TOPICS FOR SECOND TEST – Page 1
advertisement

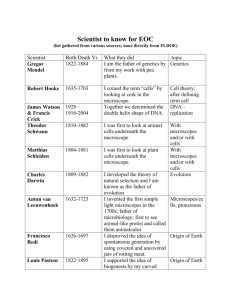
TOPICS FOR SECOND TEST – Page 1 This 2-page Study Guide for Test 2 contains all Topics discussed since Test #1: Objective Lens Properties, Refraction, Types of Light Microscopes, Electron Microscopes; Dye (Chemical & Functional groups); Simple Staining; Cell Types, Cell Platforms, and the Kingdoms. 1. IMPORTANT OBJECTIVE LENSES PROPERTIES Describe each of these and determine their various effects on resolution: a. Size of Lens Aperture b. Working Distance c. Length of the Body Tube d. For each objective lens, determine: i. Working Distance ii. Body Tube Length 2. REFRACTION AND REFRACTIVE INDEX a. Define Refraction and determine its effect on image formation b. List the effect and benefits of Immersion oil on refraction c. Recall the Refractive Index for: i. Vacuum and Air ii. Water and Liquids iii. Glass and Lenses 3. TYPES OF COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPES Describe and differentiate between the design and images of: a. Bright-field Microscope b. Dark-field Microscope 4. PHASE CONTRAST MICROSCOPY a. Explain how it works and describe what the image looks like b. Determine how it is designed differently from other Microscopes 5. DIFFERENTIAL INTERFERENCE CONTRAST MICROSCOPY a. Explain how it works and describe what the image looks like b. Determine how it is designed differently from other Microscopes 6. FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY a. Explain how it works and describe what the image looks like b. Determine how it is designed differently from other Microscopes c. Study wavelength, the range for visible light, and effect on Resolution e. Differentiate between Fluorochrome and Chromophore TOPICS FOR SECOND TEST – Page 2 7. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY a. Explain how it works and identify parts and their functions b. Describe image formation and what it look like c. Determine how illumination and magnification occur d. Compare and contrast the two types e. Trace the path of electrons in electron microscopy f. Differentiate between Light and Electron Microscopes 8. RESOLUTION: Compare limits of Resolution for: a. Human Eye (Normal vision) b. Light Microscope (LM) c. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) d. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) 9. DYES, STAINS, & MICROSCOPY a. Recall what a dye is, how it is formed, and origin of its color b. Describe the reaction that forms a salt or dye c. Determine the fate of all ions in Acid-Base reactions d. Compare Negative and Direct/Positive Staining e. Explain interaction between dyes and cells f. Which Microscopes rely on stains for contrast? 10. CHEMICAL GROUPS OF DYES a. Name some dyes and their Chemical Groups b. Which ion has color for each type of dye? c. What would you used each group for? d. Define Simple Staining, the steps, and results e. Describe how samples are prepared for staining 11. CELLS AND KINGDOMS a. Review history and Scientists linked to Cells, Microscopy, and Stains b. Name major Cell types, Platforms, and compare their sizes c. Compare and Contrast characteristics of Cells d. List the Kingdoms and identify the Cell Platform for each. e. How are cells in one Kingdom unique or different from others? f. How many Kingdoms are Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic, Unicellular, or Multi-cellular? END OF TOPICS FOR TEST 2