Supplementary Table 1 | Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding
advertisement
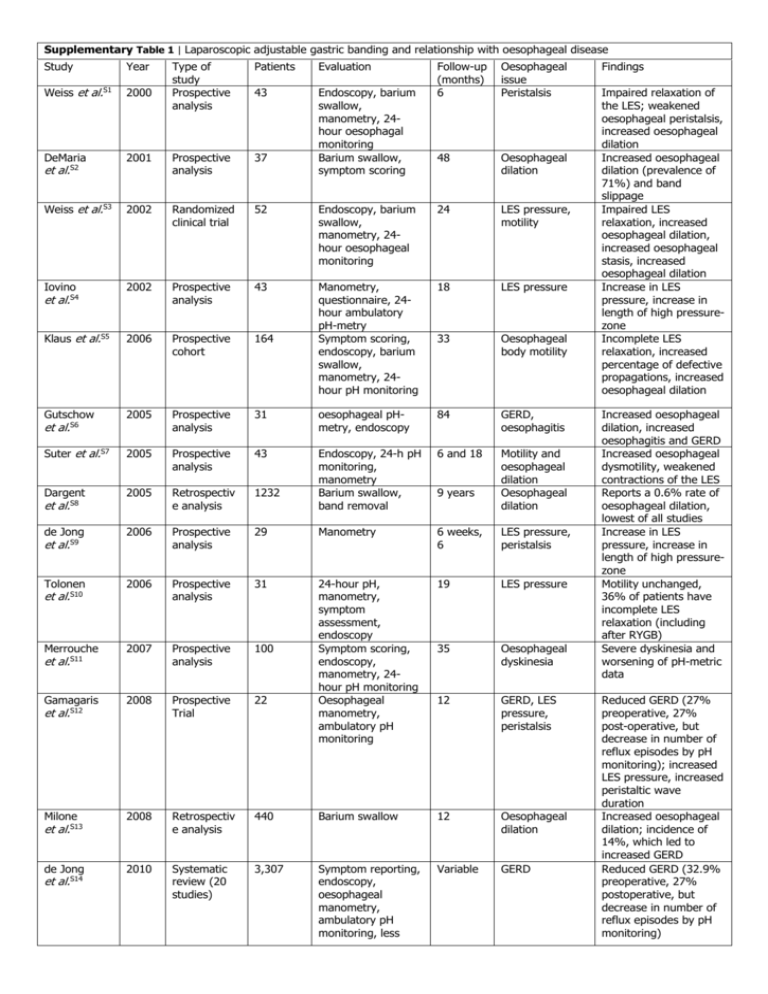
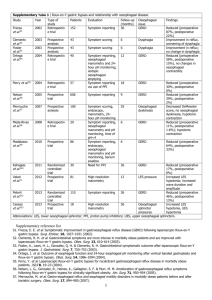
Supplementary Table 1 | Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding and relationship with oesophageal disease Study Year Type of study Prospective analysis Patients Evaluation Follow-up (months) 6 Oesophageal issue Peristalsis Weiss et al.S1 2000 43 2001 Prospective analysis 37 Endoscopy, barium swallow, manometry, 24hour oesophagal monitoring Barium swallow, symptom scoring DeMaria 48 Oesophageal dilation Weiss et al.S3 2002 Randomized clinical trial 52 Endoscopy, barium swallow, manometry, 24hour oesophageal monitoring 24 LES pressure, motility Iovino 2002 Prospective analysis 43 Manometry, questionnaire, 24hour ambulatory pH-metry Symptom scoring, endoscopy, barium swallow, manometry, 24hour pH monitoring 18 LES pressure Klaus et al.S5 2006 Prospective cohort 164 33 Oesophageal body motility Gutschow 2005 Prospective analysis 31 oesophageal pHmetry, endoscopy 84 GERD, oesophagitis Suter et al.S7 2005 Prospective analysis 43 6 and 18 2005 Retrospectiv e analysis 1232 Endoscopy, 24-h pH monitoring, manometry Barium swallow, band removal Motility and oesophageal dilation Oesophageal dilation Dargent de Jong 2006 Prospective analysis 29 Manometry 6 weeks, 6 LES pressure, peristalsis Tolonen 2006 Prospective analysis 31 19 LES pressure Merrouche 2007 Prospective analysis 100 35 Oesophageal dyskinesia Gamagaris 2008 Prospective Trial 22 24-hour pH, manometry, symptom assessment, endoscopy Symptom scoring, endoscopy, manometry, 24hour pH monitoring Oesophageal manometry, ambulatory pH monitoring 12 GERD, LES pressure, peristalsis Milone 2008 Retrospectiv e analysis 440 Barium swallow 12 Oesophageal dilation de Jong 2010 Systematic review (20 studies) 3,307 Symptom reporting, endoscopy, oesophageal manometry, ambulatory pH monitoring, less Variable GERD et al.S2 et al.S4 et al.S6 et al.S8 et al.S9 et al.S10 et al.S11 et al.S12 et al.S13 et al.S14 9 years Findings Impaired relaxation of the LES; weakened oesophageal peristalsis, increased oesophageal dilation Increased oesophageal dilation (prevalence of 71%) and band slippage Impaired LES relaxation, increased oesophageal dilation, increased oesophageal stasis, increased oesophageal dilation Increase in LES pressure, increase in length of high pressurezone Incomplete LES relaxation, increased percentage of defective propagations, increased oesophageal dilation Increased oesophageal dilation, increased oesophagitis and GERD Increased oesophageal dysmotility, weakened contractions of the LES Reports a 0.6% rate of oesophageal dilation, lowest of all studies Increase in LES pressure, increase in length of high pressurezone Motility unchanged, 36% of patients have incomplete LES relaxation (including after RYGB) Severe dyskinesia and worsening of pH-metric data Reduced GERD (27% preoperative, 27% post-operative, but decrease in number of reflux episodes by pH monitoring); increased LES pressure, increased peristaltic wave duration Increased oesophageal dilation; incidence of 14%, which led to increased GERD Reduced GERD (32.9% preoperative, 27% postoperative, but decrease in number of reflux episodes by pH monitoring) need for PPI Naef et al.S15 2011 Retrospectiv e analysis 167 Endoscopy 12 years Oesophageal dilation Khan et al.S16 2011 