DrawingandPaintingCurriculumGuide with CCSS

Calendar Required Unit/Lesson
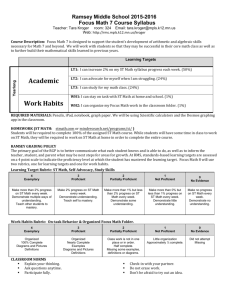
Riverside Unified School District
Drawing and Painting 1 & 2 – Curriculum Guide
Drawing & Painting 1/2 Curriculum Guide
Required Standards
Required Key
Concepts/Terms
1 st
Quarter
Unit (s)
What is Art?
- Introduction to
Observation
- Introduction to Principles and
Elements of Art -
Overview
- Introduction to Critique
Process
- Purpose of the Portfolio
Possible Lessons:
- Drawing Techniques &
Media
- Observation/Perception
- Identifying Elements of
Art
- How to Visit an Art
Museum
1.0
Artistic Perception
(Proficient
Level)
Students perceive and respond to works of art, objects in nature, events, and the environment.
They also use the vocabulary of the visual arts to express their observations.
1 Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts attending to the precise details of explanations or descriptions.
4.Determine the meaning of symbols, key
Art
Artist
Observation
Medium
Traditional
Art Critique
Portfolio
Elements of Art
Line
Shape
Value
Form
Texture
Color
Space
Museum(s)
Curator
Viewer
Patron
Lesson Application
Formative Assessment
Students will:
Demonstrate an understanding of the broad definition of art by listing traditional and nontraditional art materials and subjects.
Consider factors that contribute to something being considered a piece of art.
Perceive and describe the media and subjects of a variety of past and present artworks.3. Follow
Explain how art philosophy can help in the study of art.
Describe some of the criteria that can be used to determine if something is art.
Define aesthetic experience.
- Online Art Museum Visit
- Featured Artist(s)
- Vocabulary/Definitions terms, and other domain specific words and phrases as they are used in a specific scientific or technical context relevant to grades 9 - 10 texts and topics.
2.0
Creative Expression
(Proficient
Level)
Students apply artistic processes and skills, using a variety of media to communicate meaning and intent in original works of art.
3. Follow precisely a complex multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks, attending to special cases or expectations defined in the text.
Describe the role of art critics.
Use description, analysis, interpretation, and evaluation to critique artworks.
3.0
Historical and
Cultural Context
(Proficient
Level)
Students analyze the role and development of the visual arts in past and present cultures throughout the world, noting human diversity as it relates to the visual arts and artists.
6 Analyze the author’s purpose in providing an explanation, describing a procedure, or discussing an experiment in a text, defining the question the author seeks to address.
4.0
Aesthetic Valuing
(Proficient
Level)
Students analyze, assess, and derive meaning from works of art, including their own, according to the elements of art, the
1 st
Quarter
Line
Possible Lessons:
- Identifying Line &
Variations
- Contour Line Drawing
- Expressive Line Drawing
- Vocabulary/Definitions
- Featured
Artist(s)/Cultures principles of design, and aesthetic qualities.
5 Analyze the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text
, including relationships among key terms.
6. Analyze the author’s purpose in providing an explanation, describing a procedure, or discussing an ex periment in a text, defining the question the author seeks to address.
1.0
Artistic Perception
Level)
(Proficient
Students perceive and respond to works of art, objects in nature, events, and the environment.
They also use the vocabulary of the visual arts to express their observations.
Descriptive Line
Expressive Line
Contour Line
Implied Line
Students will:
Perceive and identify a variety of lines in their natural and constructed environment.
Explain how artists use descriptive, implied and expressive lines in their work.
Draw a variety of descriptive lines including outlines, contour lines, and
7. Translate quantitative or technical information expressed in words in a text into visual form and translate information expressed visually or mathematically into words.
2.0
Creative Expression
Level)
(Proficient
Students apply artistic processes and skills, using a variety of media to communicate meaning and intent in original works of art.
3.Follow precisely a complex multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks, attending to special cases or exceptions defined in the text. hatching.
Differentiate between contour lines and outlines and how artists use each.
Identify and explain how implied lines are used in artworks.
Describe and locate closure in pieces of art.
Identify and describe how lines can express feelings and emotions, and how lines can suggest movement in art forms.
