Unit 10 - Elementary Mathematics!
advertisement

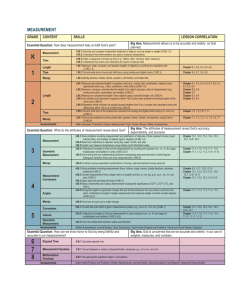
2nd Unit of Study 9: Length in Metric Measure Projected Time Allotment: 12 Days Global Concept Guides: Understanding Centimeters and Meters, Estimating Metric Length, Compare Metric Length Prior Learning: MAFS.1.MD.1.1, MAFS.1.MD.1.a Progressions Document Link Sample Show What You Know Task: Use the Go Math Ch. 9 Show What You Know TE p. 430 or the Diagnostic Interview Task TE p. 430 Comments: Mathematics Florida Standards for Mathematical Content: Measure and estimate lengths in standard units. MAFS.2.MD.1.1 Measure the length of an object by selecting and using appropriate tools such as rulers, yardsticks, meter sticks, and measuring tapes. MAFS.2.MD.1.2 Describe the inverse relationship between the size of a unit and number of units needed to measure a given object. MAFS.2.MD.1.3 Estimate lengths using units of inches, feet, centimeters, and meters. Relate addition and subtraction to length. MAFS.2.MD.1.4 Measure to determine how much longer one object is than another expressing the length difference in terms of a standard length unit. MAFS.2.MD.2.5 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve word problems involving lengths that are given in the same units, e.g., by using drawings (such as drawing or rulers) and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. MAFS.2.MD.2.6 Represent whole numbers as lengths from 0 on a number line diagram with equally spaced points corresponding to the numbers 0, 1, 2, …, and represent whole-number sums and differences within 100 on a number line diagram. Represent and interpret data. MFS.2.MD.4.9 Generate measurement data by measuring lengths of several objects to the nearest whole unit, or by making repeated measurements of the same object. Show the measurements by making a line plot, where the horizontal scale is marked off in whole-number units. This parent flyer and included video can be utilized by both you and parents to build content knowledge and understanding of the strategies highlighted in this unit. Notes on Assessment: Unit 9 Assessment – Go Math Ch. 9 Please ensure that you print this test at FULL scale. Do NOT change the margins. Prior to administering to students, measure the objects to ensure that that the measurements are correct. See common performance task link below. Unpacking the Standards for this Unit: Students will build upon their knowledge of customary units of measurement from Ch. 8. Students will apply their knowledge of customary units of measurement to measure lengths using metric units of measurement (centimeters and meters). Students will measure objects using two units of different lengths such as centimeters and meters. This is a difficult concept for young children, and will require numerous experiences for students to predict, measure, and discuss outcomes. As students estimate, they must consider the size of the metric unit. Estimation creates a problem to be solved rather than a task to be completed. Common Performance Task for this Unit: Shoes: In this performance task students will measure the length of shoes and determine the difference in lengths. Students will also use a number line to determine the different lengths of shoes. Students will be expected to explain their thinking with written responses. Click here for the performance task and rubric. Future learning: Students need to be comfortable with metric units of measure. This will enable them, in third grade, to measure accurately to the nearest centimeter and meter. They will use their knowledge of metric units when they are measuring lengths to determine perimeter and area. Global Concept 1 of 3 for this Unit of Study: Projected Time Allotment: 4 Days Understanding Centimeters and Meters Sample Essential Questions: Day 1: How do you use unit cubes to measure the lengths of objects? Day 2: How do you use a centimeter ruler to measure lengths? Day 3: How is measuring in meters different from measuring in centimeters? Day 4: How do you know if you should measure in centimeters or meters? Related Unit 9 Assessment: Go Math Ch. 9: # 1, 2, 3, 9, 10, 12, 18, 19 2nd Instructional Resources Manipulatives: Centimeter cubes to measure the length of objects and build a concrete understanding of the size of a centimeter