03-04: Universe Hierarchy and Technology
advertisement

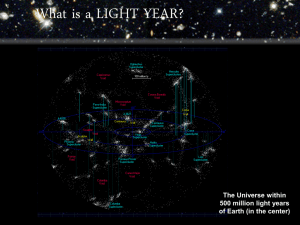
Thursday, February 23, 2011 Competency 4f – DOK 2 8th Grade – Lesson 7.10 Name: ____________________________________ Period: ____ Describe the hierarchical structure of the universe and examine the expanding universe to include its age and history and the modern techniques used to measure objects and distances in the universe. (DOK 2) Page 10 I can describe the hierarchy of the universe. Unit 7 – Earth and Space: Hierarchy of the Universe Quick Review Use the diagram at the right to answer questions 1 – 6. 1. Letter A - Name: central vacuole, Function: stores water 2. Letter B - Name: chloroplast Function: makes glucose through photosynthesis 3. Letter C - Name: mitochondria, Function: breaks down glucose to form ATP through cellular respiration 4. Letter D - Name: nucleus Function: stores DNA and controls the activities of the cell 5. Letter E - Name: rough endoplasmic reticulum, Function: site of translation, making proteins using RNA instructions 6. What type of cell is this? How do you know? This is a plant cell. It has a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a central vacuole. Key Points on the Hierarchy of the Universe: 1. The universe is made of all matter and contains everything. It is HUGE and is rapidly expanding. The universe is divided up into different pieces that are described below. 2. Planets such as ours orbit around stars. Stars are balls of hydrogen and helium gas that produce heat and light as they undergo nuclear fusion. They live for billions of years. 3. A multitude of stars will group together forming star clusters. Star clusters contain between 15 and 250 stars. These stars all move together in the same direction. 4. A galaxy is made up of a huge number of star clusters. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains 100 billion stars. a. There are three different types of galaxies based on their shape. Galaxies can be spiral, elliptical, or irregular in shape. b. The star clusters that make up galaxies all move in the same direction. 5. The largest structure in the universe is a galaxy cluster or a galactic cluster. They contain anywhere from 50 to 1,000 galaxies. a. The galaxies that make up a galaxy cluster all move in he same direction. b. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, is part of a galaxy cluster called the Local Group. 6. Since the universe is HUGE, we use the light-year to measure distance. One light year is the distance that light can travel in a year. a. Light travels about 186,000 miles every second so a light year is about 6 trillion miles. b. The closest star to the Earth (other than the Sun) is called Proxima Centauri. It is 4.2 light-years away. Thursday, February 23, 2011 Competency 4f – DOK 2 8th Grade – Lesson 7.10 Name: ____________________________________ Period: ____ Describe the hierarchical structure of the universe and examine the expanding universe to include its age and history and the modern techniques used to measure objects and distances in the universe. (DOK 2) Page 10 I can describe the hierarchy of the universe. Unit 7 – Earth and Space: Hierarchy of the Universe Quick Review Use the diagram at the right to answer questions 1 – 6. 1. Letter A - Name: , Function: stores 2. Letter B - Name: Function: 3. Letter C - Name: , Function: 4. Letter D - Name: Function: 5. Letter E - Name: , Function: site of , making using RNA instructions 6. What type of cell is this? How do you know? Key Points on the Hierarchy of the Universe: 1. The 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. is made of all and contains . It is and is rapidly . Plants such as ours orbit around . Stars are balls of and gas that produce heat and light as they undergo . They live for of years. A multitude of stars will group together forming . Star clusters contain between and stars. These stars all move together in the same . A is made up of a huge number of star clusters. Our galaxy, the , contains 100 stars. a. There are three different types of galaxies based on their . Galaxies can be , , or in shape. b. The star clusters that make up galaxies all move in the same . The largest structure in the universe is a galaxy or a cluster. They contain anywhere from to galaxies. a. The galaxies that make up a galaxy cluster all move in the same . b. Our galaxy, the , is part of a galaxy cluster called the . Since the universe is , we use the to measure distance. One light year is the distance that can travel in a . a. Light travels about 186,000 every so a light year is about 6 miles. b. The closest star to the Earth (other than the Sun) is called . It is light-years away. Thursday, February 23, 2011 Name: ____________________________________ Period: ____ The Universe: Guided Practice 1. Put the following into order from the largest to the smallest: star cluster, star, galaxy cluster, galaxy. 2. A scientist discovers a huge new body of stars numbering in the billions. They are all spinning in an elliptical pattern. How would this scientist classify this body? 3. Compare the size of the two objects using the words larger than or smaller than. A star is … a galaxy A galaxy cluster is … a star cluster A galaxy… a star The Universe: Independent Practice Answer the following questions as a scientist would, using complete sentences! 1. What is contained by the universe? 2. What is the smallest division of the Universe? 3. What are most stars made of and for how long do they live? 4. An astronomer discovers a new group of 100 stars. What name could she give to this group of stars? 5. The astronomer realizes that this group of stars, along with billions of other stars, is part of a spiral formation called Messier 87 that is similar to the Milky Way. What would Messier 87 be classified as? 6. Messier 87 along around 1,300 other elliptical and spiral bodies combine to form the Virgo Cluster. What would the Virgo Cluster be classified as? 7. If a light year is 6 trillion miles, about how many miles is the closest star (other than the Sun) from the Earth?