3.0
Historical and
Cultural Context
(Proficient
Level)
Students analyze the role and development of the visual arts in past and present cultures throughout the world, noting human diversity as it relates to the visual arts and artists.
6 Analyze the author’s purpose in providing an explanation, describing a procedure, or discussing an experiment in a text, defining the question the author seeks to address.
4.0
Aesthetic Valuing
(Proficient
Level)
Students analyze, assess, and derive meaning from works of art, including their own, according to the elements of art, the
1 st
Quarter principles of design, and aesthetic qualities.
5. Analyze the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text, including relations among key terms (e.g., force, friction, reaction force, energy).
Shape & Form
Possible Lessons:
- Identifying Shape & Form
- Shape Scene
- Drawing 3-D Simulated
Form
- Positive, Negative Shape
Collage
- Still Life
Drawing/Painting
- Vocabulary/Definitions
- Featured
Artist(s)/Cultures
1.0
Artistic Perception
(Proficient
Level)
Students perceive and respond to works of art, objects in nature, events, and the environment.
They also use the vocabulary of the visual arts to express their observations.
4. Determine the meaning of symbols, key terms, and other domain-specific words and phrases as they are used in a specific scientific or technical context relevant to
Shape
Form
Figure and Ground
Organic
Geometric
Closed Shapes
Open Shapes
Students will:
Perceive and understand how figure and ground (positive and negative shapes) are used effectively in artworks.
Understand how artists use foreshortening to suggest a threedimensional form on a flat surface.
Explain how geometric and organic shapes and forms, and closed and open shapes and forms, can be used to express emotion in artworks.
Critique an artwork by describing, analyzing, interpreting, and evaluating its shape and form.
Create artworks that feature positive and negative shapes.
Create figure drawings that emphasis foreshortening. That suggests 3-D qualities.
grades 9-10 texts and topics.
2.0
Creative Expression
Level)
(Proficient
Students apply artistic processes and skills, using a variety of media to communicate meaning and intent in original works of art.
7. Translate quantitative or technical information expressed in words in a text into visual form (e.g. in an equation) into words.
3. Follow precisely a complex multistep procedure when measurements, or performing technical tasks, attending to special cases or carrying out experiments, taking exceptions defined in the text.
3.0
Historical and
Cultural Context
Level)
(Proficient
Students analyze the role and development of the visual arts in past and present cultures throughout the world, noting human diversity as it relates to the visual arts and artists.
9. Compare and contrast findings presented in a text to those from other sources (including their own experiments), noting when the findings support or contradict previous explanations or accounts.
4.0
Aesthetic Valuing
(Proficient
Level)
Students analyze, assess, and derive meaning from works of art, including their own, according to
2 nd
Quarter the elements of art, the principles of design, and aesthetic qualities.
5 Analyze the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text, including relationships among key terms.
Unit(s):
Value & Color
- Tonal Range
- Natural/Simulated Light
- Intensity
- Color Theory
Relationships
Possible Lessons:
- Value Study
- Value Gradation Drawing
- Interior/Exterior Light
Drawing Applications
- Color spectrum applications
to a variety of painting types
- Tints, Shades & Tones
- Color Media Technique
1.0
Artistic Perception
(Proficient
Level)
Students perceive and respond to works of art, objects in nature, events, and the environment.
They also use the vocabulary of the visual arts to express their observations.
1. Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis o f science and technical texts, attending to the precise details of explanations or descriptions.
Value Scale
Gradation
Shading
Chiaroscuro
Spectrum/Palette
Hue
Primary, Secondary,
Intermediate Colors
Complementary
Monochromatic
Warm/Cool
Intensity
Students will:
Understand that color is a property of light.
Describe the relationships among colors on the color wheel.
Identify primary, secondary, and intermediate colors.
Recognize complementary, monochromatic, cool, and warm color schemes and describe how artists use these to express feelings in their artworks.
Perceive and describe how artists use value intensity and color harmonies to suggest emotion and mood in their artwork.
-Vocabulary/Definitions
- Featured
Artist(s)/Cultures
2.0
Creative Expression
Level)
(Proficient
Students apply artistic processes and skills, using a variety of media to communicate meaning and intent in original works of art.
