i recommend putting this on your notecard in some form!!!
advertisement

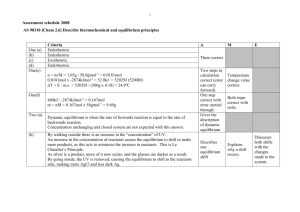
Welcome to s2i! Wednesday, February 6th Katie Seehusen Kseehusen09@winona.edu Agenda: 1. New Material: a. Radioactive Decay b. Equilibrium Constants 2. Review Older Material a. Differential Rate Laws b. Integrated Rate Laws c. Arrhenius Equation Radioactive Decay Practice: Fill in the blank: Radioactive decay obeys __first__ order kinetics. 51 23𝑉 → 42𝐻𝑒 + _ 47 21 𝑆𝑐____ 210 85𝐴𝑡 → 108 47𝐴𝑔 → 01𝑒 + 0 −1𝛽 + 210 86𝑅𝑛 108 46𝑃𝑑 Write out the reaction for Mn undergoing beta decay. 55 25𝑀𝑛 → 0 −1𝛽 + 55 26𝐹𝑒 Equilibrium Constants For the generic reaction aA + bB cC + dD, the equilibrium constant is: Kc= [𝐶]𝑐 [𝐷]𝑑 [𝐴]𝑎 [𝐵]𝑏 True or False? If false, write a correct statement in the line below. T / F Pure liquids and solids are included in the equilibrium constant. __Pure liquids and solids are NOT included in the equilibrium constant_ T / F The top of the fraction contains the reactants and the bottom contains the products. ___The products are on top and the reactants are on bottom____ Write the equilibrium expression for the generic reaction: 3A + 2B 4C + 6D [𝐶]4 [𝐷]6 Kc = [𝐴]3 [𝐵]2 What would the constant be if we specified the states like this: 3A (g) + 2B (l) 4C (s) + 6D (g) [𝐷]6 Kc= [𝐴]3 Here’s a tricky one: Write the equilibrium constant for the combustion of C4H10? Hints: a) Combustion= add O2 and get CO2 and H2O. b) Write the balanced reaction first c) Assume all of the states are gas when writing the constant. 2 C4H10 (g) + 13 O2 (g) 8 CO2 (g) + 10 H2O (g) [𝐶]4 [𝐷]6 Kc= [𝐴]3 [𝐵]2 Differential Rate Law Practice Experiment 1 2 3 [ClO2] (M) 0.060 0.020 0.020 Write the rate law for the reaction: Rate=k[ClO2]2[OH] [OH-] (M) 0.030 0.030 0.090 Rate (M/s) 0.0248 0.00276 0.00828 What is the value of the rate constant? Remember your units!! k= 230 M-2s-1 What would the rate be if [ClO2] was 0.040 M and [OH-] was 0.050 M? Rate= (230)(.04)2(.05) Rate= 0.0184 Integrated Rate Law Practice: Helpful Chart: I RECOMMEND PUTTING THIS ON YOUR NOTECARD IN SOME FORM!!! Order zero 1st 2nd Rate law rate = k rate = k[A] rate = k[A]2 Integrated rate law [A]t=−kt+[A]0 ln[A]t=−kt+ln[A]0 1/[A]t=kt+1/[A]0 Straight-line plot [A] vs. t ln[A] vs. t 1/[A] vs. t Slope −k −k k Half-life (t1/2) [A]o/2k 0.693/k 1/k[A]0 Time (s) 0 50 100 150 200 [C5H6] 0.040 0.030 0.024 0.020 0.0174 1/[C5H6] Given the following data, use Excel to determine if the reaction is 0, 1st or 2nd order for [C5H6]. 70y = 0.1632x + 25.172 60 R² = 0.9996 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 100 200 Time (s) 300 What is the value of the rate constant? Because the most linear graph has 1/[C5H6] on the y axis, the reaction is second order. Looking at the chart above, for second order the slope= k so the rate constant is 0.1632 M-1s-1 What is the half-life of the reaction? t1/2= 1/k[A]0 = 1/(0.1632*0.04) = 153 seconds Given the following graphs, what is the order of the reaction? Most linear graph has axis of ln (A) so the reaction is first order. 