Centimeter ruler to measure the length of objects Meter stick to measure the length of objects Lesson Ideas: Go Math Lesson 9.1-Essentials: Reteach Tier 1 TE p. 433B, Listen and Draw TE p. 433 (use the guiding questions in the margin of the TE), Model and Draw TE p. 434 (use guiding questions in TE margin), On your Own TE p. 435 (have students select 2 questions to complete independently), Problem Solving TE p. 436 Go Math Lesson 9.3-Essentials: Reteach Tier 1 TE p. 441B, Model and Draw TE p. 442 (use guiding questions in TE margin), On your Own TE p.443 (have students select 2 questions to complete independently) Problem Solving TE p. 444 Go Math Lesson 9.5-Essentials: Reteach Tier 1 TE p. 449B, Engage TE p. 449, Listen and Draw TE p. 449 (use guiding questions in TE margin), Problem Solving TE p. 452 Measurement record chart-Students can record their measurements (using centimeter cubes) of objects around the classroom (Option for Day 1- Use in place of Lesson 9.1) Centimeter record chart-Students can record their measurements (using a centimeter ruler) of objects around the classroom. Appropriate measurement-Give students specific objects to measure and they would determine if they should use cm or m. For more information about integrating the content within this GCG click here for the PowerPoint. Sample HOT Questions: Use these to facilitate student discussions. (SMP 1, 3) Is it more efficient to measure using one unit cube or several unit cubes? Explain your thinking. How would your measurement change if you left space between the cubes? How could you measure the length of the teacher’s desk using only a centimeter ruler? Can you use a meter stick to measure the width of your math book? Explain your thinking. Is there ever a time where you would measure the length of an object using both centimeters and meters? If so give an example. How is using a ruler measuring centimeters similar to measuring inches? How is it different? What would happen if you didn’t start at 0? Adam measured his string and said 9 inches. Lesley measured her string and said it was much longer than Adam’s because it was 23 centimeters. Is Lesley correct? Students are better able to… Because as teachers we… Select the most appropriate unit of measurement Are providing students hands-on opportunities to to measure lengths of objects in the classroom measure objects (SMP 4, 5). (SMP 5). Provide hands-on opportunities for students to Precisely measure a variety of objects using discover the relationship between centimeters and centimeters and meters (SMP 4, 6). meters (SMP 4, 7). Understand the relative sizes and relationship Facilitate discussions about selecting the between centimeters and meters (100cm is the appropriate units and tools to use when measuring same as 1m) (SMP 7). (SMP 3). For more info on SMP’s click here. Global Concept 2 of 3 for this Unit of Study: Estimating Metric Projected Time Allotment: 3 Days Length Sample Essential Questions: Day 1: How do you use known lengths to estimate unknown lengths? Day 2: How do you estimate the lengths of objects in meters? Day 3: How do you know if you should estimate length using centimeters or meters? Related Unit 9 Assessment: Go Math Ch. 9: #4, 7, 8, 13, 17 2nd Instructional Resources Manipulatives: Centimeter cubes to check their estimated measurements in centimeters. Centimeter ruler to check the estimated measurements they make. Meter stick to check the estimated measurements they make. Ten rods are approximately 10cm long and can be used as a “known” length to estimate the length of unknown objects. Lesson Ideas: Go Math Lesson 9.2-Essentials: Reteach Tier 1 TE p. 437B, Listen and Draw TE p. 437 (use the guiding questions in the margin) Model and Draw TE p. 438 (use the guiding questions in the margin), Problem Solving TE p. 440 Go Math Lesson 9.6-Essentials: Reteach Tier 1 TE p. 453B, Listen and Draw TE p. 453 (use the guiding questions in the margin) Model and Draw TE p. 454 (Refrain from using the student page and focus on the T.E. guiding questions), Problem Solving TE p. 456 Estimate length in centimeters chart-This chart can be used to help students gain proficiency when estimating lengths in centimeters. Estimating Lengths Students can solve these problems on Day 1 Estimate length in meters chart-This chart can