LC-MS/MS METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF
advertisement
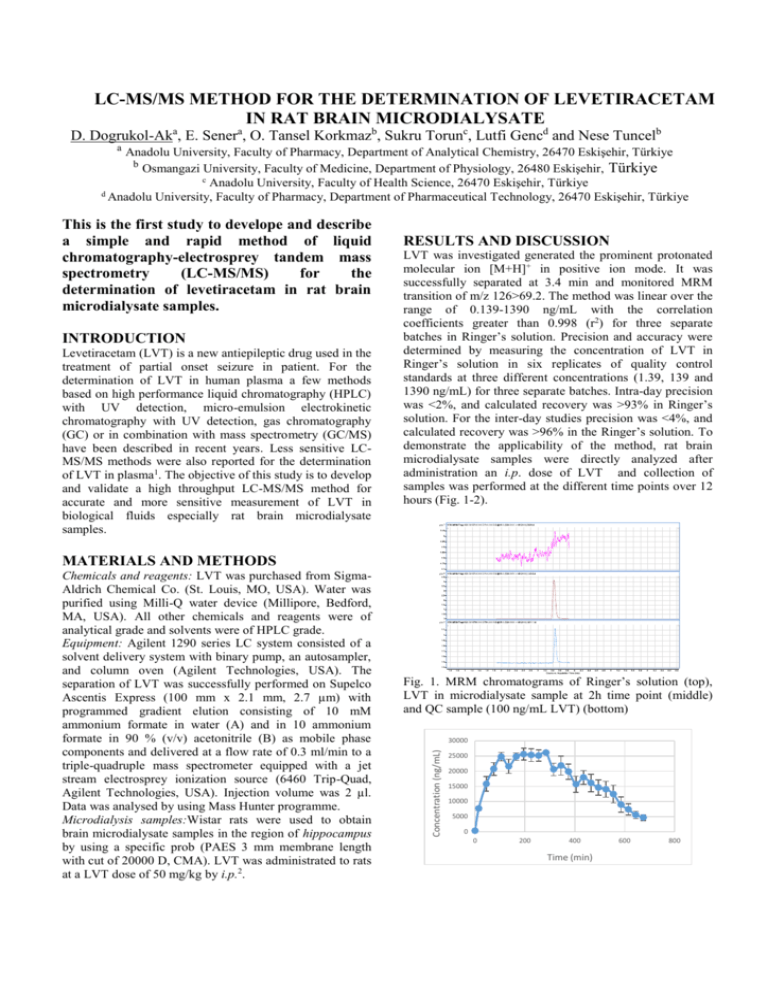
LC-MS/MS METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF LEVETIRACETAM IN RAT BRAIN MICRODIALYSATE D. Dogrukol-Aka, E. Senera, O. Tansel Korkmazb, Sukru Torunc, Lutfi Gencd and Nese Tuncelb a Anadolu University, Faculty of Pharmacy, Department of Analytical Chemistry, 26470 Eskişehir, Türkiye b Osmangazi University, Faculty of Medicine, Department of Physiology, 26480 Eskişehir, Türkiye c Anadolu University, Faculty of Health Science, 26470 Eskişehir, Türkiye d Anadolu University, Faculty of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, 26470 Eskişehir, Türkiye This is the first study to develope and describe a simple and rapid method of liquid chromatography-electrosprey tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) for the determination of levetiracetam in rat brain microdialysate samples. INTRODUCTION Levetiracetam (LVT) is a new antiepileptic drug used in the treatment of partial onset seizure in patient. For the determination of LVT in human plasma a few methods based on high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection, micro-emulsion electrokinetic chromatography with UV detection, gas chromatography (GC) or in combination with mass spectrometry (GC/MS) have been described in recent years. Less sensitive LCMS/MS methods were also reported for the determination of LVT in plasma1. The objective of this study is to develop and validate a high throughput LC-MS/MS method for accurate and more sensitive measurement of LVT in biological fluids especially rat brain microdialysate samples. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION LVT was investigated generated the prominent protonated molecular ion [M+H]+ in positive ion mode. It was successfully separated at 3.4 min and monitored MRM transition of m/z 126>69.2. The method was linear over the range of 0.139-1390 ng/mL with the correlation coefficients greater than 0.998 (r2) for three separate batches in Ringer’s solution. Precision and accuracy were determined by measuring the concentration of LVT in Ringer’s solution in six replicates of quality control standards at three different concentrations (1.39, 139 and 1390 ng/mL) for three separate batches. Intra-day precision was <2%, and calculated recovery was >93% in Ringer’s solution. For the inter-day studies precision was <4%, and calculated recovery was >96% in the Ringer’s solution. To demonstrate the applicability of the method, rat brain microdialysate samples were directly analyzed after administration an i.p. dose of LVT and collection of samples was performed at the different time points over 12 hours (Fig. 1-2). MATERIALS AND METHODS Fig. 1. MRM chromatograms of Ringer’s solution (top), LVT in microdialysate sample at 2h time point (middle) and QC sample (100 ng/mL LVT) (bottom) 