600 500 1/ [A] [A] 400 300 200 100 0 0 5000 10000 Time (s) 15000 0.03 0.025 0.02 0.015 0.01 0.005 0 0 5000 10000 Time (s) 15000 7 ln(A) 6 5 4 3 0 5000 10000 Time (s) 15000 If the equation of the linear trendline is y= -0.0002 + 6.2251, what is the value of the rate constant? Slope= -k so k= 0.0002 s-1 What is the half-life of the reaction? t1/2= 0.693/k =3465 seconds What will the [A] be at t= 10,000 seconds if the original concentration is 500 M? (I forgot to add this) ln[A]10000=−(0.0002)(10000)+ln(500) [A]10000= 67.67 M Arrhenius Equation Practice Remember, when we are looking at how the rate constant changes when we change temperature, we will use this form: 𝒌𝟏 𝑬𝒂 𝟏 𝟏 𝐥𝐧 ( ) = ( − ) 𝒌𝟐 𝑹 𝑻𝟐 𝑻𝟏 If a reaction has a rate constant of 6.67x 10-2 s-1 when the temperature is 250 K and a rate constant of 8.89 x 10-1 s-1 when the temperature is raised to 320 K, what is the activation energy? 𝟔. 𝟔𝟕 𝒙 𝟏𝟎−𝟐 𝑬𝒂 𝟏 𝟏 𝐥𝐧 ( ) = ( − ) 𝟖. 𝟖𝟗 𝒙 𝟏𝟎−𝟏 𝟖. 𝟑𝟏𝟒 𝟑𝟐𝟎 𝟐𝟓𝟎 Ea= 24.6 kJ/mol If a reaction has an activation energy of 31 kJ/mol and has a rate constant of 20 s-1 when the temperature is 300 K, what will the rate constant be when the temperature is lowered to 275 K? 𝟐𝟎 𝟑𝟏𝟎𝟎𝟎 𝟏 𝟏 𝐥𝐧 ( ) = ( − ) 𝒌𝟐 𝟖. 𝟑𝟏𝟒 𝟐𝟕𝟓 𝟑𝟎𝟎 k2= 6.46 To wrap up, let’s review some concepts with some multiple-choice questions: 1. Which of the following is true when a reaction has reached its equilibrium? a. Products are being formed faster than reactants b. Reactants are being formed faster than products c. Products and reactants are changing at the same rate d. No reactant is being made into product and no product is being made into reactant. 2. What “reaction” occurs fastest? a. Solid + liquid b. Solid+ gas c. Liquid + gas d. Gas + gas 3. Rank the following letters from lowest to highest on probability of reacting with each other: a. 0.002 M H2O and 0.002 M CO2 b. 1.0 M H2O and 1.0 M CO2 A, c, b, d c. 0.03 M H2O and 0.03 M CO2 d. 5 M H2O and 5 M CO2 4. True or False? The units for the rate constant, k, for a 5th order reaction are M-5s-1? i. They are M-4s-1 5. If something undergoes alpha decay, it’s mass number will change by: a. -4 b. +4 c. -2 d. +2 6. If an element were to undergo radioactive decay, what equation would be used to solve for the half life? a. [A]o/2 b. 0.693/k c. 1/k[A]0 d. [A]0/2k 7. Which of the following would NOT be included in the equilibrium constant given the expression 4CH3 (l) + 7O2 (g) 4CO2 (g) + 6H2O (aq) ? a. CH3 (l) b. O2 (g) c. CO2 (g) d. H2O (aq) 8. What would the overall equilibrium constant be given the following steps of an equation: A + B C + D equilibrium constant= K1 C + E A + F equilibrium constant = K2 B + E D + F overall constant= ? a) b) c) d) K1 + K2 K1*K2 K2 / K1 A number unrelated to the individual Ks.