everyday math pacing guide 2012
advertisement

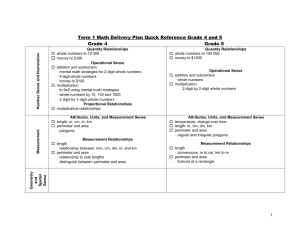
EVERYDAY MATH PACING GUIDE 2012-2013 THIRD GRADE Implement 5 minutes of fact fluency everyday. o Netbooks o EM games o Math Facts in a Flash o Holey cards o teacher games Consult the Curriculum Framework for specific SOL topics and information. Display Word Walls from DOE Resources. Include elapsed time in daily routine. Other topics to include on flex days: o adding and subtracting fractions with like denominators o comparing fractions o subtraction with regrouping o rounding algorithm o multi-step problem solving Consult resources such as (other resources may be used as well for flex days): o Enhanced Scope and Sequence o AIMS o VA Master Everyday Math correlation notebook which can be accessed on E-planner o Exam View o Interactive Achievement Everyday Math Rubric Conversion of RSA’s o 4 = 100% o 3 = 90% o 2 = 80% o 1 = 70% o 0 = 50% Third Grade Flex Calendar THIRD GRADE PACING GUIDE – EVERYDAY MATHEMATICS Week Dates 1 Aug. 27-31 2 Sept. 3-7 Description Review types & uses of numbers Introduce the Math Message routine and review patterns on number grids Introduce Student Reference Book and establish a set of work rules/routine Review telling time, measuring, lengths, and calculators and Identify & draw three dimensional shapes Review data concepts and find data landmarks & use graphs to draw conclusions Review the idea that there are many names for numbers Introduce the vocabulary of chance Identify number grid patterns & use them to find differences between pairs of numbers Review calculator skills (adding, subtracting, and skip counting forward and backward) and provide practice for place-value Review money amounts with coins and write dollars-and-cents notation; compare money amounts Solve problems involving money, determine the need for an exact answer and estimation, and practice estimation skills Explore number patterns Review telling time and finding elapsed time and introduce the Length-of-Day project Review fact & number families and review the inverse relationship between addition and subtraction Review ways basic addition & subtraction are used for solving larger problems Review and solve “What’s My Rule?” problems Use parts-and-total diagrams & solve number stories 3 10-14 4 17-21 5 24-28 Lessons 1.1-1.4 1.5-1.7 1.8-1.11 1.12-1.14 2.1-2.4 6 Oct. 1-5 7 8-12 8 15-19 9 22-26 10 Oct. 29Nov. 2 11 5-9 12 12-16 13 19-23 Use change diagrams to solve number stories Use comparison diagrams to solve number stories Make ballpark estimates and model & practice partial-sums algorithm for 2- and 3digit numbers Review ballpark estimates and review counting-up & trade-first algorithms Review ballpark estimates and review counting-up & trade-first algorithms Solve number stories with 3 or more addends Discuss the need for standard units of measure and create a unit of length and measure with it Measure line segments to the nearest inch, ½ inch, ¼ inch, ½ centimeter, and millimeter Review U.S. customary and metric units of length and estimate and measure lengths to the nearest inch & centimeter Review polygons & concepts of perimeter Collect, tabulate, and interpret experimental data, make rectangles with given perimeters, relate tiling to area, and construct triangles using given lengths & find their perimeters Develop the concept of area, demonstrate the measure of area using foot and yard squares, and find area by counting squares Develop the concept of area by measuring with identical squares and demonstrate how to calculate area of rectangles using number models Relate circumference & diameter through the about 3 times rule Review multiplication and equal groups and provide opportunities to solve and write number stores involving equal groups Use arrays, multiplication/division diagrams, number models to represent and solve multiplication number stories Review division as equal sharing and equal grouping Model division number stories with arrays, mult/div diagrams, and number models Discuss multiplications facts and importance of fact power and review facts shortcuts Review fact families and mult/div facts table Practice mult/div facts Estimate the number of dots in a large array, solve problems involving factors of whole numbers and practice mult. Facts Introduce the use of a map scale to estimate distances Guide students to develop intuition about equally likely events 2.5-2.8 2.8-2.10 3.1-3.3 3.4-3.7 3.8-4.1 4.2-4.4 4.5-4.8 4.9-4.10 14 26-30 15 Dec. 3-7 16 10-14 17 17-21 18 Jan. 2-4 19 7-11 20 14-18 21 21-25 22 Jan. 28Feb. 1 Review place-value through ten-thousands Practice reading, writing, comparing, and ordering numbers less than 100,000 Extend place-value