Geometry-Q4-2015-16
advertisement

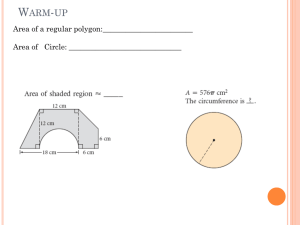
Instructional Map 4th Nine Weeks TN State Standards Essential Understandings Geometry Content & Tasks CLIP Connections Unit 6: Angles and Segments in Circles (6 days) G-C Circles Understand and apply theorems about circles G-C.A.2 Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. Include the relationship between central, inscribed, and circumscribed angles; inscribed angles on a diameter are right angles; the radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent where the radius intersects the circle. G-C.A.3 Construct the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle, and prove properties of angles for a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle. G-C Circles Understand and apply theorems about circles G-C.A.2 G-C.A.3 Construct a tangent line from a point outside a given circle to the circle. G-CO Congruence Make geometric constructions G.CO.D.12 Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; and constructing a line parallel to a given line through a point Subject to revision Lesson 10-4 – Inscribed Angles Identify and describe relationships involving inscribed angles. Prove properties of angles for a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle. Lesson 10-5 – Tangents Identify and describe relationships among tangents and radii. Identify and describe relationships among circumscribed angles and central angles. Construct a tangent line from a point outside a circle to the circle. Lesson 10-4 pp. 709-715 H.O.T. Problems p.715 #50 Compare and contrast inscribed angles and central angles of a circle. If they intercept the same arc, how are they related? Lesson 10-5 pp.718-725 H.O.T. Problems p.724 # 39 How many tangents can be drawn from a point outside a circle, from a point on a circle, and from a point inside a circle? Explain your reasoning. Tangent Lines and the Radius of a Circle Shelby County Schools 2015/2016 1 of 6 Instructional Map 4th Nine Weeks TN State Standards not on the line. G-CO Congruence Make geometric constructions G.CO.D.12 G.CO.D.13 Construct an equilateral triangle, a square, and a regular hexagon inscribed in a circle. G-C Circles Understand and apply theorems about circles G.C.A.3 G-C Circles Understand and apply theorems about circles G-C.A.2 G-C Circles Understand and apply theorems about circles G-C.A.2 Essential Understandings Extend Lesson 10-5 Geometry Lab: Inscribed and Circumscribed Circles Construct an equilateral triangle, a square, and a regular hexagon inscribed in a circle. Construct the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle Lesson 10-6 Secants, Tangents, and angle measures Find measures of angles form by lines intersecting on or inside a circle. Find measures of angles formed by lines intersecting outside the circle. Lesson 10-7 Special Segments in Circles Find measures of segments that intersect in the interior of a circle Find measures of segments that intersect in the exterior of a circle. Geometry Content & Tasks Lesson 10-5 p. 726 Use geometry software or graphing calculator such as TI-Nspire or the Cabri Jr. APP on the TI-84 to investigate. A regular compass and straight edge can also be used. CLIP Connections Why is the term “incenter” a good term for the intersection of the three angle bisectors? Explain your reasoning. Lesson 10-6 p. 727-735 Chords Secants and Tangents p.58 Lesson pp. 736-742 Chords Secants and Tangents p.58 H.O.T. Problems p. 741 #31 Describe the relationship among segments in a circle when two secants intersect inside a circle. Unit 6 (part 2): Arc Length, Sector Area, and Equations of Circles (8 days) G-C Circles Understand and apply theorems about circles G-C.A.2 G-C Circles Find arc length and areas of sectors of circles Subject to revision Lesson 10-2 – Measuring Angles and Arcs Derive and apply the formula for arc length. Derive the fact that the length of the arc intercepted by an angle is proportional to the radius. Define and apply radian measure. Lesson pp. 692-700 Circles and their Relationships among Central Angles, Arcs and Chords Investigating Angle Relationships in Circles H.O.T. Problems p.699 #62 Describe the three different types of arcs in a circle and the method for finding the measure of each one. Arc length and Area Sector p.85 Shelby County Schools 2015/2016 2 of 6 Instructional Map 4th Nine Weeks TN State Standards G.C.B.5 Derive using similarity the fact that the length of the arc intercepted by an angle is proportional to the radius, and define the radian measure of the angle as the constant of proportionality; derive the formula for the area of a sector. G-C Circles Find arc length and areas of sectors of circles G.C.B.5 G-GPE Expressing Geometric Properties with Equations Translate between the geometric description and the equation of a conic section G-GPE.A.1 Derive the equation of a circle of given center and radius using the Pythagorean Theorem; complete the square to find the center and radius of a circle given by an equation. Essential Understandings Lesson 11-3 – Areas of Circles Derive a formula for the area of a sector of a circle. Find the area of circles and sectors of circles Lesson 10-8 – Equations of Circles and Graphing Technology Lab 10.8 (using TI-Nspire) Derive the equation of a circle given the center and the radius. Complete the square to find the center and radius of a circle by an equation. Geometry Content & Tasks CLIP Connections Lesson 11-3 pp.782 - 788 Arc Length and Area of Sector Grain Storage Task H.O.T. Problems p.787 # 49 If the radius of a circle doubles, will the measure of a sector of that circle double? Will it double if the arc measure of that sector doubles? Lesson 10-8 pp.743 - 749 Equations of Circles 1 H.O.T. Problems p.748 # 40 Describe how the equation for a circle changes if the circle is translated a units to the right and b units down. Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically G.GPE.B.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1,√3) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0, 2). Subject to revision Shelby County Schools 2015/2016 3 of 6 Instructional Map 4th Nine Weeks TN State Standards Essential Understandings Geometry Content & Tasks CLIP Connections Unit 7 (part 2): Visualizing Solids ( 7 days) G-MG Modeling with Geometry Apply geometric concepts in modeling situations G-MG.A.1 Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects (e.g., modeling a tree trunk or a human torso as a cylinder).★ Lesson 12-1 – Representations of Three- Dimensional Figures Investigate cross sections of three-dimensional figures G-GMD Geometric Measurement and Dimension Visualize relationships between twodimensional and three-dimensional objects G-GMD.B.4 Identify the shapes of twodimensional cross- sections of three dimensional objects, and identify threedimensional objects generated by rotations of two-dimensional objects. Volumes of Cylinders, Cones, Pyramids, and Spheres G-MG Modeling with Geometry Apply geometric concepts in modeling situations G-MG.A.3 Apply geometric methods to solve design problems (e.g., designing an object or structure to satisfy physical constraints or minimize cost; working with typographic grid systems based on ratios).★ Lesson 12-2 – Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders G-MG Modeling with Geometry Apply geometric concepts in modeling situations G-MG.A.3 Lesson 12-3 – Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones Subject to revision Lesson pp. 823-828 Unit on Area, Perimeter, and Volume with multiple tasks Boxing Basketballs p.5 Great Pyramid p.13 Walter and Juanita’s Water Troughs p.17 Greenhouse p.23 Find the lateral area and surface area of prisms. Find the lateral area and surface area of cylinders. Find the lateral area and surface area of pyramids. Find the lateral area and surface area of cones. Lesson 12-2 pp.830-837 Cereal Box Project H.O.T. Problems p.836 #40 Compare and contrast finding the surface area of a prism and finding the surface area of a cylinder. Lesson 12-3 pp.838-846 H.O.T. Problems p.845 #41 Describe how to find the surface area of a regular polygonal pyramid with an ngon base, height h units and an apothem of a units. Shelby County Schools 2015/2016 4 of 6 Instructional Map 4th Nine Weeks TN State Standards G-MG Modeling with Geometry Apply geometric concepts in modeling situations G-MG.A.3 Essential Understandings Lesson 12-6 – Surface Areas of Spheres Geometry Content & Tasks Lesson 12-6 pp.864-871 CLIP Connections Describe the difference between the surface area of a sphere and the volume of a sphere. Find the surface area of a sphere Unit 5 (part 2): Trigonometry with All Triangles ( 4 days) *Optional Section – No CCSS Lesson 8-6 – The Law of Sines and Cosines Derive a trigonometric formula for the area of a triangle Prove and apply the Law of Sines Subject to revision Introduction – How Big is the Bermuda Triangle? H.O.T. Problems p.590 Prove and apply the Law of Cosines Shelby County Schools 2015/2016 5 of 6 RESOURCE TOOLBOX Textbook Resources ConnectED Site - Textbook and Resources Glencoe Video Lessons Hotmath - solutions to odd problems Comprehensive Geometry Help: Online Math Learning (Geometry) I LOVE MATH NCTM Illuminations New Jersey Center for Teaching & Learning (Geometry) Calculator Finding Your Way Around TI-83+ & TI-84+ (mathbits.com) Texas Instruments Calculator Activity Exchange Texas Instruments Math Nspired STEM Resources Casio Education for Teachers *Graphing Calculator Note: TI tutorials are available through Atomic Learning and also at the following link: Math Bits graphing calculator steps Some activities require calculator programs and/or applications. Use the following link to access FREE software for your MAC. This will enable your computer and TI Calculator to communicate: Free TI calculator downloads Subject to revision CCSS Common Core Standards - Mathematics Common Core Standards - Mathematics Appendix A TN Core CCSS Flip Book with Examples of each Standard Geometry Model Curriculum http://www.ccsstoolbox.org/ http://insidemathematics.org/index.php/high-school-geometry http://www.azed.gov/azcommoncore/mathstandards/hsmath/ http://learnzillion.com/common_core/math/hs http://www.livebinders.com/play/play/454480 https://www.livebinders.com/play/play?id=464831 http://www.livebinders.com/play/play?id=571735 North Carolina – Unpacking Common Core http://thegeometryteacher.wordpress.com/the-geometry-course/ http://mathtermind.blogspot.com/2012/07/common-coregeometry.html Utah Electronic School - Geometry Ohio Common Core Resources Chicago Public Schools Framework and Tasks Mathy McMatherson Blog - Geometry in Common Core Videos Math TV Videos The Teaching Channel Teacher Tube Khan Academy Videos (Geometry) Interactive Manipulatives GeoGebra – Free software for dynamic math and science learning NCTM Core Math Tools http://www.keycurriculum.com/products/sketchpad (Not free) Any activity using Geometer’s Sketchpad can also be done with any software that allows construction of figures and measurement, such as Cabri, Cabri Jr. on the TI-83 or 84 Plus, TI-92 Plus, or TI-Nspire CLIP Resources Glencoe Reading & Writing in the Mathematics Classroom Graphic Organizers (9-12) (teachervision.com) Shelby County Schools 2015/2016 6 of 6