Cell Cycle
advertisement
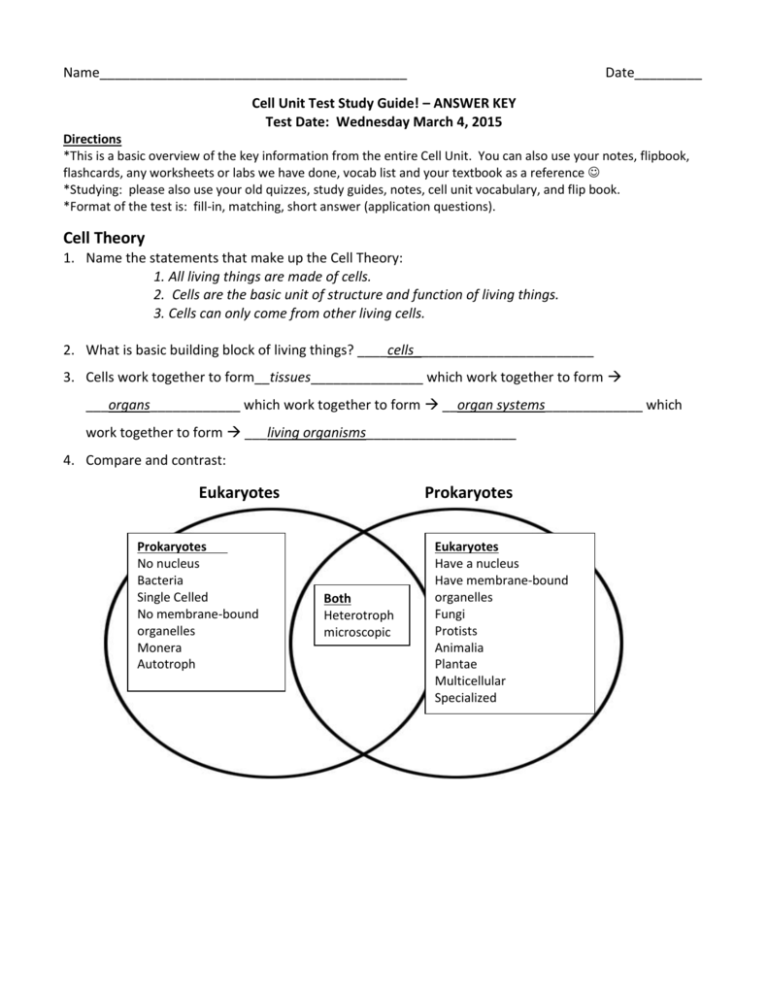
Name_________________________________________ Date_________ Cell Unit Test Study Guide! – ANSWER KEY Test Date: Wednesday March 4, 2015 Directions *This is a basic overview of the key information from the entire Cell Unit. You can also use your notes, flipbook, flashcards, any worksheets or labs we have done, vocab list and your textbook as a reference *Studying: please also use your old quizzes, study guides, notes, cell unit vocabulary, and flip book. *Format of the test is: fill-in, matching, short answer (application questions). Cell Theory 1. Name the statements that make up the Cell Theory: 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of living things. 3. Cells can only come from other living cells. 2. What is basic building block of living things? ____cells________________________ 3. Cells work together to form__tissues_______________ which work together to form ___organs____________ which work together to form __organ systems_____________ which work together to form ___living organisms____________________ 4. Compare and contrast: Eukaryotes Prokaryotes No nucleus Bacteria Single Celled No membrane-bound organelles Monera Autotroph Prokaryotes Both Heterotroph microscopic Eukaryotes Have a nucleus Have membrane-bound organelles Fungi Protists Animalia Plantae Multicellular Specialized Cell Diagrams Cell Organelle Functions Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Nucleus Cytoplasm Chromosomes Mitochondria Chloroplast Vacuole Function -Flexible, elastic, and contains pores -Allows cell to change shape - Controls movement into and out of the cell Strong, stiff, non-living outermost layer. -Made of cellulose -Supports and protects the cell -Allows plants to stand upright -Control center of eukaryotic cells (Brain) -Regulates all cell activities and organelle functions -Jelly-like substance in the cell that holds all of the organelles -Moves organelles and materials within the cell -Structures found in the nucleus made of DNA-(genes) (deoxyribonucleic acid) -Directs all cell activity -Passes on traits to new cells -Breaks down sugar and oxygen to create energy for the cell called ATP (adenosine triphosphate) -Known as the “PowerHouse” of the cell -Large, round, green structure that contains chlorophyll -Where photosynthesis occurs and sunlight energy is changed into a glucose (sugar) molecule and O2 (oxygen) -stores water and nutrients for cell Plant/Animal/Both Both Plant Both Both Both Both Plant Large in Plant cells Small in animal cells Lysosome Endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes -small round sac that contains digestive enzymes (enzyme=protein that makes something happen) -breaks apart and digests cell wastes and dead/damaged cell parts -tubular passageways through cell -transportation system of cell that carries materials out of the nuclueus -produces protein for the cell which is transported by the ER Common in animal cells Rare in plant cells Both Both Cell Transport 1. What direction do materials move into and out of the cell? -Materials move into and out of the cell from a high concentration to a low concentration in order to maintain homeostasis and to provide the cell with its needs, and to get rid of wastes 2. What materials can move into and out of the cell? -Oxygen, water, and nutrients travel into the cell -Wastes, water, and carbon dioxide travel out of the cell 3. Define Passive Transport-The movement of materials through a cell membrane without the use of energy from the cell 4. What is a real life example of passive transport? - Air fresheners, food coloring in water, nutrients moving into the cell 5. What are the 2 kinds of passive transport? - Osmosis, Diffusion 6. Define Active Transport- The movement of materials through a cell membrane with the use of energy from the cell. (energy made in mitochondria) 7. What are the kinds of active transport? - Endocytosis and exocytosis 8. What is Diffusion? - The movement of a substance from an area of high concentration (density) to an area of lower concentration (density) 9. What is Osmosis? -diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane 10. Define Semi-permeable membrane- Material that allows only certain substances to pass through. 