Retrospectiv e analysis 6 Manometry, symptom scoring 12 peristalsis Woodman 2012 Prospective Trial 395 Symptom reporting 24 GERD et al.S17 Increase in oesophageal dilation (25.5% of patients) Increase of aperistalsis mimicking achalasia, reversible with band removal Reduced GERD (43% preoperative, 3% postoperative) Abbreviations: LES, lower oesophageal sphincter; RYGB, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Supplementary reference list S1. Weiss, H. G. et al. Treatment of morbid obesity with laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding affects esophageal motility. Am. J. Surg. 180, 479–482 (2000). S2. DeMaria, E. J. et al. High failure rate after laparoscopic adjustable silicone gastric banding for treatment of morbid obesity. Ann. Surg. 233, 809–818 (2001). S3. Weiss, H. G. et al. Adjustable gastric and esophagogastric banding: a randomized clinical trial. Obes. Surg. 12, 573–578 (2002). S4. Iovino, P. et al. Abnormal esophageal acid exposure is common in morbidly obese patients and improves after a successful Lapband system implantation. Surg. Endosc. 16, 1631–1635 (2002). S5. Klaus, A. et al. Prevalent esophageal body motility disorders underlie aggravation of GERD symptoms in morbidly obese patients following adjustable gastric banding. Arch. Surg. 141, 247–251 (2006). S6. Gutschow, C. A., Collet, P., Prenzel, K., Holscher, A. H. & Schneider, P. M. Long-term results and gastroesophageal reflux in a series of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 9, 941–948 (2005). S7. Suter, M., Dorta, G., Giusti, V. & Calmes, J. M. Gastric banding interferes with esophageal motility and gastroesophageal reflux. Arch. Surg. 140, 639–643 (2005). S8. Dargent, J. Esophageal dilatation after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding: definition and strategy. Obes. Surg. 15, 843–848 (2005). S9. de Jong, J. R., van Ramshorst, B., Timmer, R., Gooszen, H. G. & Smout, A. J. Effect of laparoscopic gastric banding on esophageal motility. Obes. Surg. 16, 52–58 (2006). S10. Tolonen, P., Victorzon, M., Niemi, R. & Makela, J. Does gastric banding for morbid obesity reduce or increase gastroesophageal reflux? Obes. Surg. 16, 1469–1474 (2006). S11. Merrouche, M. et al. Gastro-esophageal reflux and esophageal motility disorders in morbidly obese patients before and after bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 17, 894–900 (2007). S12. Gamagaris, Z. et al. Lap-band impact on the function of the esophagus. Obes. Surg. 18, 1268–1272 (2008). S13. Milone, L. et al. Esophageal dilation after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Surg. Endosc. 22, 1482–1486 (2008). S14. de Jong, J. R., Besselink, M. G., van Ramshorst, B., Gooszen, H. G. & Smout, A. J. Effects of adjustable gastric banding on gastroesophageal reflux and esophageal motility: a systematic review. Obes. Rev. 11, 297–305 (2010). S15. Naef, M. et al. Esophageal dysmotility disorders after laparoscopic gastric banding—an underestimated complication. Ann. Surg. 253, 285–290 (2011). S16. Khan, A., Ren-Fielding, C. & Traube, M. Potentially reversible pseudoachalasia after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 45, 775–779 (2011). S17. Woodman, G. et al. Effect of adjustable gastric banding on changes in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and quality of life. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 28, 581–589 (2012).