3. Follow precisely a complex multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks, attending to special cases or expectations defined in the text.
3.0
Historical and
Cultural Context
(Proficient
Level)
Students analyze the role
Understand and describe how artists use shading or chiaroscuro to make flat shape look three-dimensional.
Describe how secondary and intermediate hues are created with primary colors.
Complete a formal critique of a painting.
and development of the visual arts in past and present cultures throughout the world, human diversity as it relates to the visual arts and artists.
2. Determine central ideas or themes of the text and analyze their development; summarize the key supporting details and ideas.
4.0
Aesthetic Valuing
(Proficient
Level)
Students analyze, assess, and derive meaning from works of art, including their own, according to the elements of art, the principles of design, and aesthetic qualities.
5. Analyze the author’s purpose in providing an explanation, describing a
2 nd
Quarter procedure, or discussing an experiment in a text, defining the question the author seeks to address.
Space
- Perspective
- 3-D Mass
Possible Lessons:
- 1 pt. 2 pt. 3pt. Drawings
- Diminishing Size – Forms
- Atmospheric
- Interior/Exterior Space
- Vocabulary/Definitions
- Featured
Artist(s)/Cultures
1.0
Artistic Perception
Level)
(Proficient
Students perceive and respond to works of art, objects in nature, events, and the environment.
They also use the vocabulary of the visual arts to express their observations.
1.Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts, attending to the precise details of explanations or descriptions.
2.0
Creative Expression
Level)
(Proficient
Positive/Negative
Space
Picture Plane
Linear Perspective
Vanishing Point
Eye Level
Horizon Line
Aerial Perspective
1, 2, 3 pt. perspective
Students will:
Identify and use a variety of ways to show depth and space on a flat surface, such as foreshortening, diminishing size, overlapping, placement, and linear and aerial perspective.
Recognize and discuss means that artists and architects use to manipulate threedimensional space.
Analyze and create artworks drawn with one, and two point perspective by identifying the horizon line, vanishing points, and converging lines.
Create artworks that effectively utilize space and that reflect the classic principles of compositional arrangement.
Perceive and understand how artists design figure/ground relationships on a picture plane to create effective
Students apply artistic processes and skills, using a variety of media to communicate meaning and intent in original works of art.
3. Follow precisely a complex multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks, attending to special cases or expectations defined in the text.
7. Translate quantitative or technical information expressed in words in a text into visual form (e.g. in an equation) into words.
3.0
Historical and
Cultural Context
(Proficient compositions.
Level)
Students analyze the role and development of the visual arts in past and present cultures throughout the world, noting human diversity as it relates to the visual arts and artists.
2. Determine the central ideas or conclusions of a text; trace the text’s explanation or depiction of a complex process, phenomenon, or concept; provide an accurate summary of the text.
4.0
Aesthetic Valuing de(Proficient
Level)
Students analyze, assess, and derive meaning from works of art, including their own, according to the elements of art, the principles of design, and aesthetic qualities.
2 nd
Quarter
Texture
- Implied
- Actual
- Political
Possible Lessons:
- Surface Texture Illusion
in Drawings & Paintings
- Bas Relief 2-D
- Collage
- Current Event Portrayal
- Vocabulary/Definitions
- Featured
Artist(s)/Cultures
5. Analyze the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text, including relationships among key terms (e.g., force, friction, reaction force, energy).
1.0
Artistic Perception
(Proficient
Level)
Students perceive and respond to works of art, objects in nature, events, and the environment.
They also use the vocabulary of the visual arts to express their observations.
1. Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts, attending to the precise details of explanations or descriptions.
4. Determine the
Matte
Implied Texture
Actual Texture
Simulated Texture
Invented Texture
Students will:
Perceive and describe textures in the environment and in artworks.
Differentiate between actual and simulated textures in artworks.
Understand how texture can be used to suggest emotional and realistic qualities in art.
Create a variety of artworks that emphasize the difference between actual and simulated textures in art.
Recognize the role that textures play in natural and human-made environments.
meaning of symbols, key terms, and other domain-specific words and phrases as they are used in a specific scientific or technical context relevant to topics.
2.0
Creative Expression
Level)
(Proficient
Students apply artistic processes and skills, using a variety of media to communicate meaning and intent in original works of art.