11. What is Endocytosis? - Process by which cell uses energy to form a vesicle around a molecule of a substance to carry it INTO the cell 12. What is Exocytosis? -Process by which cell uses energy to form a vesicle around a molecule of a substance to carry it OUT 13. When would a cell need to perform endocytosis? -When the cell needs to move a substance into the cell that is either too big to fit through the membrane or in too low a concentration to flow into the cell on its own. 14. When would a cell need to perform exocytosis? - When the cell needs to move a substance out of the cell that is either too big to fit through the membrane or in too low a concentration to flow out of the cell on its own. Cell Processes 1. How do cells create energy -cells create energy using glucose and oxygen. Oxygen is consumed and used to break down glucose to release ATP (energy) 2. Where is energy made? ___mitochondria____________ 3. What is cellular respiration? - The process by which plant and animal cells use oxygen to break apart glucose (either ingested in food or created during the process of photosynthesis) to produce energy for the cell (in the form of ATP). 4. What are the molecular and word formulas for cellular respiration? - Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP (energy) - C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP (energy) 5. What is ATP and where would you find it? - A molecule that the cell uses as energy. ATP is created in mitochondria. (Adenosine Triphosphate) 6. What is the function of the chloroplast? - Organelle containing green chlorophyll where photosynthesis occurs and sunlight energy is changed into a glucose (sugar) molecule and O2 (oxygen). 7. What is photosynthesis and why is it so important to the cell? - The process by which plants, algae and some bacteria use sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide to glucose and oxygen. This is the process all plants use to make their own food. The glucose created during photosynthesis will travel from the chloroplast to the mitochondria for cellular respiration. 8. What is the function of chlorophyll? - Chlorophyll is green pigments that are found in the chloroplasts of plants and in other photosynthetic organisms. It is what makes plants green and is responsible for absorbing the sunlight energy plants need to perform photosynthesis. 9. What is the molecular and word formula for photosynthesis? - Carbon Dioxide + Water + sunlight energy Glucose + Oxygen - 6CO2 + 6H2O + sunlight energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 10. What is glucose and where does it go after the chloroplast? -Glucose is a simple sugar that is created in the chloroplasts of cells during photosynthesis, or ingested in food by animals.. Glucose is used by the mitochondria to create energy. The chemical formula for glucose is C6H12O6 11. Why did the bromothymol blue solution turn yellow faster after exercise? -When we exercise our body needs to produce more energy through cellular respiration. So, we need to take in more oxygen and therefore create more carbon dioxide. 12. Can the mitochondria perform its job in the plant cell without the chloroplast? Explain -The mitochondria can’t perform its job without the chloroplast in a plant cell. Glucose is an ingredient for cellular respiration and plant cells create glucose in the chloroplast during photosynthesis. Animal cells can survive without a chloroplast because they ingest food. 13. Can plant cells function with a chloroplast but not mitochondria? -No, plant cells need both a chloroplast and mitochondria. Both organelles have a different function to keep the plant cell alive. The chloroplast makes food for the cell in the form of glucose. The mitochondria use the glucose to make ATP energy. Without a mitochondria, the plant cell would have no energy to perform any functions. 14. Cells perform photosynthesis and cellular respiration in order to maintain ____homeostasis 15. Compare and contrast: Photosynthesis -Plant cells make food -produces glucose and oxygen -needs carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight energy -Takes place in chloroplast -needs chlorophyll -products from chloroplast travel to mitochondria -in plant cells Respiration -Needed for cell to make energy -reactants for one are product for other -occur inside an organelle -take place in plants -All cells make ATP (energy) -carbon dioxide and water are waste -needs oxygen and glucose -takes place in mitochondria -in plant and animal cells Cell Cycle 1. What are the 3 stages of the cell cycle? -interphase -mitosis -cytokinesis 2. What is the most important event during interphase? -interphase: chromosomes duplicate so new cell will have same chromosomes as parent cell 3. What is the most important event during mitosis? -mitosis: nucleus divides and 2 new nuclei form 4. What is the most important event during cytokinesis? -cytokinesis: 2 new identical daughters form 5. What is the goal of the cell cycle -The goal of the cell cycle is to produce new cells to replace old or damaged cells 6. What is the original cell called? ____parent cell____________________ 7. What are the 2 new identical cells called? ___daughter cells___________ 8. Label the 4 phases of mitosis: 1. prophase 3. anaphase 2. metaphase 4. telophase