30000 Concentration (ng/mL) Chemicals and reagents: LVT was purchased from SigmaAldrich Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). Water was purified using Milli-Q water device (Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA). All other chemicals and reagents were of analytical grade and solvents were of HPLC grade. Equipment: Agilent 1290 series LC system consisted of a solvent delivery system with binary pump, an autosampler, and column oven (Agilent Technologies, USA). The separation of LVT was successfully performed on Supelco Ascentis Express (100 mm x 2.1 mm, 2.7 µm) with programmed gradient elution consisting of 10 mM ammonium formate in water (A) and in 10 ammonium formate in 90 % (v/v) acetonitrile (B) as mobile phase components and delivered at a flow rate of 0.3 ml/min to a triple-quadruple mass spectrometer equipped with a jet stream electrosprey ionization source (6460 Trip-Quad, Agilent Technologies, USA). Injection volume was 2 µl. Data was analysed by using Mass Hunter programme. Microdialysis samples:Wistar rats were used to obtain brain microdialysate samples in the region of hippocampus by using a specific prob (PAES 3 mm membrane length with cut of 20000 D, CMA). LVT was administrated to rats at a LVT dose of 50 mg/kg by i.p.2. 25000 20000 15000 10000 5000 0 0 200 400 Time (min) 600 800 Fig. 2. The concentration time profiles in rat brain tissue after administration of 50 mg/kg of LVT to individual rats (n=5) CONCLUSIONS Rapid LC-MS/MS method for the quantitation of LVT in rat brain microdialysate samples was developed and validated. It was successfully applied to the analysis of rat brain microdialysate samples obtained from brain hippocampal region after i.p. LVT application and it was showed the concentration time profile of LVT in rat brain. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work was supported by the Scientific Research Projects Commission of Anadolu University (Project No 1301S009). The authors acknowledge the instrumental support of Anadolu University Medicinal Plants and Medicine Research Center (AUBIBAM). All animal experiments were performed in accordance with the principles of animal use and care approved by the ethical committee of the Medical Faculty of Osmangazi University (Approval File No. 04/2007) REFERENCES 1. Gou, T., Oswald L.M., Mendu D.R., Soldin S.J., Determination of levetiracetam in human plasma/serum/saliva by liquid chromatographyelectrosprey tandem mass spectrometry. Clinica Chimica Acta, 2007, 375, 115-118. 2. Clinckers R., Smolders I., Meurs A., Ebinger G., Michotte Y., Quantitative in vivo microdialysis study on the influence of multidrug transporters on the blood-brain barrier passage of oxcarbazepine: Concomitant use of hippocampal monoamines as pharmacodynamic markers for the anticonvulsant activity. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 2005, 314, 725-731.