3. Follow precisely a complex multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks, attending to special cases or expectations defined in the text.
3.0
Historical and
Cultural Context
(Proficient
Level)
Students analyze the role and development of the visual arts in past and present cultures throughout the world, noting human diversity as it relates to the visual arts and artists.
6. Analyze the author’s purpose in providing an explanation, describing a procedure, or discussing an experiment in a text,defining the question the author seeks to address.
4.0
Aesthetic Valuing
Level)
(Proficient
Students analyze, assess, and derive meaning from works of art, including their own, according to
3 rd
Quarter
Unit (s)
Principles of Design
-
Unity
- Variety
- Emphasis
- Rhythm
- Movement
- Balance
- Pattern
- Proportion
Possible Lessons:
- Currency Design
(Pattern)
- Seasonal Collage (Unity)
- Comic Strip Animation
(Movement)
- Four Quadrant Designs the elements of art, the principles of design, and aesthetic qualities.
5. Analyze the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text, including relationships among key terms. (e.g., force, friction, reaction force, energy).
1.0
Artistic Perception
(Proficient
Level)
Students perceive and respond to works of art, objects in nature, events, and the environment.
They also use the vocabulary of the visual arts to express their observations.
1. Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts attending to the precise details of explanations or descriptions.
Principles of Design:
· Unity
· Variety
· Emphasis
· Rhythm
· Movement
· Balance
· Pattern
· Proportion
Students will:
Identify and analyze the principles of design.
Describe how artists create unity using proximity, similarity, and continuation.
Identify and describe variety and focal points in artworks.
Explain and describe how artist create emphasis, movement and rhythm in visual arts.
Identify and describe symmetrical, asymmetrical, radial, and approximately symmetrical balance.
Recognize, discuss and create pattern in
(Balance) for Banners
- Graphic Design Project
(Emphasis)
- Depth of Field Landscape
(Proportion)
- Art Critique, Step by Step
- Vocabulary/Definitions
- Featured
Artist(s)/Cultures
2.0
Creative Expression
(Proficient
Level)
Students apply artistic processes and skills, using a variety of media to communicate meaning and intent in original works of art.
1. Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical text, attending to the precise details of explanations or descriptions.
3.0
Historical and
Cultural Context
Level)
(Proficient
Students analyze the role and development of the visual arts in past and present cultures throughout the world, their artworks.
Understand and analyze how artists use proportion in their art.
List, describe and define the principles of design.
Create artworks that emphasize applications of the principles of design.
noting human diversity as it relates to the visual arts and artists.
2. Determine the central ideas or conclusions of a text; trace the text’s explanation or depiction of a complex process
,phenomenon, or concept; provide an accurate summary of the text.
4.0
Aesthetic Valuing
(Proficient
Level)
Students analyze, assess, and derive meaning from works of art, including their own, according to the elements of art, the principles of design, and aesthetic qualities.
5. Analyze the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text, including relationships among key terms.
3 rd
Quarter
(e.g., force, friction, reaction,force, energy).
7. Translate quantitative or technical information expressed in words in a text into visual form.
Units(s)
2-Dimensional Media
- Drawing
- Painting
- Printmaking
- Photography
- Video Art
- Computer Art
- Mixed Media
Potential Lessons:
- Basic Portrait Drawing
(Various Media)
- Abstract Portrait Drawing
(Mixed Media)
- Figure/Proportion
- Drawing & Painting
- Scratch Art/Etching
- Linoleum Block Printing
- Travel Brochure or
1.0
Artistic Perception
Level)
(Proficient
Students perceive and respond to works of art, objects in nature, events, and the environment.
They also use the vocabulary of the visual arts to express their observations.
4. Determine the meaning of symbols, key terms, and other domain-specific words and phrases as they are used in a specific scientific or technical context relevant to grades 9-10 texts and topics.
Medium
Drawing
Painting
Printmaking
Photography
Film
Video Art
Computer Art
Mixed Media
Portrait
Figure
Proportion
Students will:
Understand that 2-D artworks are flat.
Recognize and identify media use to create drawings, paintings, mosaics, prints, photographs, film, video, computer art, and mixed media.
Demonstrate an understanding of the processes and techniques used in drawing, painting, printmaking, photography, filmmaking, video, collage, and computer art.
