Study guide - Chapter 07
advertisement

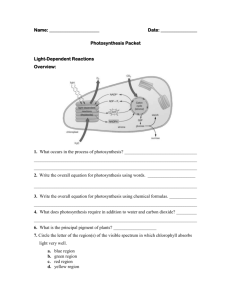
NSB 121 – GENERAL BIOLOGY I CHAPTER 07 – STUDY GUIDE 1. What is an autotroph? 2. What is a photoautotroph? 3. What is a chemoautotroph? 4. What is a heterotroph? 5. Name four examples of photoautotrophic organisms. 6. What is the major site of photosynthesis in green plants? 7. What is chlorophyll? 8. What are stomata? What is their function? 9. What is the function of leaf veins? 10. What type of cells in the plant has the most chloroplasts? 11. Molecular oxygen (O2) is released by plants during photosynthesis. What is the source of the oxygen atoms? 12. In which product of photosynthesis is the carbon from CO2 found? 13. Write out the chemical equation for photosynthesis. What compound is being oxidized? What compound is being reduced? 14. The chemical reaction of photosynthesis requires energy. Is it an exergonic or an endergonic reaction? 15. In what structure of the chloroplast does the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur? 16. Briefly describe the events in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. 17. What are photons? 18. Why do we perceive most plants in green? 19. Where in the chloroplast do we find light-absorbing pigments? 20. What pigments are normally found in chloroplasts? Which one is the most abundant? 21. Why are carotenoids beneficial for plants? 22. What happens when a pigment molecule, such as chlorophyll, absorbs a photon of light? 23. What is a photosystem? How many photosystems participate in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis? 24. Why is the chlorophyll a in the PSII called P680? 25. Why is the chlorophyll a in the PSII called P700? 26. What are the products of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis? 27. Why is a water molecule split during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis? 28. How is ATP generated in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis? 29. What is photophosphorylation? 30. Compare and contrast oxidative phosphorylation and photophosphorylation. 31. Briefly describe the events in the Calvin cycle. 32. What components are necessary to produce sugars by means of the Calvin cycle? 33. What enzyme is responsible for the carbon-fixation step in the Calvin cycle? 34. How many molecules of ATP and NADPH are consumed to produce one molecule of G3P? 35. How many runs of the Calvin cycle are necessary for a plant cell to produce a molecule of glucose? 36. C3 plants get their CO2 directly from the air. Why are these plants called C3? 37. What happens to C3 plants in hot and dry weather? 38. What is photorespiration? Why is it a waste of energy for the plant? 39. If photorespiration is not beneficial for plants, why does it happen? 40. What alternate modes of carbon fixation are observed in plant species found in hot, dry climates? What is the purpose of having these alternate modes of carbon fixation? 41. Briefly describe how carbon fixation in C4 and CAM plants is different than in C3 plants. 42. What are sugars produced by photosynthesis used for by plant cells? 43. Name the greenhouse gases. Why are these important for the planet? 44. How is CO2 related to global climate change? 45. What are the predicted consequences of continued warming-up of the planet? 46. What are possible ways of reducing CO2 levels in the atmosphere? 47. What are CFCs? What are the consequences of increased concentration of CFCs in the atmosphere?