Human Effects on Soil, Water and Air Humans and the Environment
advertisement

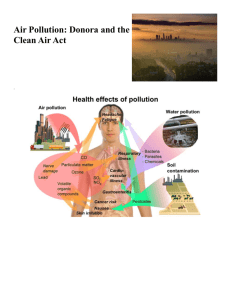
Human Effects on Soil, Water and Air Humans and the Environment What is the human problem right now with the environment?____________________________ SOIL Crops can only be grown on about ______ of the land on earth. The soil we have on earth cannot keep up with the demand for food as the population of humans on earth increases. Just _______ of Canada is farmland. What is soil? Growth of cities: As the populations of cities ___________, they need more and more land for houses and other buildings. Cities were originally founded near the ___________________for farming. This means, we often build on or pave over the best, ___________________________ Where is one of the cities we have built over farm land? Farming Technology: Fortunately, the output from our farms continues to increase because of _______________________________________________ (Unfortunately, the use of chemicals causes other problems). Erosion What is erosion? (it is described in the video) Soil Erosion Soil can be eroded by __________________________________. If unprotected, our planet's precious topsoil can be blown or washed away. Farmers have to be very careful to make sure that topsoil stays where it is Clear Cutting: We need many wood products in our lives, but the practice of clear cutting is still common in many areas and severely damages the soil and ecosystems of the area. Trees hold the soil together, so when forests are clear cut they can have ______________________________________________________. Often logging, mining and manufacturing leave behind _________________________________ that harm the environments they are in. These are often difficult to remove; they can affect all life that lives near them. Brownfields: Large chunks of polluted land, abandoned by industries are called ____________________ Once the industry has moved out or went out of business, cities are often left to clean up the mess. Many times they are just left unused since clean up of the soil is _______________________________ Where is a local Brownfield? Human Effects on Water Human activity causes incredible harm to our water systems. There are many paths for contaminants to take to get into our water. List 2 discussed as a class Drinking Water: Without proper care of our _______________, drinking water can become contaminated and unhealthy to drink. This is a very serious problem in poor countries. Garbage Island Since plastic will not ___________________________, it stays around for a long time. When a plastic bottle is dumped into a river, it eventually makes its way to the ocean. It will join garbage island. After many years of plastics making their way into our oceans, there is now a giant patch of plastic in the Pacific Ocean bigger than Texas. Human Effects on Air Fossil Fuels: Most of the damage we do to our air comes from the use of ________________________________ that we use for driving, heating, manufacturing and generating electricity. They include: ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ When fossil fuels are burned, they release molecules into the air. Some of these are _________________________________________________ Some such as ______________________________ is completely normal in the atmosphere, but too much is a problem. Smog: Some of these molecules that are released in the air create smog: a haze of mostly ________________ made when ____________________________________________ combined with heat from the sun. Smog is the disastrous result of too much exhaust from ___________________________ being emitted close to large city centres. It is such a problem now, that air quality information is included in the weather report. It's called ___________________________________________________ Smog causes _____________________ early deaths in Canada every year. List 5 health effects of smog: Acid Precipitation: Acid Precipitation is rain and snow that has pH values below ___________ When ____________________________________ rise in the air they can dissolve into the vapour in clouds creating sulphuric and nitric acids. These acids come down with the rain. Global Warming: Global Warming refers to the average annual (yearly) increase in global temperatures that has occurred since around _____________________