Perceive, appreciate, and explain how past artists have effectively utilized the unique properties of various 2-D art media in their art.
Create and critique artworks effectively using a variety of
2-D media.
Package
Design
- Art Critique, Step by Step
- Vocabulary/Definitions
- Featured
Artist(s/Cultures
5. Analyze the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text, including relationships among key terms (e.g. force, friction, reaction force, energy).
2.0
Creative Expression
(Proficient
Level)
Students apply artistic processes and skills, using a variety of media to communicate meaning and intent in original works of art.
3. Follow precisely a complex multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks, attending to special cases or exceptions defined in the text.
3.0
Historical and
Cultural Context
Level)
(Proficient
Students analyze the role and development of the visual arts in past and present cultures throughout the world, noting human diversity as it relates to the visual arts and artists.
5. Analyze the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text, including relationships among key terms.
4.0
Aesthetic Valuing
Level)
(Proficient
Students analyze, assess, and derive meaning from works of art, including their own, according to the elements of art, the principles of design, and aesthetic qualities.
4 th
Quarter
5. Analyse the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text, including relationships among key terms (e.g., force, friction, reaction force, energy).
Unit(s)
3-Dimensional Media
- Sculpture Type & Process
Overview
Potential Lessons:
- Sculpture Observation &
Reaction (WS)
- Rock Painting, Form &
Contour
-Jewelry Design (Drawing
Form Only)
- Art Critique, Step by Step
- Vocabulary/Definitions
- Featured
Artist(s)/Cultures
1.0
Artistic
Perception
Level)
(Proficient
Students perceive and respond to works of art, objects in nature, events, and the environment.
They also use the vocabulary of the visual arts to express their observations.
1. Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts, attending to the precise details of explanations or descriptions.
4. Determine the meaning of symbols, key
Relief Sculpture
Conceptual Art
Performance Art
Environmental Art
Installation Art
Fiber Art
Soft Sculpture
Students will:
Recognize and identify 3-D art forms.
Explain how sculptures may be carved, cast, modeled, or assembled.
Understand and describe how the elements and principles of design are applied in the creation of 3-D art forms.
Perceive and understand how artists create various 3-D art forms, such as: constructions, assemblages, performance and environmental art, and the process for repousse, cloisonné, blown glass, stained glass and the variety of basic steps and techniques expressed through these forms.
terms, and other domain-specific words and phrases as they are used in a specific scientific or technical context relevant to grades 9-10 texts and topics.
2.0
Creative Expression
Level)
(Proficient
Students apply artistic processes and skills, using a variety of media to communicate meaning and intent in original works of art.
3. Follow precisely a complex multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks, attending to special cases or expectations defined in the text.
3.0
Historical and
Cultural Context
Level)
(Proficient
Students analyze the role and development of the visual arts in past and present cultures throughout the world, noting human diversity as it relates to the visual arts and artists.
6. Analyze the author’s purpose in providing an explanation, describing a procedure, or discussing an experiment in a text.
Defining the question the author seeks to address.
4.0
Aesthetic Valuing
Level)
(Proficient
Students analyze, assess, and derive meaning from works of art, including
4 th
Quarter their own, according to the elements of art, the principles of design, and aesthetic qualities.
5. Analyze the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text, including relationships among key terms (e.g., force, friction, reaction force, energy).
Architecture
- Basic Drafting
- Perspective Drawing
- Historical Survey of
Architectural Elements &
Design
Lessons:
- Thematic Building Design
(Teacher prescribes theme)
-Floor Plan Draft Drawing
- Art Critique, Step by Step
-Vocabulary/Definitions
– Featured
Architect(s)/Cultures
1.0
Artistic Perception
(Proficient
Level)
Students perceive and respond to works of art, objects in nature, events, and the environment.
They also use the vocabulary of the visual arts to express their observations.
1 Cite textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts, attending to the precise details of
Architect
Post & Lintel
Arch
Corbelled Arch
Dome
Frame Construction
Ferroconcrete
Coliseum
Parthenon
Cathedral
Stupa
Pavilion
Palace
Student will:
Comprehend the principles of basic construction techniques.
Understand how construction techniques and technologies influenced architecture.