be used to help students gain proficiency when estimating lengths in meters. Let me Refer You To-Lesson from “Voyages” that helps students use referents to make better estimates. For more information about integrating the content within this GCG click here for the PowerPoint. Sample HOT Questions: Use these to facilitate student discussions. (SMP 1, 3) Sammy said that 100 meters is the same as 1 centimeter. She estimated the length of her math book to be 12 meters long. Do you agree or disagree with Sammy’s estimate? Please justify your reasoning. Ronda and Kura are arguing over the best way to estimate the height of their younger sister, who is in kindergarten. Ronda thinks they should use centimeters and Kura thinks they should use meters. Who do you think is correct and why? Sharon wants to measure her pencil using a meter stick. Do you think that Sharon has selected a good tool for this measurement? Explain why you agree or disagree with her. Students are better able to… Because as teachers we… Estimate the length of objects because they have Provide students ample opportunities to estimate begun to develop an understanding of the lengths and distances and confirm their accuracy structure of centimeters and meters (SMP 7). with actual measurements (SMP 7). Choose the appropriate unit of measurement to Provide opportunities for students to explore the use when estimating based on the relationship of relationship between the size of the unit and the the size of the unit to the length being measured size of the object being measured (SMP 5). (SMP 5). For more info on SMP’s click here. Global Concept 3 of 3 for this Unit of Study: Compare Metric Projected Time Allotment: 3 Days Length Sample Essential Questions: Day 1: How can measurement tools help me solve problems involving length? Day 2: How can using a number line help when solving problems about length? Day 3: How do you find the difference between the lengths of two objects? Related Unit 9 Assessment: Go Math Ch. 9: #5, 6, 11, 14, 15, 16, 20, 21 2nd Instructional Resources Manipulatives: Centimeter ruler to create a referent or to measure 2 or more lengths to compare the lengths Meter stick to create a referent or to measure 2 or more lengths to compare the lengths Lesson Ideas: Go Math Lesson 9.4-Essentials: Access Prior Knowledge TE p. 445, Try Another Problem TE p. 446 (use the guiding questions in the margin), Share and Show TE p. 447 Go Math Lesson 9.7-Essentials: Access Prior Knowledge TE p. 457, Listen and Draw TE p. 457 (use the guiding questions in the margin),Model and Draw TE p. 458 (use the guiding questions in the margin), Problem Solving TE p. 460 Problem Solving Metric-Word problems to draw a quick picture to solve problems about metric length on Day 1 Problem Solving Scenarios- Students can solve these problems on Day 3 Estimate Measure-Word problems to estimate answers to help students check reasonableness of their answers For more information about integrating the content within this GCG click here for the PowerPoint. Sample HOT Questions: Use these to facilitate student discussions. (SMP 1, 3) What real-world scenarios would require you to compare the lengths of objects? Cynthia estimated her pencil was 10 meters long. When she measured, she thought her estimate made sense and her answer was reasonable. Do you agree with Cynthia’s estimate and answer? What mistake might she have made? What strategy makes the most sense to use when comparing lengths and why? Students are better able to… Because as teachers we… Use correct vocabulary when comparing and Use precise language such as centimeters, meters, estimating lengths to check for the estimate, greater than, less than, and equal to reasonableness of their answers (SMP 6). when discussing measurement with our students (SMP 6). Use a variety of tools such as centimeter rulers, meter sticks, number lines, and quick pictures to Provide rich tasks involving the measurement of solve word problems involving measurement real-world objects rather than relying on less (SMP 5). authentic, book-based measurement tasks (SMP 4). For more info on SMP’s click here. Have centimeter rulers and meter sticks readily available for students to measure with (SMP 5). Model how to use number lines and quick pictures to help with measurement (SMP 5).