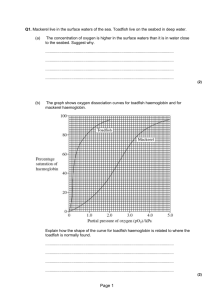
Blood Q & A
advertisement

Condition of the blood resulting from a deficiency of haemoglobin. Symptoms include tiredness, paleness and breathlessness after activity. A deficiency in haemoglobin results in less oxygen being brought to the body cells less oxygen available for respiration less respiration less energy A fluid tissue, a transport system of nutrients in the human body, circulating in arteries and veins. It consists of a liquid plasma containing white blood cells, red blood corpuscles and platelets. produced tiredness. anaemia blood Any one of the four types of blood into which human blood can be divided according to its compatibility in transfusions. This compatibility is based on the presence or absence of antigens on the red blood corpuscles and antigens in the serum. The main types are: A, B, AB and O. Classification of blood by the type of antigen present on the red blood corpuscles. blood group(s) blood grouping Clear liquid portion of the blood, composed of 90% water in which red blood corpuscles, white blood cells and platelets are suspended together with a number of the following dissolved substances: products of digestion, waste products, hormones, plasma proteins, antibodies, enzymes and salts. The transfer of blood from one individual to another. It is the antigen coming in that has to be considered. The antigens of the donor must be compatible with the antibodies of the recipient. (blood) plasma blood transfusions Coagulation or the conversion of a liquid blood into a solid clump of fibres in which blood cells are caught. A cell, especially one floating in fluid such as blood or a sensory nerve ending enclosed in a capsule, e.g. Meissner's. (blood) clotting corpuscle(s) Refers to a compound, e.g. haemoglobin, which has oxygen removed from it. The innermost layer of cells lining the heart, blood vessels and lymphatic vessels and makes up the wall of the capillaries. deoxygenated endothelium Bi-concave discs. Have no nucleus (akaryotic) and no mitochondria. Made in bone marrow of long bones, Insoluble protein threads which form a mesh over a wound and traps parts of the blood to form a scab. e.g. ribs, sternum. Contain haemoglobin (iron necessary for their formation). Joins with oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin. Effete (worn out) ones broken down in liver. Haem (iron) part retained and stored, rest forms part of bile. erythrocyte(s) or red blood corpuscles fibrin Soluble protein found in blood. Converted to fibrin by thrombin. Oxygen-carrying respiratory pigment containing iron. Present in red blood corpuscles of animals. Joins with oxygen to form an oxygen rich compound. fibrinogen haemoglobin These are white blood cells that are formed in the bone marrow and bring about the immune response. They include T-cells and B-cells. The largest of the white blood cells. Formed in the bone marrow. Amoeboid. Engulf bacteria and dead cells. lymphocyte(s) monocytes Oxygenated haemoglobin (Hb4O8), i.e. haemoglobin with oxygen attached. Formed in the red blood corpuscles as blood passes through the lungs. White blood cells that can engulf and destroy viruses and bacteria by phagocytosis. oxyhaemoglobin phagocytes Small fragments of larger cells, formed in marrow. No nuclei. Important in blood clotting. An antigen that may be present on the surface of red blood cells. People who have this antigen are described as Rh positive, while those who lack the antigen are Rh negative. The two blood types are incompatible platelets or thrombocytes rhesus factor Blood plasma without fibrinogen. It does not clot. Refers to the group of cells with a similar function involved in the transport of substances, i.e. xylem and phloem in plants, and blood in animals. serum vascular tissue Chemical used in large quantities in rat poison. Prevents the clotting of blood and rats die from excessive bleeding (haemorrhaging). Use in small quantities in human medicines to prevent blood clotting. Have a nucleus but no definite shape. Protect the body against disease. There are two main types lymphocytes and monocytes, each with different functions. warfarin white blood cell(s)