Identify architectural features and construction techniques in the built environment.
Appreciate architectural achievements around the world throughout various cultures and time periods.
Create architectural designs and drawings according to students’ imagination,
4 th
Quarter
Architecture (cont) explanations or descriptions.
4 Determine the meaning of symbols, key terms, and other domain-specific words and phrases as they are used in specific scientific or technical context relevant to texts and topics.
2.0
Creative Expression
(Proficient Level)
Students apply artistic processes and skills, using a variety of media to communicate meaning and intent in original works of art.
3. Follow precisely a complex multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks, attending to studied construction styles and teacher’s lesson prompts.
special cases or expectations defined in the text.
3.0
Historical and
Cultural Context
Level)
(Proficient
Students analyze the role and development of the visual arts in past and present cultures throughout the world, noting human diversity as it relates to the visual arts and artists.
6.Analyze the author’s purpose in providing an explanation, describing a procedure’ or discussing an experiment in a text, defining the question the author seeks to address.
4.0
Aesthetic Valuing
Level)
(Proficient
Students analyze, assess, and derive meaning from
works of art, including their own, according to the elements of art, the principles of design, and aesthetic qualities.
5. Analyze the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text, including relationships among key terms (e.g., force, Friction, reaction force, energy).
6. Analyze the author’s purpose in providing an explanation, describing a procedure, or discussing an experiment in a text, defining the question the author seeks to address.
5.0
Connections,
Relationships,
Applications
(Proficient Level)
Students apply what they learn in the visual arts across subject areas.
4 th
Quarter
Unit(s):
Careers in Art
- Environmental Design
- Graphic Design
- Industrial Design
- Product/Fashion Design
- Multimedia Design
- Curator/Conservator
They develop competencies and creative skills in problem solving, communication, and management of time, and resources that contribute to lifelong learning and career skills. They also learn about careers in and related to the visual arts.
9 Compare and contrast findings presented in a text to those from other sources noting when the findings support or contradict previous explanations or accounts.
1.0
Artistic Perception
(Proficient
Level)
Students perceive and respond to works of art, objects in nature, events, and the environment.
They also use the vocabulary of the visual arts to express their
- Curator
- Conservator
- Designer:
Fashion
Computer l
Graphics
Environmenta
Set/Theater
Students will:
Become familiar with the wide range of careers in art.
Consider the differences between fine art and design careers.
Identify skills and responsibilities associated with specific art careers.
4 th
Quarter
Lessons:
- Survey of Careers in Art
- Chosen Arts Career Step
Ladder
Presentation Board
- Art Career Commonalities
- Featured Artist Biography
Careers in Art (cont)
Lessons:
- Prom Fashion Design
- Landscape Design
- Classroom Art Museum observations.
1 Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts, attending to the precise details of explanations and descriptions.
2.0
Creative Expression
(Proficient Level)
Students apply artistic processes and skills, using a variety of media to communicate meaning and intent in original works of art.
3. Follow precisely a complex multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical ns age
Industrial
Communicatio
Product/Pack
Multi-Media
Print Media
Costume
Display
Culinary
Interior
Understand the importance of maintaining a portfolio and the significance of collegiate arts training and possible arts internships.
Create mock-up of artist self-promotional packets and potential resume.
tasks, attending to special cases or expectations defined in the text.
3.0 Historical and
Cultural Context
(Proficient
Level)
Students analyze the role and development of the visual arts in past and present cultures throughout the world, noting human diversity as it relates to the visual arts and artists.
6. Analyze the author’s purpose in providing an explanation, describing a procedure, or discussing an experiment in a text, defining the question the author seeks to address.
4.0
Aesthetic Valuing
(Proficient
Level)
Students analyze, assess,
and derive meaning from works of art, including their own, according to the elements of art, the principals of design, and aesthetic qualities.
5 Analyze the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text including relationships among key terms.
5.0
Connections,
Relationships,
Applications
(Proficient Level)
Students apply what they learn in the visual arts across subject areas.
They develop competencies and creative skills in problem solving, communication, and management of time, and resources that contribute to lifelong learning and career skills. They also learn about careers in and
related to the visual arts.
9 Compare and contrast findings presented in a text to those from other sources noting when the findings support or contradict previous explanations or accounts.