Measurements - Adventist Education
advertisement

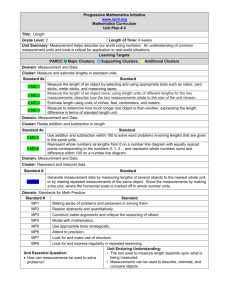
MEASUREMENT GRADE CONTENT SKILLS Essential Question: How does measurement help us fulfill God’s plan? K K.M.1 Describe and compare measurable attributes of objects, such as length or weight (K.MD.1,2) K.M.2 Understand that thermometers are used to measure temperature Time Time K.M.3 Order a sequence of events by time (e.g., before, after, morning, night, seasons) K.M.4 Understand that clocks and calendars are used to measure time 1.M.1 Measure, order, compare, and express lengths of objects by counting non-standard units (1.MD.1,2) 1.M.2 Tell and write time in hours and half-hours using analog and digital clocks (1.MD.3) Money 1.M.3 Identify pennies, nickels, dimes, quarters, half-dollars, and dollar bills Length 2 Time Money Assessments Measurement Money Measurement/ Conversion 4 Angles 5 3.M.1 Solve problems involving measurement and estimation of intervals of time (nearest minute), liquid volume (liter), and masses of objects (gram, kilogram) (3.MD.1,2) 3.M.2 Read and understand a calendar using day, week, month, and year 3.M.3 Explain and measure temperature using Celsius and Fahrenheit scales 3.M.4 Understand concepts of area and its measurement by counting unit squares (cm , m , in , ft ); apply multiplication and addition to area (3.MD.5,6,7) 3.M.5 Solve real-world and mathematical problems recognizing area and perimeter of plane figures; distinguish between linear and area measurements (3.MD.8) 2 2 4.M.1 Solve problems involving measurement (time, volume, mass, money, simple fractions, decimals, distance) (4.MD.2) 4.M.2 Convert measurement from a larger unit to a smaller unit (km, m, cm; kg, g; lb, oz; L, mL; hr, min, sec) (4.MD.1) 4.M.3 Apply area and perimeter formulas (4.MD.3) 4.M.4 Read a Fahrenheit and Celsius thermometer knowing the significance of 32°F, 212°F, 0°C, and 100°C 4.M.5 Recognize angles as geometric shapes that are formed wherever two rays share a common end point; understand concepts of angle measurement and measure angles in whole-number degrees (4.MD.5,6,7) 4.M.6 Know how to count up to make change Conversion 5.M.1 Convert like units within a given measurement system (e.g., cm to m, m to cm) (5.MD.1) Volume 5.M.2 Understand concepts of volume measurement in cubic measure (cm , in , ft ) and apply to multiplication and addition (5.MD.3,4,5) 3 3 3 Chapter 7.8, 7.9,7.10, 7.11 Chapter 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6, 7.7 Chapter 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.4, 10.5, 10.7, 10.8, 10.9 Chapter 11.4, 11.5, 11.6, 11.7, 11.8 Chapter 11.1, 11.2, 11.3, 11.9, 11.10 Chapter 9.5, 12.7, 12.9, 12.10 Chapter 12.1, 12.2, 12.3, 12.4, 12.6, 12.7, 12.8, 12.11 Chapter 13.1, 13.2, 13.3, 13.4,13.5 Chapter 11.1, 11.2, 11.3, 11.4, 11.5 Chapter 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.4, 10.5, 10.6, 10.7 Chapter 11.5, 11.6, 11.7, 11.8, 11.9, 11.10, 11.11, 11.12 5.M.3 Know the relationship between radius and diameter Written Assessments; Journal Entries; Class Discussions; Open-ended Projects and Problems; Visual and Virtual Models; Diagrams Big Idea: God is concerned that we be accurate and orderly in our use of weights, measures, and numbers. Elapsed Time 6.M.1 Calculate elapsed time Measurement Systems 7.M.1 Convert between a variety of standard/metric measures (e.g., in to cm, cm to in) Mathematical Precision Assessments Chapter 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.7, 8.8, 9.1, 9.2, 9.3, 9.6 Chapter 8.6, 9.5 Chapter 9.7 Chapter 8.5, 9.4 Chapter 8.5, 9.4 3.M.6 Construct various equivalent combinations of money; add and subtract money amounts Essential Question: How can we show honor to God by being faithful and accurate in our measurements? 6 7 8 2 Money Geometric Measurement Assessments Chapter 9.6, 9.7, 9.8, 9.9 Big Idea: The attributes of measurement reveal God’s accuracy, dependability, and precision. 2 Geometric Measurement Chapter 9.1, 9.2, 9.3, 9.4, 9.5 2.M.1 Measure and estimate lengths in standard units (e.g., inches, feet, centimeters, meters) using appropriate tools (e.g., rulers, yardsticks, meter sticks) (2.MD.1,3) 2.M.2 Measure, compare, and describe the length of an object using two units of measurement (e.g, inches and yards, centimeters and meters) (2.MD.2) 2.M.3 Measure to compare the length of two objects using a standard length unit (2.MD.4) 2.M.4 Use addition and subtraction equations within 100 to solve word problems involving lengths of the same unit (2.MD.5) 2.M.5 Represent whole numbers as equally spaced lengths from 0 on a number line; represent sums and differences within 100 on a number line (2.MD.6) 2.M.6 Tell and write time to the nearest five minutes from analog and digital clocks using a.m. and p.m. (2.MD.7) 2.M.7 Solve word problems involving dollar bills, quarters, dimes, nickels, and pennies, using $ and ¢ (2.MD.8) Math Interviews; Checklists; Graphs; Measurement Tools, Clocks, Money; Written Assessments Essential Question: What do the attributes of measurement reveal about God? 3 Big Idea: Measurement allows us to be accurate and orderly as God planned. Measurement Length 1 LESSON CORRELATION 8.M.1 Use appropriate significant digits in calculations Open-ended Projects and Problems; Written Assessments; Journal Entries; Class Discussions; Oral Reports; Visual and Virtual Models