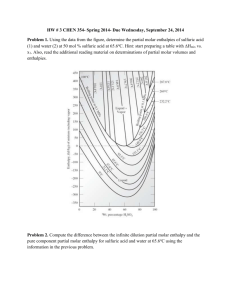
Molar mass indicates the total of all of the masses of the elements
advertisement

Molar mass indicates the total of all of the masses of the elements that make up a compound. The molar mass indicates the number of grams per one mole of that compound. Knowing the grams per mole allows chemists to convert a compound from moles into grams. Instructions 1. 2. 3. Look up the atomic mass of all of the elements in the compound using the periodic table. For instance, note that on a periodic table, the atomic weight of carbon equals 12.01 grams and oxygen's atomic weight equals 16.00 grams for the compound of CO2. Note the number of each element in the compound and multiply each of the atomic weight by the number of atoms of that element in the compound. For example, CO2 contains one carbon and two oxygen atoms. Multiply carbon's atomic weight (12.01 grams) by the number of carbon atoms in the compound (1) to find: 1 x 12.01 = 12.01 grams. Repeat the process with oxygen to find: 2 x 16.00 = 32.00 grams. Add all of the weights of the elements in the compound together to find the molar mass. For the example, add 12.01 + 32.00 = 44.01 grams/mole (g/mol) for the molar mass of CO2. Example Name sulfur dioxide Dinitrogen dioxide Formula SO2 N2O2 Name 1. sulfuric acid 2. sodium chloride 3. glucose 4. 5. H2SO4 C6H12O6 chlorine dioxide PCl5 carbon monoxide 8. 9. Formula CCl4 6. 7. Molar Mass 64.07 g/mol 60.00 g/mol BaCO3 silver bicarbonate 10. Cl2 11. helium 12. iron(III) bicarbonate 13. 14. sodium hydroxide NH4ClO4 Name iron III oxide ammonium nitride Formula Fe2O3 (NH4)3N Molar Mass Molar Mass 159.70 g/mol 68.12 g/mol Name 15. hydrochloric acid Formula HCl 16. barium bromide 17. NO2 18. ammonia 19. CS2 20. hydrogen 21. SiO2 22. tin(II) chloride 23. Ba(OH)2 24. iodine 25. Ag2S 26. magnesium hydroxide 27. Zn3(PO4)2 28. ammonium nitrate 29. O2 30. potassium iodide 31. KNO3 32. hydrogen peroxide 33. F2 34. sodium acetate 35. N2 36. ammonium phosphate 37. Br2 38. zinc sulfite 39. 40. dihydrogen monoxide CaI2 Molar Mass Answer Key Name Formula sulfur dioxide Dinitrogen dioxide Name SO2 N2O2 Formula Molar Mass 64.07 g/mol 60.00 g/mol Molar Mass Name Name Formula iron III oxide ammonium nitride Formula Molar Mass Molar Mass 159.70 g/mol 68.12 g/mol Fe2O3 (NH4)3N Name Formula Molar Mass sulfuric acid H2SO4 98.09 g/mol hydrochloric acid HCl 36.46 g/mol oxygen O2 32.00 g/mol sodium chloride NaCl 58.44 g/mol barium bromide BaBr2 297.13 g/mol potassium iodide KI 165.99 g/mol glucose C6H12O6 180.18 g/mol nitrogen dioxide NO2 46.00 g/mol potassium nitrate KNO3 101.09 g/mol carbon tetrachloride CCl4 153.81 g/mol ammonia NH3 17.03 g/mol hydrogen peroxide H2O2 34.02 g/mol chlorine dioxide ClO2 67.45 g/mol carbon disulfide CS2 78.15 g/mol fluorine F2 38.00 g/mol phosphorous pentachloride carbon monoxide PCl5 208.22 g/mol hydrogen H2 2.02 g/mol sodium acetate NaC2H3O2 82.04 g/mol CO 28.01g/mol silicon dioxide SiO2 60.09 g/mol nitrogen N2 28.00 g/mol barium carbonate BaCO3 197.34g/mol tin(II) chloride SnCl2 189.61 g/mol (NH4)3PO4 149.09 g/mol silver bicarbonate AgHCO3 168.89 g/mol barium hydroxide Ba(OH)2 175.35 g/mol ammonium phosphate bromine Br2 159.80 g/mol chlorine Cl2 70.09 g/mol iodine I2 253.80 g/mol zinc sulfite ZnSO3 145.48g/mol helium He 4.00 g/mol silver sulfide Ag2S 247.81 g/mol calcium iodide CaI2 293.88 g/mol iron(III) bicarbonate Fe2(CO3)3 291.70 g/mol magnesium hydroxide Mg(OH)2 58.33 g/mol dihydrogen monoxide H2O 18.02 g/mol ammonium perchlorate sodium hydroxide NH4ClO4 117.49 g/mol zinc phosphate Zn3(PO4)2 386.17 g/mol NaOH 40.00 g/mol ammonium nitrate NH4NO3 80.04 g/mol