to millions and read and write numbers through millions Read, write, and compare large numbers and express relationships as differences and ratios Develop a sense of very large numbers Count base-10 blocks, identify polygons, and compare perimeters and areas Model decimals with base-10 blocks and review decimals with money Model tenths and hundredths with base-10 blocks and model exchanges between tenths and hundredths Demonstrate the use of decimal notation for metric measures and the conversion of centimeters to meters Introduce thousandths by revisiting millimeters and provide opportunities to interpret data from a map Provide practice for decimal place value to thousandths Analyze data from the sunrise-sunset routine and demonstrate how to make and read a line graph Review line segments and introduce rays and lines Model and draw polygons, parallel and intersecting line segments, rays and lines Use angles to record rotations Explore various types of triangles Explore various types of quadrilaterals Review the characteristics of polygons, emphasizing regular polygons Draw angles as records of rotations Measure angles Review symmetry and explore properties of symmetric shapes Explore the concept of congruence, draw line segments, and practice naming decimals Review 3-dimensional shapes and identify bases of pyramids and prisms Explore the characteristics of prisms Review square-number facts, multiplication, and division patterns Determine which multiplication facts they still need to learn Practice multiplication and division facts Introduce parentheses in number models Express numbers as sums of products using number models that contain parentheses Multiply 1-digit numbers by multiples of 10, 100, and 1000 and divide such multiples by 1-digit numbers 4.11-5.3 5.4-5.7 5.8-5.11 5.12-6.2 6.3-6.4 6.5-6.7 6.8-6.11 6.12-7.1 7.2-7.5 23 4-8 24 11-15 25 18-22 26 Feb. 25Mar. 1 27 4-8 28 11-15 29 18-22 30 Apr. 1-5 31 8-12 32 15-19 Determine when an estimate is appropriate and practice making estimates Multiply multiples of 10 by multiples of 10 Explore similar polygons, solve ratio problems, and explore geometric configurations Use fractions to name a of b equal parts Make predictions based on outcomes and construct situations that meet given conditions Explore fractional relationships, spatial relationships, and combinations Introduce the number line as a model for fractions Find equivalent fractions Compare fractions using region models Demonstrate naming quantities greater than 1 with fractions and mixed numbers Solve number stories involving fractions Multiply and divide with multiples of 10,100, and 1000 Use mental math to multiply 1-digit numbers by multi-digit numbers Model multiplication with base-10 blocks, explore area relationships, and find fractions of fractions Multiply 1-digit numbers by multi-digit numbers using a partial-products algorithm Multiply using mental math and the partial-products algorithm Identify whole number factors of whole numbers Share whole-dollar amounts equally Explore computational strategies for division and interpret remainders Introduce the lattice method of multiplication Explore 2-digit multiplication, number patterns, and the rigidity of triangles Extend the partial-products method to products of 2-digit numbers and 2-digit multiples of 10 Extend the partial-products algorithm to products of any two 2-digit numbers Investigate positive and negative numbers Review of units, tools, and measuring length in U.S. customary and metric systems Explore the volume of rectangular prisms Review of metric and U.S. customary units of weight, examine different kinds of scales, and read weights on scales Order objects by volume, building rectangular prisms having the same volume but different dimensions, and measuring weight using various scales Explore the concept of capacity and demonstrate equivalencies between measures of capacity Introduce the mean of a set of data and review median of a set of data Calculate the mean of a set of data and review median Introduce the memory keys on a calculator Make frequency tables and find median, mean and mode of data sets 7.6-7.9 7.10-8.3 8.4-8.6 8.7-9.1 9.2-9.4 9.5-9.8 9.9-9.12 9.13-10.1 10.2-10.5 10.6-10.9 33 22-26 34 Apr. 29-May 3 35-36 Introduce plotting coordinates on coordinate grids Read and interpret line and bar graphs Organize, graph, and interpret data Collect and interpret data from spinner experiments with outcomes that are equally likely and not equally likely Represent the likelihood of outcomes with visual models Organize and analyze survey data, predict outcomes and estimate the make-up of populations of people and objects SOL Review & Test 10.10-11.2 11.3-11.6