Review PAP Pre-Calculus Final Exam 2015
advertisement

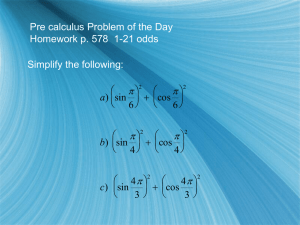
Review PAP Pre-Calculus Final Exam 2015 1. Domain & range of basic trig functions State the domain and range for the following functions. Domain Range Sin(x) Cos(x) Tan(x) Cot(x) Sec(x) Csc (x) 2.Graph and describe the function below a. f(x)=cos(x-𝜋) b. f(x)=-cos(x+𝜋) PAP PreCal Spring Final Exam Review 1 c. f(x)= 2sin(2x) 𝑥 d. f(x)=2sin( ) 2 𝜋 e. f(x)=-2sin(2x− 2 ) PAP PreCal Spring Final Exam Review 2 3. Name the equation of following graph X axis: Tick Unit is 𝜋 4 Y axis Tick Unit is 0.5 a.__________________________________________ X axis: Tick Unit is 𝜋 4 Y axis Tick Unit is 0.5 b.__________________________________________ X axis: Tick Unit is 𝜋 4 Y axis Tick Unit is 0.5 c.________________________________ PAP PreCal Spring Final Exam Review 3 X axis: Tick Unit is 𝜋 4 Y axis Tick Unit is 0.5 d.________________________________________ X axis: Tick Unit is 𝜋 4 Y axis Tick Unit is 0.5 e.______________________________________ X axis: Tick Unit is 𝜋 4 Y axis Tick Unit is 0.5 f.____________________________________ PAP PreCal Spring Final Exam Review 4 4. Given the graph of y=f(x) below, graph and describe the following transformation X axis: Tick Unit is 1 Y axis Tick Unit is 1 a.f(x)= -f(x) b. f(x)= f(-x) c. f(x)= 2f(x+2) d. f(x)= f(x)+2 e. f(x)= -f(2x)-2 f. f(x)= -2f(2-x)+2 1 2 PAP PreCal Spring Final Exam Review 5 5. Find the values of the following problems if the graphs of f(x) and g(x) is given below? a. f(g(4))= ? b. f(g(2))= ? c. g(f(1))= ? d. g(f(-1))= ? e. g(f(0))= ? 6. Let f ( x) 2 x 3 ; g ( x) x 2 1; h( x) 1 ; k(x)= 2x+1 ; j(x)=ln(x)+1 x a. Find f◦g, g◦f, h◦f, g(h(x)), g(g(x)) b. Find the domain of f◦g, h◦g, h(f(x)) c. Find the inverse of given functions above 7. Describe the following functions ( ex: domain, range , asymptotes, symmetry, even/ odd functions, one to one functions etc.) 𝑥 a. f(x)= ( ) 𝑙𝑜𝑔2𝑥−1 e. g(x)= 𝑥 3 −27 𝑥−3 𝑥+1 b. f(x)= ( ) 𝑙𝑜𝑔3𝑥−1 4𝑥−4 g. g(x)= 𝑥 3 −𝑥2 −4𝑥+4 c. f(x)=−𝑒 −𝑥 +5 h. g(x)= sin(x) 1 d. f(x)= 𝑥 2 g. g(x)= cos(x) PAP PreCal Spring Final Exam Review 6 Establish trig identities I. Reciprocal Identities 1 csc 1 B) cos sec 1 C) tan cot A) sin II. Quotient Identities 1 sin 1 E) sec cos 1 F) cot tan D) csc III. Pythagorean Identities sin cos cos B) cot sin A) sin 2 cos2 1 A) tan B) tan 2 1 sec 2 C) cot 2 1 csc 2 Guidelines for Verifying Trig Identities A. B. C. D. E. F. Begin with the most complicated side Work on one side only Rewrite sums or differences of quotients as one single quotient Rewrite in terms of sine and cosine only Factor ( GCF or Difference of Squares) Multiply ( Foil or Distributive Property) 8. Verify the following Trig Identities a. csc sin sin 2 cos2 c. csc cot csc cot 1 e. csc x cot x sin x 1 cos x b. sin cot tan sec d. csc 4 csc 2 cot 4 cot 2 f. 8 csc 2 3 cot 2 3 5 csc 2 PAP PreCal Spring Final Exam Review 7 g. 1 1 2 cot 2 1 sec 1 sec h. 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃 1−𝑡𝑎𝑛𝜃 + 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜗 1−𝑐𝑜𝑡𝜃 = 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃 + 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃 9. Exact Value 3 6 a. y= 2 sec( ) 3 cot( ) what is value of y? b. y= csc c. y= sin( d. y= tan 5 what is value of y? 12 12 ) 3 cos( 23 ) what is value of y? 12 7 what is value of y? 12 e. Given that cos θ= m, and 90 o ≤ θ <180o, what expression best represents tan θ ? f. Given that cos θ= √5 , 5 and 0 o ≤ θ <90o, what is exact value of tan θ ? g. Given that sin θ= −7 , 25 and 270 o ≤ θ <360o, what is exact value of sec θ ? h. What is exact value of sec ( tan-1(-1)) if 270 o ≤ θ <360o? PAP PreCal Spring Final Exam Review 8 Law of sine and cosine 10. Find the height of the building in the figure below to the nearest foot. 11. At the end of the day, Gabe and his friends decided to go out in the dark and light some fireworks. Gabe’s grandma provided the fireworks. She told Gabe that she had been saving these bottle rockets (fireworks) ever since her childhood. Unfortunately, all the fireworks were outdated, therefore all of them were in poor condition. Tenzin, Gabe’s mom realized that all the firework devices went up in air for about 4 meters at an angle of 45◦ and descended 6.5 meters from the highest point to the ground. She proposed a question to Gabe and his friends. The question was to figure out how far it landed from the origin. 