and critique the reasonableness of solutions. Mullets http://mrvaudrey.com/2012/05/03/the-onlylesson-theyll-remember/ 16. Dan Meyer: Finals Week http://threeacts.mrmeyer.com/finalsweek/ 17. Proportional Application - Bungee http://illuminations.nctm.org/LessonDetail. aspx?id=L646 18. Dan Meyer: Bone Collector https://s3.amazonaws.com/threeacts/boneco llector.zip 19. Proportions Application - Chris Shore Counting Fish. See Appendix A 20. Proportional Application - Racing proportional to height. http://www.mathalicious.com/lesson/onyour-mark/ 21. Sample Task Items: http://www.illustrativemathematics.org/stan dards/hs Rewrite formulas for specified variable. Apply reasoning to justify the process of manipulating formulas using properties of real numbers. Evaluate and compare various processes for rewriting a formula. Solve and critique methods for solving equations that include radicals.** Unit 3: Inequalities Essential Questions: How can inequalities be used to solve problems in context? How can the structure of an inequality help determine a solution strategy? CCSS Standards (5 days) = Major □ = Supporting ○= Additional ★= Modeling ○N-RN.3, □N-Q.1, □N-Q.2, □N-Q.3, Single Variable Inequalities in Context Compound Inequalities in Context A-SSE.1a, A- SSE.1.b, A-SSE.2 A-CED. 1Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. Include equations arising from linear and quadratic functions, and simple rational and exponential functions. Tasks are limited to linear, quadratic, or exponential equations with integer exponents. A-CED.3 Represent constraints by equations or inequalities, and by systems of equations and/or inequalities, and interpret solutions as viable or non- Core Content (High School Standards) Represent a situation in a context with an algebraic inequality. Identifying constraints within a context to determine if a solution is viable or non-viable. Solve inequalities and interpret their solution. Key Vocabulary: Equivalent, Variable, Coefficient, Constant, Like Terms, Simplifying, Distribution, Factor, Properties, Absolute Value, Modeling, Reasoning, Structures, Units, Estimate, Translate, Represent, Strategic, Equations, Inverse Operations, Reciprocal, Identity, Reasonable Solutions, Critique, Rearrange, Quantity of Interest, Inequality, Compound Statements, Union, Intersection, Line Graphs Tier 3 Support Identify and interpret word problems using math symbols including substituting letters for values such as let “s” represent Sally’s salary etc. Assessment Formal Quiz Unit Test Informal Understand and Apply inverse operations. Substitute values in inequalities to check if solutions are correct. Checking for Understanding Resources 1. Multiple Solutions Intro to Inequalities http://map.mathshell.org/materials/downloa d.php?fileid=778 2. 3-Act Lesson http://www.101qs.com/2327woodys-raise 3. Interactive http://www.classzone.com/cz/books/algebr a_1_2011_na/get_chapter_group.htm?cin= 6&rg=animated_math&at=animations&npo s=2&spos=6&var=animations Questioning Updated: 2/8/2016 LEONA QSI Curriculum Map Algebra 1A 2014-2015 Teacher: Course Group: Algebra 1 A,B,C Pre-Requisites: None Course: Algebra 1A Department: Math Grade(s): 9-12 Solve Absolute Value Inequalities** viable options in a modeling context. For examples, represent inequalities describing nutritional and cost constraints on combinations of different foods. A-REI.3 Solve linear equations and inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters Mathematical Practices MP.1-8 ** Not tested – Advanced Concept . Summarize processes for solving inequalities. Combine like terms to simplify expressions. Completion of Project/Activity/ Apply 2-Column style proof to justify the process of solving inequalities using properties of real numbers. Apply the distributive property to expressions with integers and fractions. Assignment Compare and evaluate various strategies for solving multistep inequalities. Draw a number line by appropriately placing positives, negatives, and zero Translate meaning of inequalities graphed on a number line. Graph inequalities on a number line. 4. Sample Task Items: http://www.illustrativemathematics.org/stan dards/hs Summarizatio n of Learning Daily Exit Slip Express constraints symbolically based on the given context and related to the solution and inequality. Evaluate and critique the reasonableness of solutions. Solve and critique methods for solving inequalities that include absolute value.** Updated: 2/8/2016