form 3 food chain and wbs2012
advertisement

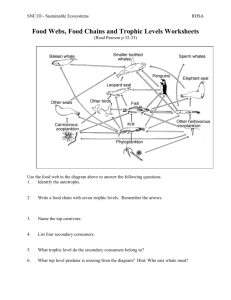
Producer – makes its own food from simple inorganic substances e.g. plants and some bacteria Consumer – relies on eating other organisms for food e.g. herbivores, carnivores, omnivores detrivores and decomposers. Herbivores –eat only plants and so have teeth incisors, premolars and molars e.g. grasshopper and cow Carnivores – are meat eaters and have incisors, enlarged carnassials teeth (canines) e.g. dogs and cats Omnivore – eat both meat and plant matter thus have incisors, canines, premolars and molars e.g. man Detrivores – feed on the dead e.g. maggots and vultures Decomposers – breakdown dead organic matter and waste recycling minerals e.g. nitrogen used in protein synthesis Trophic level – the level at which an organism feeds e.g. trophic level one is occupied by organisms that produce their own food Primary consumers – are organisms that occupy trophic level 2 and feed only on plant or producers of trophic level one Arrows of a food chain or web point from food source to the consumer maize birds Energy flows in one direction from food to next consumer while minerals are recycled Energy is lost 90% between trophic levels by feeding, respiration, digestion, excretion and heat. Since only 10% of the energy available at each trophic/feeding level is passed food chains have an average limited length of 5 e.g. plant caterpillar wasp bird hawk Food web – this is formed by a group of interlinked food chains, that is, at some point a food chain is linked to another by a common prey or predator. 1. Create a fully labelled food web using the following data organism Aphid (insects), rabbits and snails Toad Shrew (small rodent) Snake owl What’s for lunch plant aphids Aphids and snails Rabbits, toads and shrews Snake and shrew 2. Create 6 food chains that can be food in the food web