12. Triangulation can be used to find the location of an object by measuring the angles to the object from two points at the end of a baseline. Two lookouts 20 miles apart on the coast spot a ship at sea. Using the figure below find the distance, d, the ship is from shore to the nearest tenth of a mile. PAP PreCal Spring Final Exam Review 9 13. Two lighthouses are 𝟑𝟎 mi. apart on each side of shorelines running north and south, as shown. Each lighthouse keeper spots a boat in the distance. Lighthouse A keeper notes the location of the boat as 𝟒𝟎˚ east of south, and the lighthouse B keeper marks the boat as 𝟑𝟐˚ west of south. What is the distance from the boat to the lighthouse A at the time it was spotted? Round your answers to the nearest mile. A B The problems of conics 14. Graph the following equations and identify the conic section A. B. C. 15. Find the center, circumference and area of the circle from the given endpoints of diameter A. P (-3,7) and Q (2, -5) B. P (-3,6) and Q (3, -2) PAP PreCal Spring Final Exam Review 10 12. Write the stand equations for with the given characteristics Parabola A. Focus (2,7), directrix y= -3 B. Vertex(0,0), focus (-4,0) C. Graph the parabola below. Label the directrix, vertex, focus. Ellipses D. vertices (0,-12) and (0, 12); co-vertices (-5,0) and (5,0) F. Graph the ellipse below. Label the center, vertices, co-vertices, foci. PAP PreCal Spring Final Exam Review 11 Hyperbola G. vertices (-7,0) and (7, 0); co-vertices (0,-8) and (0,8) H. Graph the hyperbola below. Label the center, vertices, co-vertices, foci, and asymptotes I. An elliptical track has a major axis that is 100 yards long and a minor axis that is 80 yards long. Find an equation for the track if its center is (0, 0) and the major axis is the y-axis.? 13. Fill in the table and sketch the parametric equation for t [-2,6] x = t2 + 1 y=2–t t x y -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 PAP PreCal Spring Final Exam Review 12 14. For the curve a. b. c. d. (x + 3)2 (y - 4)2 1 + 16 = 1 complete the following: Write a pair of parametric equations for the curve. Give an appropriate window and sketch the graph. How could you graph just the right side of the curve? How could you graph just the bottom half of the curve? 15. Eliminate the parameter to write the parametric equations as a rectangular equation. 1 a. x = t - 2 y = 4t + 5 b. x = ½t + 4 y = t3 d. x = 4 sec t y = 3 tan t e. x = 4 + 2 cos t y = -1 + 4 sin t c. . x = 3 cos t y = 3 sin t 16. Plot the following: A. 6, 7 6 C. 8, E. 5, B. 3, 3 4 D. 6, 11 6 5 3 F. 4, 2 3 PAP PreCal Spring Final Exam Review 13 17. Change the following polar equations to rectangular equations: a. r 8 b. r cos 6 c. r 5 csc d. r 7 sin 18. Change the following rectangular equations to polar equations: 2 2 a. x y 81 b. y 5 2 c. y 10 x d. 3xy 7 19. Identify the polar graph (circle, spiral, cardioid, limacon, rose): If a circle, name the center (in polar coordinates) and the radius. If a limacon, name the type. If a rose, state the number of petals. a. r 4 cos b. r 5 2 sin e. r 4 7 sin f. r 4 g. r 2 sin j. r 8 k. r 8 6 cos i. r 8 cos 5 c. r 7 sin 10 d. r 6 f. r 6 6 cos 20. Find u v . Draw a diagram to represent “tail-to-head” addition of the two vectors. Find the magnitude of the resultant vector. a. u <-2,4> , v <6,1 > b. u <4,0> , v <1, -3> c. u <-2,-2> , v <0,3 > PAP PreCal Spring Final Exam Review 14 21. A boat is heading across a river at a velocity of 25 mph. The river is flowing downstream at 10 mph. What is the actual velocity of the boat? 22. An airplane is flying 340 km/hr at 12o East of North. The wind is blowing 40 km/hr at 34o South of East. What is the plane’s actual velocity? 24. Now, let’s assume that A, B, C, and D from above are each the resultant of 2 component vectors (x and y). Start by drawing each of these 4 vectors separately and then determine what 2 vectors would be needed to produce each one of them. PAP PreCal Spring Final Exam Review 15